Name
advertisement

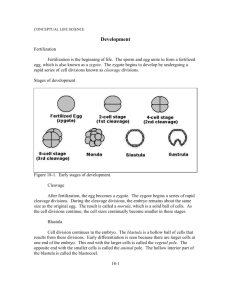
Name _____________________________________________ Date __________ Period ______ Unit 3, Descriptive Embryology, Review Packet Directions: Read the statements below and circle the correct answer choice. 1. Most biologists of the 17th and 18th centuries believed in ____________, the concept that gametes contain miniaturized versions of all of the elements present in the adult. A. biogenesis B. epigenesis C. preformation D. spontaneous generation 2. The study of animal development from the fertilized egg to the formation of all major organ systems is called _____________. A. comparative anatomy B. entomology C. embryology D. molecular biology 3. The specialized organelle at the head of the sperm that releases lysins is called ______________. A. the vitelline llayer B. a mitochondrion C. microvilli D. the acrosome 4. Egg activation is a series of biochemical changes in the egg that ensures the completion of fertilization and initiates embryonic development. A. true B. false 5. A protective envelope that forms around a fertilized egg is known as ______________. A. a fertilization membrane B. an acrosome C. the egg cortex D. the vitelline layer 6. The region of the zygote referred to as the ______________ contains less yolk and is more metabolically active than the opposite pole. A. North Pole B. South Pole C. vegetal pole D. animal pole 7. What are cell divisions during embryonic development called? A. blastulas B. cleavages C. meiosis D. gastrulas 8. Cleavages produce blastomeres which divide synchronously for a short time. A. true B. false 9. Cleavages that completely divide an egg are _______________. A. meroblastic B. semi-blastic C. holoblastic D. blastocoels 10. ___________ forms the inner lining of the digestive cavity of an embryo. A. Ectoderm B. Mesoderm C. Endoderm D. Blastoderm 11. ___________ forms muscle, blood, skeletal elements and other connective tissues. A. Ectoderm B. Mesoderm C. Endoderm D. Blastoderm 12. In vertebrates, the ectoderm forms nervous tissue, sensory organs, and the gut tract lining. A. true B. false 13. A stage of embryology usually consisting of a hollow ball of cells is called the ____. A. morula B. blastula C. gastrula D. archenteron 14. Invagination or involution of cells in embryo occurs during a process called ______. A. gastrulation B. neurulation C. blastulation D. epiboly 15. Which of the following characteristics are true of all chordates? A. dorsal, tubular nerve cord B. notochord C. pharyngeal slits or pouches D. postanal tail E. all of the above 16. Vertebrates are not members of the phylum Chordata. A. true B. false 17. Animals with a vertebral column are known as ____________. A. chordates B. invertebrates C. vertebrates D. echinoderms 18. A process in which the ectoderm spreads over the entire embryo is known as ____. A. epiboly B. polyploidy C. diploid D. haploid 19. The development from a nondescript form in the early embryo to their form in late embryonic development is known as ________________________. A. primary germ layers B. holoblastic C. meroblastic D. differentiation 20. The ________ is the outermost extra-embryonic membrane of the embryo. A. allantois B. amnion C. ectoderm D. chorion 21. In their feeding habits, zebrafish are characterized as ____________. A. carnivores B. omnivores C. herbivores 22. Female zebrafish lay eggs that are then fertilized by the male. This is known as _________. A. internal fertilization B. external fertilization C. parthenogenesis D. sexual dimorphism 23. Which of the following is the correct sequence of the stages of development in zebrafish? A. zygote, cleavage, blastula, gastrula, segmentation, pharyngula, hatching B. zygote, blastula, cleavage, gastrula, segmentation, pharyngula, hatching C. cleavage, zygote, blastula, gastrula, segmentation, pharyngula, hatching D. zygote, cleavage, blastula, gastrula, pharyngula, segmentation, hatching 24. What is the main event of the cleavage period in zebrafish? A. a diploid zygote is formed B. cells cleave to form an embryo with 64 cells C. germ layers of the embryo form D. the pharyngeal region develops 25. What is the main event of the segmentation period in zebrafish? A. a diploid zygote is formed B. the pharyngeal region develops C. the embryo develops a spine and the features of a chordate D. germ layers of the embryo form 26. What is the main event of the gastrula period in zebrafish? A. a diploid zygote is formed B. cells cleave to form an embryo with 64 cells C. germ layers of the embryo form D. the embryo develops a spine and the features of a chordate 27. What is the main event of the blastula period in zebrafish? A. epiboly begins B. cells cleave to form an embryo with 64 cells C. germ layers of the embryo form D. the pharyngeal region develops 28. What is the main event of the hatching period in zebrafish? A. a diploid zygote is formed B. a fluid-filled cavity called a blastocoel forms C. the embryo breaks free from the chorion D. germ layers of the embryo form 29. On average, how many days after fertilization does it take a zebrafish to hatch? A. three to four B. five to eight C. nine to eleven D. twelve to fifteen 30. Examine the picture to the right. In what stage would this zebrafish embryo be placed? A. blastula B. cleavage C. gastrula D. zygote 31. Examine the picture to the right. In what stage would this zebrafish embryo be placed? A. blastula B. gastrula C. pharyngula D. segmentation 32. Examine the picture to the right. In what stage would this zebrafish embryo be placed? A. gastrula B. hatching C. pharyngula D. segmentation 33. Examine the picture to the right. In what stage would this sea star embryo be placed? A. zygote B. cleavage C. morula D. blastula E. gastrula 34. Examine the picture to the right. In what stage would this sea star embryo be placed? A. zygote B. cleavage C. morula D. blastula E. gastrula 35. Examine the picture to the right. In what stage would this sea star embryo be placed? A. zygote B. cleavage C. morula D. blastula E. gastrula 36. Which of the following is the correct order of the stages of a sea star embryo? A. blastula, gastrula, morula, zygote, cleavage, bipinnaria larva B. zygote, blastula, cleavage, gastrula, morula, bipinnaria larva C. zygote, cleavage, blastula, morula, gastrula, bipinnaria larva D. zygote, cleavage, morula, blastula, gastrula, bipinnaria larva 37. In the sea star embryo, a solid ball of 16-64 cells is known as a ______________. A. blastula B. gastrula C. morula D. zygote 38. A zygote is a fertilized egg. A. true B. false 39. Examine the picture below of early cleavage patterns. Which would be representative of the early cleavage pattern in sea stars? A. row A B. row B C. row C 40. Which of these embryos has a large quantity of yolk? A. row A B. row B C. row C D. none of the above Questions 39 & 40