Bell Work 3-10
Write today’s assignments in your planner.
Write down and answer the following:
What is the hormone that is present in the urine during
pregnancy that is detectable by home pregnancy tests?
HCG
Chapter 9 Concept Map Review
Endocrine system
Secondary messenger system
Endocrine gland
stimuli
hormones
glands
chemistry
mechanisms
Chemistry of hormones
Amino acid based
Proteins, peptides,
and amines
steroid
cholesterol
Sex hormones
and adrenaline
prostaglandin
lipids
Endocrine gland stimuli
Hormonal
Hormone stimulates
Endocrine glands
Hypothalamus to
anterior pituitary
to target glands
humoral
Changes blood
level of ions
PTH and
calcium
neural
Nerves stimulate
hormone release
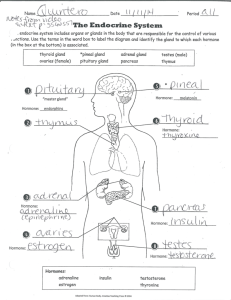
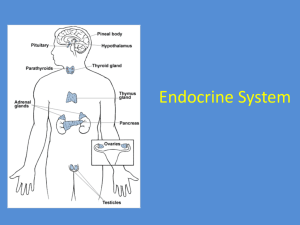
Endocrine glands
pineal
hypothalamus
pituitary
thyroid
parathyroid
thymus
adrenal
pancreas
ovary
testis
Pineal Gland
melatonin
controls sleep cycles
Fits in turk’s
saddle
Pituitary Gland
Grape
sized
Master gland
Anterior
Posterior
Glandular
tissue
Growth hormone
Prolactin
neural tissue
bones and muscles
mammary glands
Follicle-stimulating & Luteinizing
Thyrotropic
Adrenocorticotropic
gonads
thyroid
adrenal gland
Posterior Pituitary
Oxytocin
Stimulates contractions
Stimulates milk ejection
Stops postpartum bleeding
Induces labor
Antidiuretic hormone
Increase
blood
pressure
Stops
urine
production
Prolactin (PRL)
Protein based
Pro – for, lact -milk
Stimulates milk production
Unknown function in males
Growth Hormone (GH)
Builds protein
General metabolic
Breaks down fats
Maintains blood sugar homeostasis
Hyposecretion causes dwarfism
Hypersecretion causes gigantism
Hypothalamus Gland
Controls pituitary
Thyroid Gland
At base of Adam’s apple
Thyroid hormone
calcitonin
Body’s major
metabolic hormone
Thyroxine (T4)
Triiodothyronine (T3)
Antagonist to
Parathyroid
hormone
iodine
Thymus Gland
Thymosin
Matures the T cells
Pancreas
islets
alpha cells
beta cells
glucagon
insulin
Gets glucose
into blood
= hyperglycemic
Gets glucose out
of blood
= hypoglycemic
Parathyroid Gland
Parathymone (PTH)
Regulates calcium in blood
If calcium levels too low =
uncontrollable spasms (tetany)
Adrenal Gland
cortex
glandular
corticosteroids
mineralocorticoids
glucocorticoids
sex hormones
neural
medulla
catecholamines
Epinephrine and
norepinephrine
aldosterone
cortisone, cortisol
Androgens, estrogens
Ovary
Estrogen
Produced by
Graafian follicles
Progesterone
Produced by
Corpus luteum
Testis
Androgens
Testosterone
Produced by
interstitial cells