Molecular Shapes
advertisement

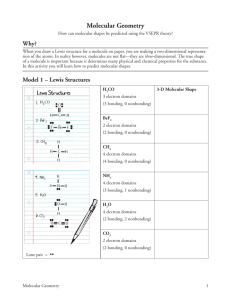
Two bonds on the same atom will try to get as (close to/far from) each other as possible. A lone pair of electrons and a bonded pair of electrons will (push away from/move toward) each other. Standard 3, Assignment 20 name _____________________________________ Molecular Shapes Read This! The VSEPR (Valence Electron Pair Repulsion) molecules Why are we doing this? — When you draw aShell Lewis dot structure for a mTheory olecule helps on ppredict aper, ythe ou shapes are mofaking a 2-­‐ and is based on the premise that electrons around a central atom repel each other. Electron domains are areas dimensional representation of the atoms. In reality owever, molecules re not flat — they ofare 3-­‐dimensional. of high electron density such ashbonds (single, double oratriple) and lone-pairs electrons. In simple The true shape is important bterms ecause it determines physical and chemical roperties for the sdomains ubstance. VSEPR means that m allany electron bonding domains andpelectron nonbonding around a central atom need to be positioned as far apart as possible in three-dimensional space. Big Question — How can the 11. number and placement of valence electrons e used why to pthese redict hape of molecules? VSEPR theory specifies “valence shell” electrons.bExplain arethe the smost critical electrons for determining molecular shape based on your exploration of Model 1. The VSEPR (Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion) Theory helps predict the shapes of molecules and is based on the premise that electrons around a central atom repel each other. Electron domains are areas of high electron 12. In the VSEPR theory, what is repelling what? density such as bonds (single, double or triple) and lone-­‐pairs of electrons. In simple terms VSEPR means that all electron bonding domains and electron nonbonding domains around a central atom need to be positioned as far 13. Based on the information in the Read This! section, sketch one of the molecular shapes shown apart as possible in three-­‐dimensional space. below in each of the boxes provided in Model 1. Linear Trigonal planar Three-Dimensional These are the five 3-­‐D Molecular Shapes molecular shapes you will be responsible for identifying. This chart will be provided on Tetrahedral Pyramidal Bent all assessments. When deciding a molecule’s structure you will need to look at: • the number of atoms Molecular that are Geometry bonded to the central atom (single, double, triple bond – doesn’t matter which), 3 • the number of non-­‐bonding electron domains (lone pairs) around the central atom. Substance Lewis Structure Electron Domains What is the 3-­‐D molecular shape? Number of atoms Number of lone bonded to the pairs central atom H2CO BeF2 CH4 Substance Lewis Structure NH3 H2O CO2 Electron Domains Number of atoms Number of lone bonded to the pairs central atom What is the 3-­‐D molecular shape? Practice: 1. a. Draw the Lewis structure for PF3. b. What is the 3-­‐D shape of PF3? ____________________________________________ c. What is the bond angle in this molecule? _______________ d. What is the name of PF3? ____________________________________________ e. What is the molar mass of PF3? ____________________________________________ 2. a. Draw the Lewis structure for H2S. b. What is the 3-­‐D shape of H2S? ____________________________________________ c. What is the name of H2S? ____________________________________________ d. What is the bond angle in this molecule? _______________ e. How many total protons are in a molecule of H2S? ____________________________________________ 3. a. Draw the Lewis structure for PH3. b. What is the 3-­‐D shape of PH3? ____________________________________________ c. What is the name of PH3? ____________________________________________ d. What is the bond angle in this molecule? _______________ 4. a. What is the formula for carbon tetrachloride? _________________ b. Draw the Lewis structure for carbon tetrachloride. c. What is the 3-­‐D shape of carbon tetrachloride? ____________________________________________ d. What is the bond angle in this molecule? _______________ 5. a. Draw the Lewis structure for CS2. b. What is the 3-­‐D shape of CS2? ____________________________________________ c. What is the bond angle in this molecule? _______________ d. What is the name of CS2? ____________________________________________ e. What is the molar mass of CS2? ____________________________________