Keynesian Vs Classical Economics comparison.doc
advertisement
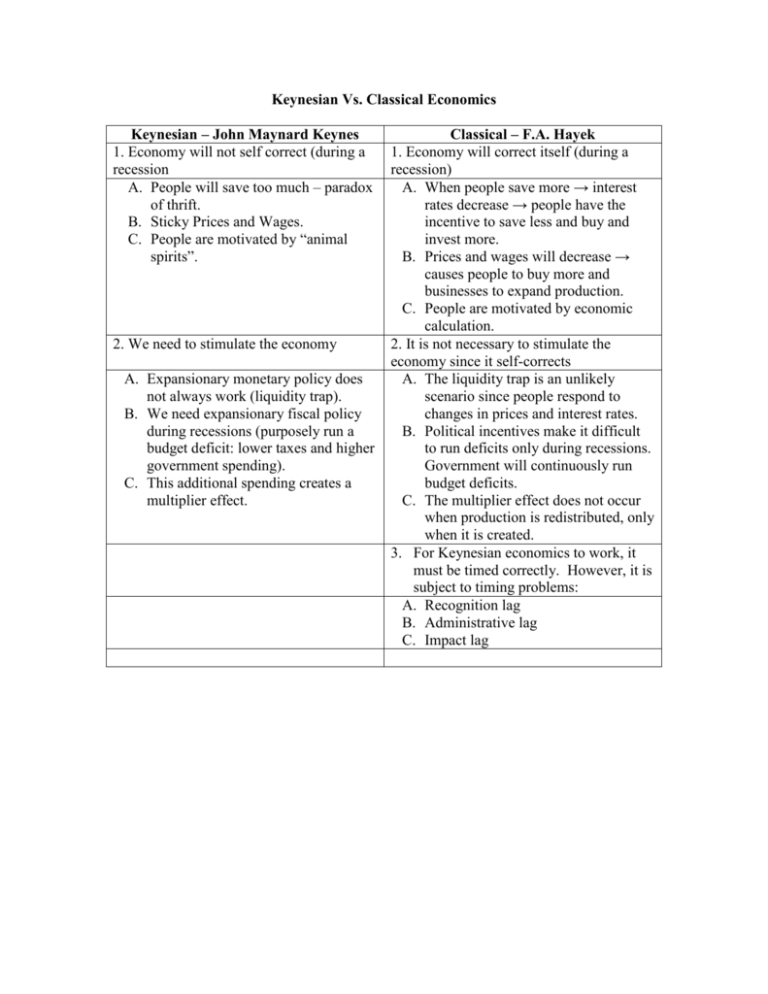
Keynesian Vs. Classical Economics Keynesian – John Maynard Keynes 1. Economy will not self correct (during a recession A. People will save too much – paradox of thrift. B. Sticky Prices and Wages. C. People are motivated by “animal spirits”. 2. We need to stimulate the economy A. Expansionary monetary policy does not always work (liquidity trap). B. We need expansionary fiscal policy during recessions (purposely run a budget deficit: lower taxes and higher government spending). C. This additional spending creates a multiplier effect. Classical – F.A. Hayek 1. Economy will correct itself (during a recession) A. When people save more → interest rates decrease → people have the incentive to save less and buy and invest more. B. Prices and wages will decrease → causes people to buy more and businesses to expand production. C. People are motivated by economic calculation. 2. It is not necessary to stimulate the economy since it self-corrects A. The liquidity trap is an unlikely scenario since people respond to changes in prices and interest rates. B. Political incentives make it difficult to run deficits only during recessions. Government will continuously run budget deficits. C. The multiplier effect does not occur when production is redistributed, only when it is created. 3. For Keynesian economics to work, it must be timed correctly. However, it is subject to timing problems: A. Recognition lag B. Administrative lag C. Impact lag











