Embryo stem cells pictures and statements
advertisement

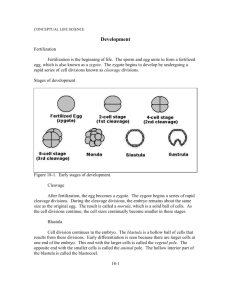
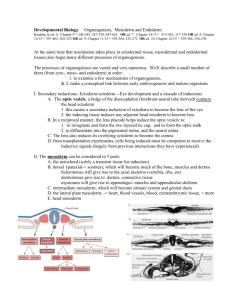
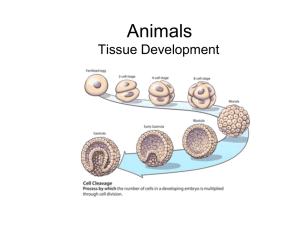
EMBRYO STEM CELLS Fertilisation Cleavage Blastocyst formation Gastrulation Organogenesis ADVICE AND GUIDANCE FOR PRACTITIONERS (NATIONAL 5, BIOLOGY) © Crown copyright 2012 1 EMBRYO STEM CELLS A male sperm and female egg fuse to form a zygote (fertilised egg). The zygote can produce all the cell types needed to make a complete human . When? 0–24 hours The zygote starts dividing (cleaving) into identical cells as it passes down the oviduct towards the uterus. By the time it gets there, the process has repeated sufficiently to form a ball of around 100 cells. When? 1–4 days The ball of cells begins to specialise, forming an outer layer of cells with a cluster of cells inside (inner cell mass), which can form most cell types of the human body. When? 3–8 days The cells in the inner cell mass move to form three layers: the ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm. The ectoderm forms the skin, brain and nervous system; the mesoderm forms muscle and the skeletal and circulatory systems; and the endoderm forms the gut lining and many of the internal organs. When? Week 3 The formation of body organs. The embryo is called a foetus at 8 weeks, by which time the structures that will give rise to all the major organs are present. When? Week 3–8 2 ADVICE AND GUIDANCE FOR PRACTITIONERS (NATIONAL 5, BIOLOGY) © Crown copyright 2012 ADVICE AND GUIDANCE FOR PRACTITIONERS (NATIONAL 5, BIOLOGY) © Crown copyright 2012 3