Integument system

Contents:
Integumentary System
1.
Skin: as an organ
2. Structure of the skin
Epidermis
Dermis
3.Types of skin: Thick & thin skin
4. Functions of the skin
5. a. Thermoregulation
b. Protective function
c. Cutaneous sensations
d. Synthesis of Vit. D
e. Excretion & absorption
1.
Skin:
Largest organ in the body
Dermatology: Branch of Medicine that deals with the diagnosis and treatment of skin disorder.
2.
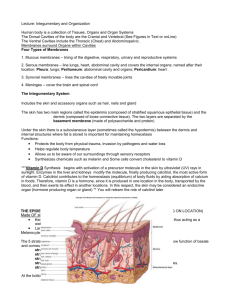
Structure of the skin: a.
Consists of 2 principal parts: i.
Epidermis ii.
Dermis
Deep to Dermis is subcutaneous layer
2a. Epidermis: i.
There are 4 principal types of cells.
Keratinocytes: 90% of all cells
Melanocytes: 8% of all cells
Langerhan cell: Concerned with immune system
Markel cell: Concerned with sensation of touch ii.
Layer (Strata) of cells in Epidermis: a.
Stratum Basale: Deeper most (Innermost) layer consists of single layer of cuboidal cells b.
Stratum Spinosum: 8-10 layer of Keratinocytes c.
Stratum Granulosum: Cells contain deep granules d.
Startum Lucidum: Present only in thick skin e.
Stratum Cornium: Consists of 20-25 layers of dead keratinocytes. Water repellent barrier.
2b. Dermis: Divided into i. Superficial Papillary region
ii.Deeper reticular region
i.
Papillary region: ii.
Consists of collagen and elastic fibers
Surface area is increased by Dermal Papillae
Reticular region: Gives strength and elasticity to the skin
3.
Types of skin: Two major types
Thick skin (Hairy )
Thin skin ( Haieless)
3a. Comparison of thick and thin skin
Feature i. Epithelial thickness: thin skin
0.1 – 0.15mm thick skin
0.6-4.5mm ii.Distribution: all parts except palm Palm & sole
and sole iii. Epidermal strata: Stra. Lucidum lacking Str. Lucidum
present iv. Hair follicle: present absent v. Sensory receptors: Sparse Dense
4.
Functions of skin: a.
Regulate body temperature (Thermoregulation) b.
Serve as water repellent & protective barrier c.
Contain sensory nerve endings d.
Synthesize active Vit D e.
Excrete salt and organic compounds f.
Has some capacity to absorb
5.
Functions in detail a.
Thermoregulation: is done i.
by liberating sweat ii.
by adjusting the diameter of blood vessels and flow of blood b.
Protector:
physical and chemical barrier
Kills surface bactaria
Melanin protects against damage caused by ultra-violet
Light c.
Cutaneous sensation: Tactile
Thermal
Pain d.
Synthesis of Vit D
Vit D3 help absorb calcium from intestine e.
Excretion and absorption:
Excretes water, salt & CO2
Absorb fat soluble vitamin, Lead, Murcury & Arsenic
Skin and Homeostasis a.
Skeletal system: Skin activates Vit D which is needed
for absorption od dietary Calcium b.
Endocrine system: Skin activates Vit D to Calcitrol a
hormone that aids absorption of Ca c.
Cardiovascular system: Dermis contais big blood
vessels which constrict & dilate
to adjust blood flow in skin d.
Nervous system: Nerve endings in skin provide input
(send impulse) to the brain for touch,
pressure, thermal and pain sensation. e.
Reproductive system: Nerve endings in skin respond to stimuli and contribute sexual pleasure
* Suckling of baby stimulates nerve
endings and causes milk ejection.
*Skin stretches during pregnancy
as fetus enlarges
Homeostatic imbalances:
Skin cancer: 3 common forms i.
Basal cell carcinoma 75% ii.
Squamous cell carcinoma 20% iii.
Malignant melanoma 2%
Burns: Tissue damage by excessive heat. i.
First degree:Involve epidermis with mild pain No blister, skin functions intact ii.
Second degree: Involve epidermis and part of Dermis. Redness, blister, edema
and pain present iii.
Third degree: Involve full thickness of skin
Including subcutaneous layer.
Most skin functions are lost