Bus 342 Fundamentals of Corporate Finance
advertisement

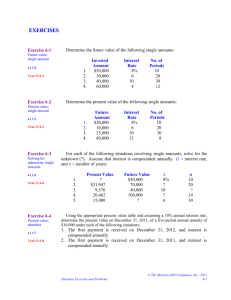
Bus 342 Fundamentals of Corporate Finance Chapter 6 Discounted Cash Flow Valuation Timeline and Cash Flows – $150 Now $100 $100 1 year later Cash Flows 2 years later 3 years Timeline Positive Cash Flow : Cash You Receive, Up Arrows Negative Cash Flow: Cash You Pay, Down Arrows Present Value with Multiple Cash Flows 1 A Second Way of Calculating the Present Value Financial Calculators PV I/YR PMT N FV Annuities A series of constant or level cash flows that occur at the end of each period for some fixed number of periods is called an ordinary annuity. Constant cash flow, at the beginning of each period: annuity due. 2 Annuities – Finding Present Value Annuities – Finding Payments Annuities – Finding Interest Rate 3 Annuities – Finding the Number of Payments Annuities – Finding Future Value Perpetuities • Just like an annuity, except that the cash flow stream continues forever. Also called consols. • Payment each period: C. Interest rate: r . 4 Ordinary Annuity Present Value and Future Value C: constant cash flow every period; r: interest rate; t: number of periods. PV = C ⎡ ⎢ 1 − ⎢ ⎢ ⎢⎣ FV = C ⎡ (1 + ⎢ ⎣ 1 (1 + r r ) r r ) t t ⎤ ⎥ ⎥ ⎥ ⎥⎦ − 1 ⎤ ⎥ ⎦ Effective Annual Rates and Compounding • Quoted as “10% per annum compounded semiannually”, or “10% compounded semiannually”. • Means paying 5% every six months. Effective Annual Rates and Compounding • Quoted as “12% per annum compounded monthly”, or “12% compounded monthly”. • Means paying 1% every month. 5 Effective Annual Rates and Compounding • Quoted as “q per annum compounded m times a year”. • Means paying q / m each time for m times in a year. From EAR to Quoted Rate APR and APY • Annual Percentage Rate (APR): The interest rate charged per period multiplied by the number of periods per year. Quoted to borrowers. • Annual Percentage Yield (APY): The effective annual rate a deposit earns. 6 Continuous Compounding Continuous Compounding: EAR = eq – 1 =2.71828.10 – 1 = 10.51709% Loan Types and Loan Amortization • Pure Discount Loans • Interest-Only Loans • Amortized Loans Pure Discount Loans • The borrower receives money today and repays a single lump sum at some time in the future. 7 Interest – Only Loans • The borrower pays interest each period, and repay the entire principal at some point in the future. Amortized Loans • A loan to be paid off by making regular principal reductions. My Own Story • “Paying mortgage on a home you purchased is building up your own equity in the home, while paying rent is just pouring money down the drain.” 8 My Own Story My Own Story 9