Animal Development
advertisement

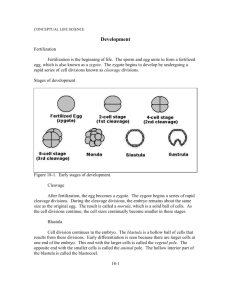
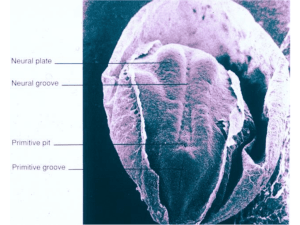
Animal Development • Embryology - study of development of the embryo 5 major stages.. 1. Gametogenesis - gamete production 2. Fertilization - gamete --> zygote 3. Cleavage - Zygote --> Blastula 4. Gastrulation - Blastula --> Gastrula 5. Organogenesis - Organ Formation -i.e. Neurulation- Gastrula --> Neurula Fertilization Fertilization-male and female gametes fuse to form a zygote Sperm must pass through 3 barriers • 1. Jelly coat • 2. Vitelline layer • 3. Plasma membrane Fertilization 1. Sperm attaches the jelly coat of the egg • Acrosome cap contains digestive enzymes that eat away at jelly layer Fertilization 2. Sperm reach vitelline envelope • Vitelline layerspecies-specific boundary involved in sperm-egg recognition • ensure other species cannot fertilize the egg Fertilization 3. Sperm /egg plasma membrane fuse • Sperm nucleus enters the egg • Fertilization occurssperm nucleus and egg nucleus form a 2N zygote Fertilization 4. Prevention of Polyspermy – entrance of multiple sperm • 1.Change of electrical potential of the egg plasma membrane- fast • 2.Confusion of sperm- Egg releases all of their Ca ions • 3.Cortical reaction- slower, mechanical block, initiated in response to Ca release Fertilization • Cortical granules - reside just below of plasma membrane • Cortical reaction – under high Ca levels granules release contents between plasma and vitelline membrane, causes water to rush in • Vitelline layer - hardens and separates from the plasma membrane= fertilization membrane formed Animal Development • Embryology - study of development of the embryo 5 major stages.. 1. Gametogenesis - gamete production 2. Fertilization - gamete --> zygote 3. Cleavage - Zygote --> Blastula 4. Gastrulation - Blastula --> Gastrula 5. Organogenesis - Organ Formation -i.e. Neurulation- Gastrula --> Neurula Cleavage • Cleavage-rapid succession of cell division • doubling with each division • each cell smaller than zygote • Blastula- multi-cellular embryo formed from a single celled zygote Cleavage • Blastula- hollow ball of cells with a large cavity surrounded by one or more layers of cells • Blastocoel – fluid filled cavity forms at the center of embryo Animal Development • Embryology - study of development of the embryo 5 major stages.. 1. Gametogenesis - gamete production 2. Fertilization - gamete --> zygote 3. Cleavage - Zygote --> Blastula 4. Gastrulation - Blastula --> Gastrula 5. Organogenesis - Organ Formation -i.e. Neurulation- Gastrula --> Neurula Gastrulation Gastrulation - sorts all the cells into distinct cell layers (ectoderm, endoderm, and mesoderm) Blastula (hollow ball of cells) transformed into the Gastrula (three layered stage) Gastrulation 1. Gastrulation begins- Blastopore formed Blastopore - midway opening on one side of the blastula • Site of cell migration from the surface into the interior • Future site of anus Gastrulation 2. Cell migrating to form layers • Archenteron – primitive gut formed (endoderm) • future mouth Gastrulation 3.Gastrulation complete - Gastrula formed • Endoderm and archenteron -replace the blastocoel • Mesoderm - forms a layer between the ectoderm and endoderm • Ectoderm- forms the outer layer except for a cluster of endodermal cells (yolk plug) • Yolk plug- (endoderm) marks the site of the blastopore and of the future anus Animal Development • Embryology - study of development of the embryo 5 major stages.. 1. Gametogenesis - gamete production 2. Fertilization - gamete --> zygote 3. Cleavage - Zygote --> Blastula 4. Gastrulation - Blastula --> Gastrula 5. Organogenesis - Organ Formation -i.e. Neurulation- Gastrula --> Neurula Neurulation Neurulation – embryonic formation of the neural tube directed by the underlying notochord • Notochord- stiff rod (mesoderm) runs down the back of the embryo provides support for other developing tissues • -Future backbone Neurulation 1. Neurulation begins neural tube formation • Neural plate – thickened region (ectoderm) arises a pair of pronounced ridges called the neural fold • Neural tube – formed when neural folds meet • future brain and spinal cord Neurulation 2. Neurulation complete - Neurula formed Neurula- an embryo with a neural tube • Somites-internal segmented structures (mesoderm) • Give rise to vertebrae and associated muscles of the backbone • Coelom – body cavity (mesoderm) developed next to somites Animal Development • Embryology - study of development of the embryo 5 major stages.. 1. Gametogenesis - gamete production (i.e. Meiosis) 2. Fertilization - union of sperm & egg cell --> 2n zygote 3. Cleavage - rapid succession of cell divisions forms hollow ball of cells called BLASTULA embryo 4. Gastrulation - period of cell migrations as BLASTULA embryo converted into a 3 layered stage called GASTRULA embryo 5. Organogenesis - Organ Formation -i.e. Neurulation- Gastrula --> Neurula Starfish Development Blastocoel Blastopore Blastula Archenteron Blastopore – Gastrulation becomes the anus Mouth Anus Frog Development Cell size difference Yolk Plug Chicken Development