The Endocrine System
advertisement

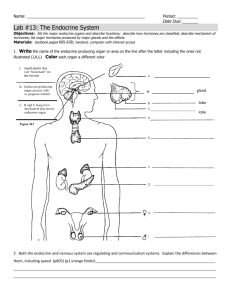
Biology 30 - Ch. 16 – Chemical Regulation Notes The Endocrine System Controls many body functions – Exerts control by releasing special chemical substances into the blood called ____________________ – ______________ affect _________________ or _________________ _______________ glands release hormones ________________________. _________ glands - transport their hormones to target tissues via ________________. The Endocrine System consists of several glands located in various parts of the body. Hormones are produced by specialized endocrine glands and travel through the circulatory system to their destination. Unlike the nervous system, the message delivered by the hormones is ____________ ______________________________________________. The hormones are delivered throughout the body. When the hormone reaches the target cell, receptors located on the target cell bind to the hormones. This causes some change to occur in the organ targeted. Types of Hormones _________________________ ____________ based hormones consist of several ______________ strung together. They are secreted by the ________________ located in the ___________. The pituitary gland is the __________ controlling all other endocrine glands in the body. _________________ (also referred to as ________________) _____________ based hormones are derived from ____________. Hormones such as ____________ secreted by the _______________ are a steroid based hormone. Steroid based hormones have a similar structure. Control of Hormone Secretion Negative Feedback Negative feedback is the body’s response to __________________________ internal conditions. An analogy for negative feedback is the thermostat in your home. Negative feedback mechanisms act like a thermostat in the home. As the temperature decreases, the thermostat detects the change and triggers the furnace to cut in and warm the house. Once the temperature reaches its thermostat setting, the furnace turns off. The endocrine system uses cycles and negative feedback to regulate physiological functions. Negative feedback regulates the secretion of almost every hormone. Cycles of secretion maintain _________________________ control. These cycles can range from ______________________ in duration. Negative feedback helps to maintain an equilibrium in the body called ____________. An example of negative feedback in the body: _____________levels in the bloodstream are regulated in part by the _____________ glands. When these glands sense that calcium levels are __________ they secrete a hormone that causes the _____________ to release ___________________. 1 Biology 30 - Ch. 16 – Chemical Regulation Notes If the stimulus is high calcium levels, once again sensed by the parathyroid glands, it causes the parathyroid glands to halt their production of the calcium-liberating hormone. Positive Feedback Positive feedback is _____________ in the body. It does not create as ____________ in the body as negative feedback does. In positive feedback the initial response ______________ the stimulus that gave rise to it. Recall that in negative feedback the initial stimulus actually decreases the initial stimulus. Example - Childbirth During childbirth the uterus stretches due to pressure from the growing infant. This causes release of the hormone _____________ which initiates a positive feedback mechanism. _____________ stimulates the uterus to _________________. The contraction of the uterus stimulates further production of ___________ which stimulates further contractions. This process leads to more stretching until finally the loop is broken upon birth of the baby. The Endocrine System Pituitary gland: a small gland located on a stalk hanging from the base of the brain Often referred to as ______________________________ – Primary function is to ________________________. – Produces many hormones. – Secretion is controlled by the ___________________ in the base of the brain. The Pituitary Gland is divided into 2 areas, which differ – ______________ and _______________________ – Each area has separate types of hormone production The two segments are: – Posterior Pituitary: produces ______________________________________________ – Anterior Pituitary: produces _________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________ Posterior Pituitary – Oxytocin Stimulates _______________________________________________ causes ______________________________________ – _________________________ causes the _____________________________. Anterior Pituitary Primarily regulates ________________________________________. 2 Biology 30 - Ch. 16 – Chemical Regulation Notes ______ stimulates the _________gland to release its hormones, thus ______________ _______________ stimulates ________________________________________. Growth hormone (GH) ______________________________ ____________________________________ as an energy source Hormone that stimulates ____________________ in children. Too much = _______________________ Too Little = _______________________ Pineal Gland The pineal gland is located near the _______________________, having the shape of a tiny cone Its hormone __________________ has significant effects on ________________ and daily physiologic cycles, most notably the ______________________________. The Thyroid Gland – Lies in the ______________ just below the ___________________. – Two lobes, located on either side of the trachea, When stimulated (by TSH or by cold), hormones are released into the circulatory system and ___________________________. __________________, when released, lowers the amount of _________ in the blood. Parathyroid Glands – Small, pea-shaped glands, located in the neck near the thyroid – Usually 4 - number can vary – Regulate the level of _____________________ in the body – Produces _____________________ - _________________________ in blood – Hypocalcaemia can result if parathyroids are removed or destroyed. Pancreas – a large key gland located in the __________________________________ – has both ________________________________ functions – secretes several key ____________________ through the ______________ into the ____________________________. ______________________________ – specialized tissues in which the endocrine functions of the pancreas occurs. Secretes 2 important hormones: _________________, essential for controlling ________________________. When blood glucose levels __________, ___the amount of _________ in the blood . The surge of ___________ stimulates the liver to release ______________________ (from __________________ and additional storage sites). 3 Biology 30 - Ch. 16 – Chemical Regulation Notes __________________ (antagonistic to __________________). _______________ the rate at which various body cells take up __________. Thus, insulin _____________________________________________. Insulin is rapidly broken down by the ___________ and must be _______________. Adrenal Glands – 2 small glands that sit atop ______________________. – Each has 2 divisions, each with different functions. the _________________ secretes the hormones _____________ and _____________. ________________ is also known as _____________________. Involved in the _______________________ reaction. ________________ speeds up ____________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ ________________________ counteracts the effects of _______________________. The ____________________ secretes 3 classes of hormones, all steroid hormones: – Some the level of _________________ in the blood – Released in response to ______________________________________ - like the hormones from the adrenal medulla. – Work to regulate the concentration of _________________________ in the body. Gonads and Ovaries: – The endocrine glands associated with human reproduction. – Female ovaries produce ______________ – Male gonads produce ________________ Both have endocrine functions. Ovaries: – located in the abdominal cavity adjacent to the uterus. The ovaries are under the control of ____________ from the _________________ and they manufacture __________________________________________ ____________and _______________ have several functions, including ___________ ______________ and preparation of the uterus for __________________________. Testes: –located in the _____________________ –produce sperm for reproduction –manufactures ________________ - promotes _____________ and _____________ –Controlled by ____________________ hormones ______________________ Endocrine Disorders: Diabetes Mellitus – one of the most common diseases in North America. 4 Biology 30 - Ch. 16 – Chemical Regulation Notes – _________________ secretion by the _______________________ in the pancreas. Complications of Diabetes: – ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ Hypoglycemia ____________________________ blood glucose levels. Body cannot mobilize stored glucose due to low levels of ____________________. Symptoms = ________________________________________________________. Goiter: Enlarged __________________________ Cause: Not enough _________________ ingested to make _____________________ Addison’s Disease Normal _____________ levels cannot be maintained due to low levels of _________. Results in incomplete digestion of ________________________________________. Symptoms = low blood sugar, weakness or sluggishness, weight loss, increased skin pigmentation, reduced tolerance to stress. Anabolic Steroids Anabolic steroids, which are synthetic versions of the primary male sex hormone testosterone, can be injected, taken orally, or used transdermally. While anabolic steroids can enhance certain types of performance or appearance, they are dangerous drugs, and when used inappropriately, they can cause a host of severe, long-lasting, and often irreversible negative health consequences. Research has shown that the inappropriate use of anabolic steroids can have catastrophic medical, psychiatric and behavioural consequences. These drugs can stunt the height of growing adolescents, masculinize women, alter sex characteristics of men and may cause sterility. Anabolic steroids can lead to severe acne, premature heart attacks, strokes, liver tumours, kidney failure and serious psychiatric problems. In addition, because steroids are often injected, users risk contracting or transmitting HIV or hepatitis. 5