SKIN
advertisement
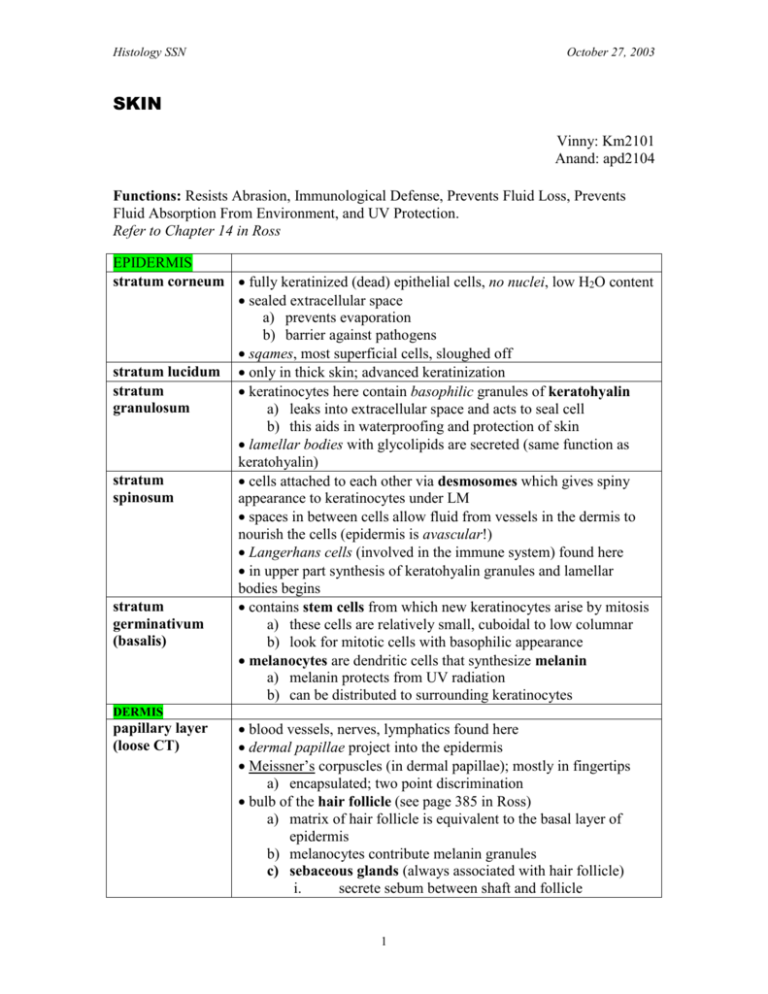
Histology SSN October 27, 2003 SKIN Vinny: Km2101 Anand: apd2104 Functions: Resists Abrasion, Immunological Defense, Prevents Fluid Loss, Prevents Fluid Absorption From Environment, and UV Protection. Refer to Chapter 14 in Ross EPIDERMIS stratum corneum fully keratinized (dead) epithelial cells, no nuclei, low H2O content sealed extracellular space a) prevents evaporation b) barrier against pathogens sqames, most superficial cells, sloughed off stratum lucidum only in thick skin; advanced keratinization stratum keratinocytes here contain basophilic granules of keratohyalin granulosum a) leaks into extracellular space and acts to seal cell b) this aids in waterproofing and protection of skin lamellar bodies with glycolipids are secreted (same function as keratohyalin) stratum cells attached to each other via desmosomes which gives spiny spinosum appearance to keratinocytes under LM spaces in between cells allow fluid from vessels in the dermis to nourish the cells (epidermis is avascular!) Langerhans cells (involved in the immune system) found here in upper part synthesis of keratohyalin granules and lamellar bodies begins stratum contains stem cells from which new keratinocytes arise by mitosis germinativum a) these cells are relatively small, cuboidal to low columnar (basalis) b) look for mitotic cells with basophilic appearance melanocytes are dendritic cells that synthesize melanin a) melanin protects from UV radiation b) can be distributed to surrounding keratinocytes DERMIS papillary layer (loose CT) blood vessels, nerves, lymphatics found here dermal papillae project into the epidermis Meissner’s corpuscles (in dermal papillae); mostly in fingertips a) encapsulated; two point discrimination bulb of the hair follicle (see page 385 in Ross) a) matrix of hair follicle is equivalent to the basal layer of epidermis b) melanocytes contribute melanin granules c) sebaceous glands (always associated with hair follicle) i. secrete sebum between shaft and follicle 1 Histology SSN October 27, 2003 ii. holocrine secretion—cell is stuffed with product and necroses d) arrector pili (smooth muscle bundle) i. hair pulled to vertical position ii. goosebumps due to skin depression Reticular layer (dense CT) eccrine sweat glands (coiled tubular glands—not associated with hair follicles) a) secretion contains salts and IgA b) secretory portion in subcutaneous tissue i. secretory tubules: acidophilic layer of myoepithelium contracts to expel secretion ii. myoepithelium – sympathetic innervation c) ducts extend to epidermis i. excretory ducts: TWO layers of cuboidal cells ii. remove salt – final sweat hypotonic iii. corkscrew path in epidermis Pacinian corpuscle (found in deeper dermis and hypodermis) i. encapsulated ii. senses vibration, deep pressure HYPODERMIS subcutaneous tissue loose CT, many glands, ducts, blood vessels, lymphatics abundant adipose tissue 2 Histology SSN October 27, 2003 SKIN QUESTIONS 1. In the stratum basalis, ________ are found. They attach keratinocytes to _________. a. b. c. d. Hemidesmosomes, basal lamina Desmosomes, basal lamina Hemidesmosomes, other keratinocytes Desmosomes, Langerhans cells 2. What is the function of the structure at the pointer? a. b. c. d. senses light touch. pain and temperature sensation. deep pressure and vibration sensation. increases rate of neuronal transmission. 3. The structure is a(n) ________; it is located in the _________ layer, and its ducts terminate in the ________. a. b. c. d. sebaceous gland, hypodermal, stratum granulosum. eccrine sweat gland, dermal, stratum granulosum. eccrine sweat gland, dermal, stratum corneum. sebaceous gland, hypodermal, stratum corneum. 3 Histology SSN October 27, 2003 SKIN ANSWERS 1. Lab 8, slide 2 a) Choice A is correct b) Choice B is not correct because desmosomes attach keratinocytes to other keratinocytes. c) Choice C is not correct because hemidesmosomes attach keratinocytes to the basal lamina. d) Choice D is not correct because Langerhans cells are involved in the immune response and does not form desmosomes with neighboring keratinocytes. 2. Lab 8, slide 17 (pointer on Pacinian Corpuscle) a) senses light touch – NO. This better describes a Meissner’s corpuscle, which senses 2 point discrimination. b) pain and temp. sensation – NO. This describes free nerve endings in the epidermis. c) deep pressure and vibration sensation – YES. d) increases rate of neuronal transmission – partly true. At best, this answer is only partly correct, as the STRUCTURE is the corpuscle. A myelin sheath (composed of Schwann cells) surrounds the nerve axon entering the corpuscle and does ensure an increased rate of transmission relative to transmission in unmyelinated nerves – but the myelin sheath only extends for one or two nodes. The inner core of the corpuscle is composed of lamellae of attenuated Schwann cells, while the outer core of the corpuscle is composed of lamellae of extra-corpuscular endoneurial cells. Lymphlike fluid and collagen sit between the lamellae; displacement of lamellae causes an action potential – so the Schwann cells are also involved in whether the transmission will happen at all (their role is not limited to ensuring speed). 3. Lab 8, slide 14 a) Choice A is not correct because sebaceous glands are only associated with hair follicles. b) Choice B is not correct because if this were true, sweat would have to percolate to the outer surface of the epidermis. c) Choice C is correct. d) Choice D is not correct because, again, sebaceous glands are only associated with hair follicles. 4