Second year Natural Disasters Workbook
advertisement

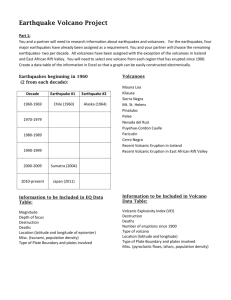
Taylor High School Faculty of Social Subjects Second Year Geography Unit 1 1 Lesson 1 Introduction What is Geography? Discuss with a partner what you think you will learn about in Geography. Write your ideas in a mind map in both your jotters. You may be asked to feedback your ideas during a class discussion about the above question! After the class discussion copy and complete the following sentence into your jotter. Geography is about ..... In this unit you will be learning about natural disasters. Working with the same partner, discuss the following question. What is a natural disaster? Write your ideas in a mind map in both your jotters. You may be asked to feedback your ideas during a class discussion about the above question! After the class discussion copy and complete the following sentence into your jotter. A natural disaster is ….. Now that you have a better idea of what you will be learning about in Geography and what natural disaster are, you can complete a title page in your jotter for the natural disaster unit. 2 Lesson 2 Earthquakes In this lesson you are going to learn about earthquakes, What they are and why they occur. What is an earthquake? An earthquake is a shaking of the ground caused by the sudden breaking and movement of large sections of the earth's rocky outermost crust. The crust of the earth is not reassuringly one large piece of solid rock. Instead it is actually broken into many parts called tectonic plates. The edges of the tectonic plates are marked by faults (or fractures). Most earthquakes occur along the fault lines when the plates slide past each other or collide against each other. The shifting masses send out shock waves that may be powerful enough to alter the surface of the Earth, thrusting up cliffs and opening great cracks in the ground and cause great damage ... collapse of buildings and other manmade structures, broken power and gas lines (and the consequent fire), landslides, snow avalanches, tsunamis (giant sea waves) and volcanic eruptions. In order to fully understand the above definition we must now learn about the structure of the earth. Some people may think that the earth is simply a large solid ball of rock. This is not the case! 3 The earth is made up of four main layers. The inner core, which is a solid ball of metals, such as iron and nickel. This is surrounded by the outer core, which is a liquid. The next layer is called the mantle and is made from molten rocks. This is the thickest of the four Layers. Finally the part of the earth we stand on is known as the crust. It might surprise you to find out that the crust is the thinnest section of the earth. Copy this diagram into your jotter. Answer the following questions in your jotter. 1) 2) 3) 4) What is an earthquake? Where do most earthquakes occur? What causes an earthquake to occur? What can the shockwaves of an earthquake be powerful enough to do? 5) List and describe the four main layers of the earth. 4 Lesson 3 In this lesson you are going to learn about the impact of an earthquake on the environment and people. Watch the DVD about the Japanese earthquake of 2011 and answer the following questions in your jotter. 1) 2) 3) 4) When did the Japanese earthquake happen? What magnitude did the earthquake register? Describe the damage caused by the initial earthquake? Why do you think the earthquake didn’t damage many of the tall buildings in Tokyo. 5) What did the initial earthquake trigger? 6) Describe the damage caused by the tsunami. 7) Where were people advised to go before the tsunami hit? You are now aware that earthquakes do not just cause damage to the environment, but they can damage people lives too. In developed countries such as the USA and Japan precautions can be taken to ensure that buildings are built to withstand earthquakes. This saves many peoples lives, however it is very costly. In developing countries it is difficult to ensure that buildings are built to be earthquake proof as this costs too much money, cities are often overcrowded and many people live in shanty towns with self constructed houses. This is why when an earthquake occurs in a developing country the death toll is much larger. Homework: Using the paper provided, write a newspaper article reporting on the Japan Earthquake. 5 Lessons 4-6 In lessons 4-6 you will be working as part of a small group in order to carry out research into a recent earthquake. You will create an information poster about this earthquake and your group will present your findings to your class. Your poster should include the following information: - Where the earthquake happened. When the earthquake happened. How powerful the earthquake was. The causes of the earthquake. The damage caused by the earthquake. The human impact of the earthquake. The final death count. The San Andreas Fault, California 6 Lesson 7 In this lesson you are going to learn about Volcanoes, what they are and why they happen. What is a Volcano? A volcano is a mountain that opens downward to a pool of molten rock below the surface of the earth. When pressure builds up, eruptions occur. Gases and rock shoot up through the opening and spill over or fill the air with lava fragments. Eruptions can cause lateral blasts, lava flows, hot ash flows, mudslides, avalanches, falling ash and floods. Volcano eruptions have been known to knock down entire forests. An erupting volcano can trigger tsunamis, flash floods, earthquakes, mudflows and rock falls. How are volcanoes formed? Volcanoes are formed when magma from within the Earth's upper mantle works its way to the surface. At the surface, it erupts to form lava flows and ash deposits. Over time as the volcano continues to erupt, it will get bigger and bigger. What are the different categories of volcanoes? Scientists have categorised volcanoes into three main categories: active, dormant, and extinct. An active volcano is one which has recently erupted and there is a possibility that it may erupt soon. A 7 dormant volcano is one which has not erupted in a long time but there is a possibility it can erupt in the future. An extinct volcano is one which has erupted thousands of years ago and there’s now no possibility of eruption. Why do volcanoes erupt? The Earth's crust is made up of huge slabs called plates, which fit together like a jigsaw puzzle. These plates sometimes move. The friction causes earthquakes and volcanic eruptions near the edges of the plates. The theory that explains this process is called plate tectonics. How many volcanoes are there? There are more than 1500 active volcanoes on the Earth. We currently know of 80 or more which are under the oceans. Answer the following questions in your jotter. 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) 7) What is a volcano? Why do volcanoes erupt? How are volcanoes formed? What is an Active volcano? What is a dormant volcano? What is an extinct volcano? Copy the diagram opposite into Your jotter. 8 Lesson 8 In this lesson you are going to learn about the impact of a volcano on the environment and people. Watch the DVD about the Mount St Helens eruption and answer the following questions in your jotter. 1) Worldwide, how many people live in the shadows of volcanoes? 2) How many square miles of land was stripped bare by the eruption of Mount St Helens? 3) What covered this area before the eruption? 4) How many miles was the exclusion zone set up by the authorities? 5) What speed did the gas, steam and rock blasted from the volcano travel at? 6) How hot was the gas cloud? 7) What effect did this have on the surrounding area? 8) How high were the mudflows and at what speed did the travel? 9) How many feet did Mount St Helens loose from its summit after the explosion. Homework: Using the paper provided, write a newspaper article reporting on the Mount St Helens eruption. Your newspaper report should include the following information: - When the eruption happened. An explanation of why volcanoes erupt. The damage caused to the natural and human environment. The human impact of the eruption. 9 Lessons 9-11 In lessons 9-11 you will be working as part of a small group in order to carry out research into a volcanic eruption. You will create an information poster about this eruption and your group will present your findings to your class. Your poster should include the following information: - Where the Volcano is. When the volcano erupted. The damage caused by the eruption to the environment. The human impact of the eruption. The final death count. Mount St Helens, U.S.A 10 Lesson 12 In this lesson you will learn about tropical storms, what they are and why they occur. What is a tropical storm? Tropical storms are intense thunderstorms that are characterised by intense wind rotation and extremely low pressure, which originates in the tropics. The strongest tropical storms are called hurricanes, typhoons or tropical cyclones. The different names all mean the same thing, but are used in different parts of the world. If these huge storms start in the Atlantic ocean off the west coast of Africa, they are called hurricanes. In an average year, over a dozen hurricanes form over the Atlantic and head westward towards the Caribbean, the east coast of Central America and the Southern USA. Hurricanes are classified into five categories based on their wind speed, central pressure, and damage potential. 11 Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Scale Scale Number (Category) Sustained Winds (MPH) 1 74-95 Minimal: Unanchored mobile homes, vegetation and signs. 4-5 feet 2 96-110 Moderate: All mobile homes, roofs, small crafts, flooding. 6-8 feet 3 111-130 Extensive: Small buildings, low-lying roads cut off. 9-12 feet 4 131-155 Extreme: Roofs destroyed, trees down, roads cut off, mobile homes destroyed. Beach homes flooded. 13-18 feet 5 More than 155 Storm Surge Damage Catastrophic: Most buildings destroyed. Vegetation destroyed. Major roads cut off. Homes flooded. Greater than 18 feet Effects of tropical storms. The intense winds of a tropical storm can destroy whole communities, buildings and communication networks. As well as their own destructive energy, the winds generate abnormally high waves and tidal surges. Sometimes the most destructive elements of a storm are the subsequent high seas and flooding. Answer the following questions in your jotter. 1) 2) 3) 4) What is a tropical storm? What are the strongest tropical storms called? Copy the table above into your jotter. What damage is expected to be caused by a category 5 hurricane? 5) Describe the effects of a tropical storm. 12 Lesson 13 In this lesson you are going to learn about the impact of a tropical storm on the environment and people. Watch the DVD about Typhoon Haiyan and answer the following questions in your jotter. 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) 7) 8) 9) What wind speed did Typhoon Haiyan reach? What was the death toll of Typhoon Haiyan? How many people were left homeless? What have scientists predicted will occur in the future with regards to tropical storms? Where are the Philippines located? During the 2013 tropical storm season, how many storms had made landfall in the Philippines before Typhoon Haiyan. How high was the storm surge created by the wind? Describe how a tropical storm forms. What date did Typhoon Haiyan form? Homework: Using the paper provided, write a newspaper article reporting on Typhoon Haiyan. Your newspaper report should include the following information: - When the Typhoon happened. An explanation of how tropical storms form. The damage caused to the natural and human environment. The impact of the storm on the people of the Philippines. 13 Lesson 14-16 In lessons 14-16 you will be working as part of a small group in order to carry out research into a recent hurricane, typhoon or cyclone. You will create an information poster about this hurricane, typhoon or cyclone and your group will present your findings to your class. Your poster should include the following information: - Where the hurricane, typhoon or cyclone happened. When the hurricane, typhoon or cyclone happened. How powerful the hurricane, typhoon or cyclone was. The damage caused by the hurricane, typhoon or cyclone. The human impact of the hurricane, typhoon or cyclone. The final death count. 14 15