APBio Lab 2 PreLabName Section
advertisement

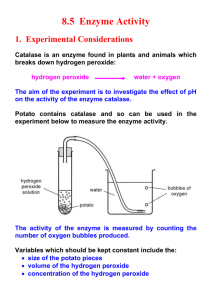
APBio Lab 2 PreLab Name Section Use your text and lab sheet to help you answer these questions. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. Give an overview of what we will be doing in this lab. Use your text and explain what it means to be a catalyst. Explain what this equation means: E + S ES E + P Identify the enzyme, substrate and products in our experiment. Explain how salt might affect an enzyme. Explain how pH might affect an enzyme. Explain how temperature affects enzymes. Explain how activators and inhibitors affect enzymes. Describe catalase. Explain why catalase is so essential that it would be found in cells of all aerobic organisms. What does the curved line in the graph on page 21 indicate? Why s the initial reaction rate usually faster than the rate as the reaction proceeds? What is the formula for determining the initial rate of reaction? Explain in words what the formula means. In our experiment, what will we measure to determine the rate of reaction? What happens when sulfuric acid is added to a solution of catalase and hydrogen peroxide? Why does this happen? Potassium permanganate is bright pink in color. What happens to that substance when it is added to hydrogen peroxide and sulfuric acid? If additional potassium permanganate is added and it does not break down and turn colorless, what does that tell us about the amount of hydrogen peroxide still present in the solution? If you added 50 drops of potassium permanganate to solution A and 10 drops of potassium permanganate to solution B before they turn pink, which solution must contain the most hydrogen peroxide? If catalase is added to hydrogen peroxide, how will it be apparent that a reaction is taking place? What causes the bubbling? What do you expect might happen to catalase when it is boiled? Name several substances/materials/things that would be expected to contain catalase.