Stock and Watson
advertisement

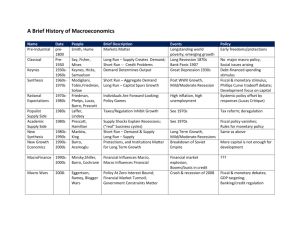
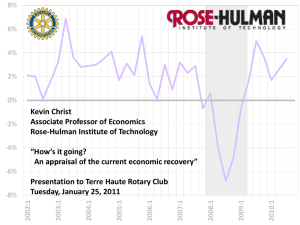
Stock and Watson Disentangling the Channels of the 2007-2009 Recession 1 Research Questions • Beyond severity, how did this recession differ from previous post-war recessions? • What specific economic shocks triggered the 2007 recession and what were their quantitative contributions? • What is responsible for the anemic recovery in output and employment? 2 Approach • • • • Dynamic Factor Model 1959:Q1 – 2011:Q2 200 Macroeconomic variables Six shocks – – – – – – Oil prices (3 instruments, taken from the literature) Monetary policy (4) Productivity (3) Uncertainty (2) Liquidity/Financial risk (3) Fiscal policy (3) 3 Answers • There is little evidence of a new factor associated with the 2007:Q4 recession and its aftermath. Rather, the factors driving this recession are those associated with previous recessions. • The response to “old” factors seems to have been the same post 2007:Q4 as pre 2007:Q4. • The shocks to “old” factors were large, particularly in fall 2008 (i.e., no need to bring in a special “financial crisis” factor). 4 Answers (2) • Interpretation of 2007-09 recession: – Economy was hit in close succession by a sequence of unusually large shocks, all of which have been experienced before, but not in such magnitude or close succession. – Specifically, an initial oil shock, followed by the financial crisis, financial market disruptions and prolonged uncertainty due to policy uncertainty. Financial crisis affected the economy through uncertainty/liquidity and financial risk (i.e., traditional channels, just larger shocks) 5 Answers (3) • Most of the slow recovery in employment and nearly all the slow recovery in output is due to a secular decline in trend labor force growth. – Traceable to demographic factors Plateau-ing of the historic increase in the female labor force participation rate (1960-1990) Somewhat smaller decline in male labor force participation rate. 6 Potential Explanations of Weak Recovery • • • • Tight monetary policy Post-financial crisis hangover Bad policy / policy uncertainty Decline in growth of labor force (demographic factors) 7