Unit 5 Notes
advertisement

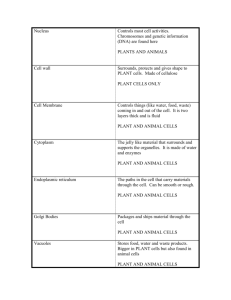
Unit 5: Introduction to Cells I. Cell Theory A. Discovery of Cells 1. Robert Hooke (1665) a. first to identify cells by looking at slices of cork under a microscope b. Hooke named cells, he thought they looked like the rooms (cells) monks lived in 2. Anton van Leeuwenhoek (1674) - made a better microscope, one of the first to describe living cells he observed swimming in a drop of pond water B. Development of the Cell Theory 1. Matthias Schleiden (1838) – first to note that plants are made of cells 2. Theodor Schwann (1839) – first to note that animals are made of cells, concluded that all living things are made of cells 3. Rudolf Virchow (1855) – reported all cells come from preexisting cells 4. Cell Theory (three parts) a. all organisms are made of cells b. all existing cells are produced by other living cells c. the cell is the most basic unit of life C. Prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells 1. Prokaryotic cells do not have a nucleus or other membrane bound organelles Examples - bacteria 2. Eukaryotic cells have a nucleus and other membranebound organelles Examples: Animals, plants, fungus, protist II. Cell Organelles – structures specialized to perform distinct processes within a cell A. Cells have an internal structure 1. Cytoskeleton – network of proteins, such as microtubules and microfilaments inside a eukaryotic cell a. Microtubules – long hollow tubes, give cell shape and act as tracks for the movement of organelles b. Microfilaments – tiny threads that enable cells to move and divide 2. Cytoplasm – jellylike substance inside cells that contains molecules, helps cells maintain shape B. Organelles involved in making and processing proteins 1. Nucleus – storehouse for genetic information (DNA) 2. Nuclear Envelope – double membrane that encloses the nucleus 3. Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) – interconnected network of thin folded membranes that produce, process and distribute proteins a. smooth ER – lacks ribosomes b. rough ER – studded with ribosomes 4. Ribosomes – tiny organelles that link amino acids together to form proteins (site of protein synthesis) 5. Golgi Apparatus – closely layered stacks of membrane-enclosed spaces that process, sort, packages, and deliver proteins 6. Vesicles – small organelle that contains and transports materials within the cytoplasm C. Other Organelles 1. Mitochondria – Supply energy to the cell, bean shaped and have two membranes, inner membrane has many folds that increases surface area 2. Vacuole – fluid-filled sack used for storage of materials needed by the cell a. animal cells usually have many small vacuoles b. plant cells have a single, large vacuole 3. lysosomes – membrane-bound organelle that contains enzymes, defends cell from invading bacteria and viruses, they also break down damaged or worn-out cell parts 4. centrosome – small region of cytoplasm that produces microtubules 5. centriole – small cylinder-shaped organelle in animal cells D. Plant cells have cell walls and chloroplast 1. Cell walls - rigid layer that surrounds the cell membrane, gives protection, support, and shape to the cell, found in plants, algae, fungi, and most bacteria, the cell wall is made primarily of cellulose 2. Chloroplasts – organelle that carries out photosynthesis