BACKGROUND INFORMATION [about Hydrogen Peroxide [H202
advertisement

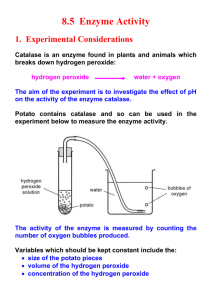
Name __________________________________________________________________________ Hr._________ A CHEMICAL REACTION OF LIVING THINGS BACKGROUND INFORMATION [about Hydrogen Peroxide [H202] and the enzyme catalase] Chemical Equation: PROCEDURE: Control Test: 1. Measure out 10 ml of H2O2 with a graduated cylinder. 2. Place the 10 mi of H2O2 in a test tube. . 3. Place the thermometer GENTLY into the test tube with the H2O2. 4. Record the starting temperature in the data table below. 5. Add 3 drops of stock enzyme solution to the test tube. 6. Stir GENTLY with the thermometer. Observe the reaction. When the reaction is finished bubbling, record the end temperature in the data table below. 7. Rinse off all equipment carefully and return it to the proper location. Enzyme Research: Why is the above procedure considered to be the control? In the control experiment, you used an enzyme called catalase to breakdown hydrogen peroxide. How long does it take hydrogen peroxide to break down without the use of catalase? What does this tell you about the function of enzymes in chemical reactions? In the next step of this lab, you will research the impact of a variable on enzyme functioning. Please see your instructor for you assigned variable. My variable _________________________ Research the impact of your variable on enzyme functioning. Include whether the variable will help or hurt enzyme functioning and why the variable has the effect. Provide evidence of your research in the space below. Based on your research, please write a hypothesis in the space below for your assigned variable. You are going to answer some thoughtful questions about the role of enzymes in the reactions of living organisms. You will need more information including the results of the following experiments. To better understand how the enzyme, catalase, is involved in the H202 reaction, let's look at how various factors affect the reaction. A. Do the control test but use cooked liver instead of the fresh liver used in the control test. Use cooked liver in step 5 above. B. Do the control test but use twice the amount of stock enzyme solution. Use 6 drops in step 5 above. C. Do the control test but use twice the amount of H2O2 (20 ml) in the test tube. Measure out 20 ml in step one above. Be sure to use a large test tube. D. Do the control test but add 8 drops of Hydrochloric Acid (HCI) to the 10 ml of H 202 before adding the stock enzyme solution. E. Do the control test but add 8 drops of Sodium Hydroxide (NaOH) to the 10 ml of H 202 before adding the stock enzyme solution. NaOH is a strong base. DATA TABLE TREATMENT H202 LIVER Control 10 10 10 20 10 10 3 3 6 3 3 3 A. Boiled liver B. Extra liver C. Extra H202 D. 8 drops acid E. 8 drops base ml ml ml ml ml ml drops drops drops drops drops drops START TEMP END TEMP C C C C C C C C C C C C DIFFERENCE NUMBER OF CALORIES C C C C C C One calorie equals the amount of energy required to raise one ml of water one degree Celsius. Calculate this by multiplying the temperature increase x number of ml = __________ small calories DISCUSSION: 1. Offer some thoughtful explanations of what caused the bubbling during the reaction. Look at the chemical equation you wrote on the other side. What gas do you think the bubbles are? 2. Look at the table for boiled enzyme. How did boiling the enzyme (treatment A] affect the reaction? What do you think cooking did to the enzyme? 3. What would you predict would happen if we simply heated up the hydrogen peroxide and catalase mixture, but didn’t boil it? You will need to use your netbook to research how an increase in temperature impacts enzymatic reactions. 3. Did the energy released in the reaction come from the H202 or the enzyme catalase? Explain your answer. To explain your answer, compare the table results for treatments B (extra enzyme] & C [extra H 202] with the control results. 4. A. Do you think acids and bases have a harmful or helpful affect on the action of the enzyme? Explain your answer by comparing the table results for treatments D [adding acid] & E (adding base] with the control results which are at a neutral pH. B. Look at the pH scale to the right. At what pH do you think the reaction would run the fastest? Hydrogen peroxide is a poisonous chemical that is continually formed by reactions in living cells. It could kill a cell. The chemical formula for hydrogen peroxide is H202. When hydrogen peroxide is placed with the enzyme catalase, water (H 20) and oxygen gas (02) are formed. Water and oxygen are not harmful to living cells. With these facts in mind, answer number 5 and 6. 5. Explain why the enzyme catalase is important to the life of a cell. 6. Hydrogen peroxide will bubble if placed on a cut finger. What does this reaction tell you about where the enzyme is found? Is this enzyme found only in the liver? How do you know? If left open in the sunlight, a bottle of hydrogen peroxide will slowly change into water and oxygen. Under these conditions it takes a very long time [months] for the reaction to happen. On the other hand, when catalase is placed in the hydrogen peroxide, the reaction takes place almost immediately. 7. What does this tell you about the function of an enzyme? In other words, what does an enzyme do to a reaction? State Standard B2.2f