11.6 Ordinary Annuities, Sinking Funds, and Retirement Investments
advertisement
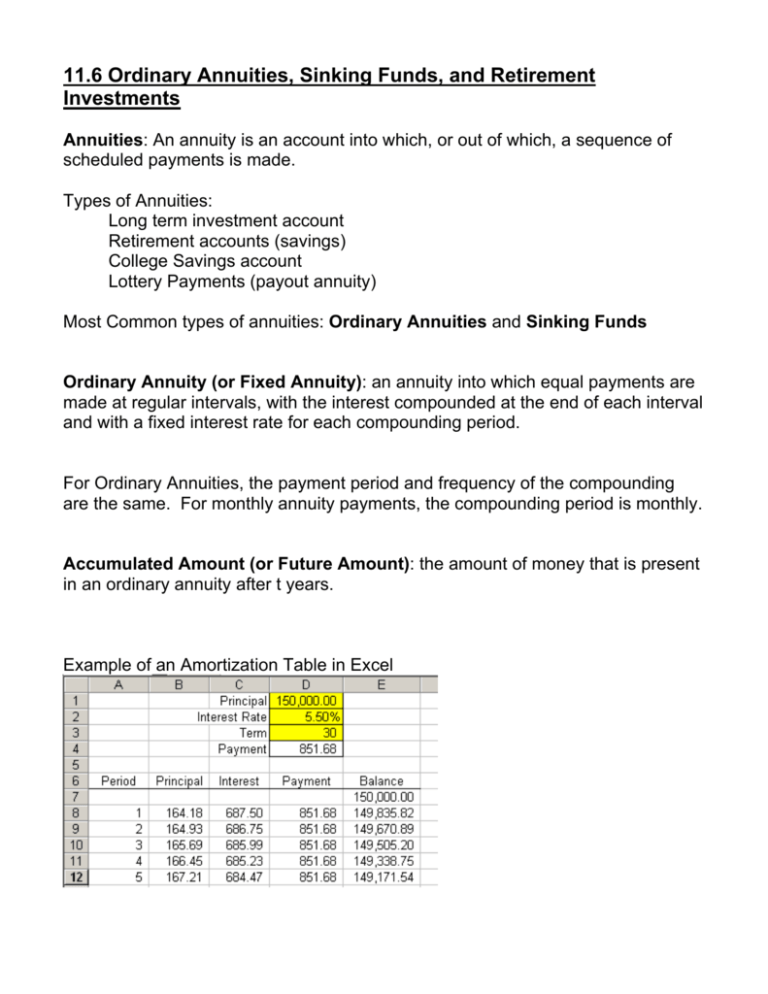
11.6 Ordinary Annuities, Sinking Funds, and Retirement Investments Annuities: An annuity is an account into which, or out of which, a sequence of scheduled payments is made. Types of Annuities: Long term investment account Retirement accounts (savings) College Savings account Lottery Payments (payout annuity) Most Common types of annuities: Ordinary Annuities and Sinking Funds Ordinary Annuity (or Fixed Annuity): an annuity into which equal payments are made at regular intervals, with the interest compounded at the end of each interval and with a fixed interest rate for each compounding period. For Ordinary Annuities, the payment period and frequency of the compounding are the same. For monthly annuity payments, the compounding period is monthly. Accumulated Amount (or Future Amount): the amount of money that is present in an ordinary annuity after t years. Example of an Amortization Table in Excel Ordinary Annuity Formula The accumulated amount, A, of an ordinary annuity with payments of p dollars made n times per year, for t years, at interest rate, r, compounded at the end of each payment period is given by the formula: ⎡⎛ r ⎞ nt ⎤ P ⎢⎜1 + ⎟ − 1⎥ ⎥⎦ ⎢⎝ n ⎠ A= ⎣ r n Ex 1 Use the ordinary annuity formula to determine the accumulated amount in each annuity. Round all answers to the nearest cent. a) $800 invested semiannually for 25 years at 7% compounded semiannually. b) $200 invested monthly for 40 years at 6% compounded monthly. Sinking Funds: a type of annuity in which the goal is to save a specific amount of money in a specific amount of time. ⎛r⎞ A⎜ ⎟ ⎝n⎠ Sinking Fund Formula: p = nt ⎛ r⎞ ⎜1 + ⎟ − 1 ⎝ n⎠ In the formula, p is the payment needed to reach the accumulated amount, A. Payments are made n times per year, for t years, into a sinking fund with interest rate r, compounded n times per year. Ex 2 Use the sinking fund formula to determine the payment needed to reach the accumulated amount. To ensure that enough is invested each period, round each answer up to the next cent. a) Annual payments with 5% interest compounded annually for 20 years to accumulate $35,000. b) Quarterly payments with 10% interest compounded quarterly for 40 years to accumulate $1,000,000. Other types of Annuities Variable Annuities: an annuity that is invested in stocks, bonds, mutual funds, or other investments that do not provide a guaranteed interest rate. Immediate Annuities: an annuity that is established with a lump sum of money for the purpose of providing the investor with regular, usually monthly, payments for the rest of the investor’s life. Other Retirement Savings Options IRA 401k 403b 11.6 Homework # 9 – 23 odd