EPIDERMIS stratum corneum • fully keratinized (dead) epithelial
advertisement

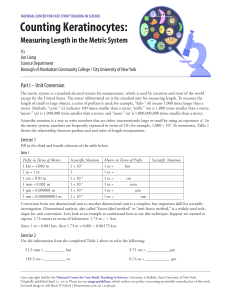
EPIDERMIS stratum corneum stratum lucidum stratum granulosum stratum spinosum stratum germinativum (basalis) DERMIS papillary layer (loose CT) layer of dense CT HYPODERMIS subcutaneous tissue • fully keratinized (dead) epithelial cells, no nuclei, low H2O content • sealed extracellular space a) prevents evaporation b) barrier against pathogens • sqames, most superficial cells, sloughed off • only in thick skin; advanced keratinization • keratinocytes here contain basophilic granules of keratohyalin a) leaks into extracellular space and acts to seal b) this aids in waterproofing and protection of skin • lamellar bodies with glycolipids (same function as keratohyalin) • cells attached to each other via desmosomes which gives spiny appearance to keratinocytes under LM • spaces in between cells allow fluid from vessels in the dermis to nourish the cells (epidermis is avascular!) • Langerhans cells (involved in the immune system) found here • contains stem cells from which new keratinocytes arise by mitosis a) these cells are relatively small, cuboidal to low columnar b) look for mitotic cells with basophilic appearance • melanocytes are dendritic cells that synthesize melanin a) melanin protects from UV radiation b) can be distributed to surrounding keratinocytes • blood vessels, nerves, lymphatics found here • dermal papillae project into the epidermis • Meissner’s corpuscles (in dermal papillae); mostly in fingertips a) encapsulated; two point discrimination • bulb of the hair follicle a) germinative matrix cells adjacent to the CT papilla – shaft, sheath formed b) melanocytes contribute melanin granules c) sebaceous glands i. secret sebum between shaft and follicle ii. holocrine secretion d) arrector pili (smooth muscle bundle) i. hair pulled to vertical position ii. goosebumps due to skin depression • eccrine sweat glands (coiled tubular glands) a) secretion contains salts and IgA b) secretory portion in subcutaneous tissue i. secretory tubules: acidophilic layer of myoepithelium contracts to expel secretion ii. myoepithelium – sympathetic innervation c) ducts extend to epidermis i. excretory ducts: TWO layers of cuboidal cells ii. remove salt – final sweat hypotonic iii. corkscrew path in epidermis d) Pacinian corpuscle (boundary b/w dermis and hypodermis) i. encapsulated ii. senses vibration • loose CT, many glands, ducts, blood vessels, lymphatics • abundant adipose tissue EXTRA Questions (These questions were from last year’s SSN workshop – they are not part of the slidebased practice practical: 1) Melanoma is likely to originate in the ___________ layer, from a mutated ___________. a. b. c. d. stratum spinosum, melanocyte stratum basalis, keratinocyte (with melanin granules) stratum basalis, melanocyte stratum basalis, stem cell answer: c 2) ____________ are found in stratum basalis. They attach keratinocytes to _____________. a. b. c. d. Hemidesmosomes, basal lamina Desmosomes, basal lamina Hemidesmosomes, other keratinocytes Desmosomes, Langerhans cells answer: a 3) Excreted sweat is isotonic / Sebum is secreted by holocrine secretion / Pacinian corpuscles detect two point touch a. b. c. d. F/F/F T/T/F F/T/F T/F/T answer: c