How did Stalin Rise to Power.doc
advertisement

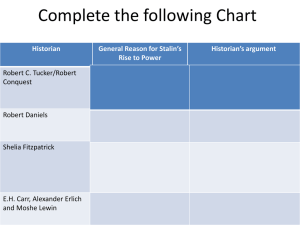
Elective History Final-Year Examination Revision Stalin’s Russia (SEQ Revision) A) How did Stalin Rise in Power? When we examine the reasons behind the rise of Stalin, there are TWO MAIN FACTORS RESPONSIBLE: Stalin’s Cunning Personality o Stalin Outwitted His Rivals o Stalin Pretended to have been Close to Lenin o Made Alliances o Used His Position as Secretary-General of the Party Favourable Circumstances o Trotsky’s Weaknesses 1) Stalin Outwitted His Rivals When Lenin died, there were four contenders to his place – Leon Trotsky, Lev Kamenev, Grigory Zinoviev and Joseph Stalin. Although Trotsky, Kamenev and Zinoviev were much more capable than Stalin, Stalin managed to outwit them and claim leadership despite Lenin’s will criticising Stalin and naming Trotsky as a successor. 2) Stalin Pretended to have been Close to Lenin Stalin tricked Trotsky and made him miss Lenin’s funeral which reflected very badly on Trotsky. Stalin also organised Lenin’s funeral and made himself the chief mourner which gave people the impression he was very close to Lenin. 3) Trotsky’s Weaknesses Stalin was also able to rise due to Trotsky’s weaknesses. Trotsky had a narrow support base limited to youths, students and the Red Army. As he was too confident of replacing Lenin, he did not bother to build a Party support base unlike Stalin. He was not well liked in the Party and his views on world revolution were not popular as the Party members preferred the more practical Stalinist view of working on Socialism within the country first. 4) Made Alliances Stalin made alliances with Kamenev and Zinoviev to have Trotsky removed and exiled from Russia. Once he had achieved his purposes, Stalin turned on Kamenev and Zinoviev using other alliances and had them removed from the Party. 5) Used his Position as Secretary-General Stalin used his position as Secretary-General of the Party to appoint his supporters to important posts, ensuring their loyalty. By controlling the central Party machine, he was able to exert great influence on the Party members and get them to vote on his policies or initiatives (e.g. voting out of Trotsky in 1925). In conclusion, when writing your essay on this issue, you MUST explain both factors and their supporting points and WEIGH which one helped Stalin REACH HIS POSITION MORE EFFECTIVELY. B) The Control of the Russian People – Fear or Propaganda When we examine how Stalin controlled the Russian people, there are TWO MAIN FACTORS RESPONSIBLE: Fear o Establishment of a Dictatorship o Development of a Terror State Propaganda o The use of Propaganda to Control o Control over the Education System & Arts o Cult of Personality 1) Establishment of a Dictatorship Stalin established an authoritarian regime where he was a dictator and held all the political power in his hands. As a dictator, Stalin could make laws without consulting other members of the government or the people of Russia. He banned other political parties from the Soviet Union and anyone who opposed Stalin was beaten, jailed or even killed. 2) The Use of Propaganda to Control Stalin used propaganda to persuade people to accept and obey him as the rightful leader of the country. Stalin often exaggerated his achievements and made writers and journalists portray him as a hero of the people. 3) Control Over the Education System & Arts Stalin also controlled the education system by centralizing it and controlling it through the government. Schools had to teach Marxist and Leninist ideas and instill complete loyalty to the state among the students. Stalin’s role in important events such as the October 1917 Revolution was increased and those of his enemies or opponents unfairly represented or ignored. Strict discipline was enforced for teachers and students who would be purged if they were anti-Stalin. Authors and artists were forced to portray Stalin in good light. Emphasis was placed on highlighting and promoting Stalin’s industrialization success and as a result there was a lack of variety in Soviet culture at the time. 4) Stalin’s Purges (Development of a Terror State) Used the high-profile murder of one of his supporters to purge his opponents in the Communist Party over the years 1934 to 1938. Arrested by the NKVD (secret police), the opponents were sent to jail, tortured, sent to labour camps or simply executed. Intellectuals, politicians, teachers, writers, workers, armed forces personnel, scientists, ordinary Russians and anyone perceived as a threat to Stalin was not spared. Those arrested were put on “show trials” where they were made to admit to ridiculous crimes and sign confessions before being jailed or executed. People lived in an atmosphere of fear and suspicion. People were encouraged to inform on one another and no evidence was necessary for persecution. Mass executions were carried out and the victims buried in mass graves. Over 20 million Russians lost their lives to the purges. Stalin became extremely powerful as no one dared to challenge or oppose him. High-ranking officials who had been purged were often removed from photographs and paintings as well. Stalin also disallowed religion and sent his young followers to spread anti-religious propaganda. Places of worship were vandalized and their leaders persecuted. 5) The Cult of Personality (Cult of Stalin) Stalin tried to make the Russian people worship him as a leader. He often portrayed himself as a cheerful, fatherly and popular man. Statues, pictures and paintings of him were placed prominently all over Russia from government offices to factories to schools to humble homes. Successes of Russia were also attributed to Stalin.