Chapter 6

Anu Singh-Cundy • Michael L. Cain
Discover Biology
FIFTH EDITION
CHAPTER 6
Cell Structure and Internal
Compartments
© 2012 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc.
Cells: The Smallest Units of Life
• The cell is the smallest and simplest unit of life
• well-‐coordinated unit
cell theory
• A unifying principle of biology
• Based on two concepts:
– Every living organism is composed of one or more cells
– All cells living today came from a preexisCng cell
Cells: The Smallest Unit of Life
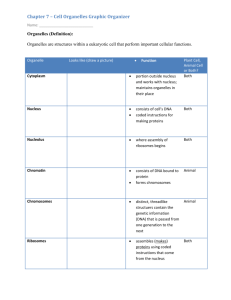
• Cytoplasm contains cytosol
• An organelle structure that performs a unique funcCon
• The nucleus contains the DNA enveloped in double membranes
• The mitochondrion (plural: mitochondria) provides the energy that fuels all cellular funcCons
• Ribosomes are important protein-‐manufacturing organelles
The Microscope Is a Window into the Life of a Cell
• The light microscope
The RaCo of Surface Area to
Volume Limits Cell Size
• ProkaryoCc cells smaller than eukaryoCc cells
Cell size is limited
MulCcellularity Enables Larger Body Size and Efficiency through Division of Labor
SAME DNA
Different parts “expressed”
The Plasma Membrane
• selecCvely permeable barrier
– Capturing needed molecules and bringing them into the cell
– Removing waste from the cell
– CommunicaCng with other cells and the environment
– Anchoring the cell in place
The fluid mosaic model proteins driQ
– Transport proteins
– Receptor proteins
– Adhesion proteins
ProkaryoCc and EukaryoCc Cells
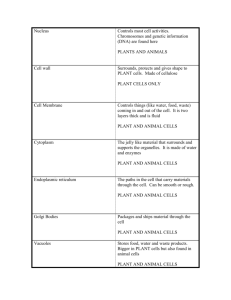
• Prokaryotes tough cell wall outside the plasma membrane
(Some bacteria have capsule)
Eukaryotes –membrane-bound organelles - division of labor
The Nucleus Houses GeneCc Material
• nuclear envelope
• DNA
• double helix chromosomes
The Nucleus Houses GeneCc Material
• nuclear pores
RNA carry direcCons for making proteins to the ribosomes
The Endoplasmic ReCculum
• endoplasmic reDculum (ER)
• smooth ER
– produce lipids
– breaks down toxins
– rough ER
– doTed with ribosomes
Transport Vesicles Move Materials
• membrane-‐enclosed
sac
• fuses with target desCnaCon
The Golgi Apparatus Sorts and Ships
Macromolecules
Lysosomes Disassemble
Macromolecules
• Lysosomes -‐interior highly acidic
Vacuoles Disassemble Macromolecules
• Plants
• storage
• poisons
• water
Mitochondria Power the Cell
• extract energy from food molecules
• The process of turning food molecules into
ATP energy is called cellular respiraDon
Chloroplasts Capture Energy from Sunlight
• Plants and algae use chloroplasts to capture energy from sunlight to produce ATP
• The ATP is then used to assemble sugar molecules from carbon dioxide and water in a process called photosynthesis
• The energy in plant sugars is used directly by plants and indirectly by all organisms that eat plants
• Oxygen is a by-‐product of photosynthesis and sustains life for humans and many other organisms
The Cytoskeleton
• Movement and strength
1. Microtubules
2. Intermediate filaments
3. Microfilaments
Microtubules rigid, hollow cylinders of protein used for:
• Positioning organelles
• Moving transport vesicles and other organelles
• Generating force to propel the cell
Intermediate filaments are ropelike cables of protein that provide mechanical reinforcement to the cell
Microfilaments are thin, flexible proteins that create cell shape and generate crawling movements in some cells
Microtubules Support Movement inside the Cell
• Microtubules are made of protein subunits called tubulin
• Disrupted in AD
• Disrupted in CBI
Microfilaments
• AcDn
Cell crawling
– amoebas and slime molds
– Wound healing
– embryonic development
Cilia and Flagella Enable
Whole Cell Movement
• Many proCsts and animals have cells covered in hairlike projecCons called cilia
Cilia and Flagella Enable
Whole Cell Movement
• Some bacteria, archaeans, proCsts, and sperm cells use flagellum (plural: flagella) to propel themselves through fluid
The EvoluCon of Eukaryotes
• EukaryoCc organelles are believed to have originally been free-‐living prokaryotes that were engulfed by a predatory cell
Concept Quiz
Where is the secreted protein insulin synthesized?
A. In the Golgi apparatus
B. On the rough ER
C. On ribosomes in the cytoplasm
D. In the nucleus
Concept Quiz
The boundary structure that physically defines a cell is the .
A.Cell wall
B.Selective permeability
C.Plasma membrane
D.Protein coat