Cells and Reproduction
advertisement
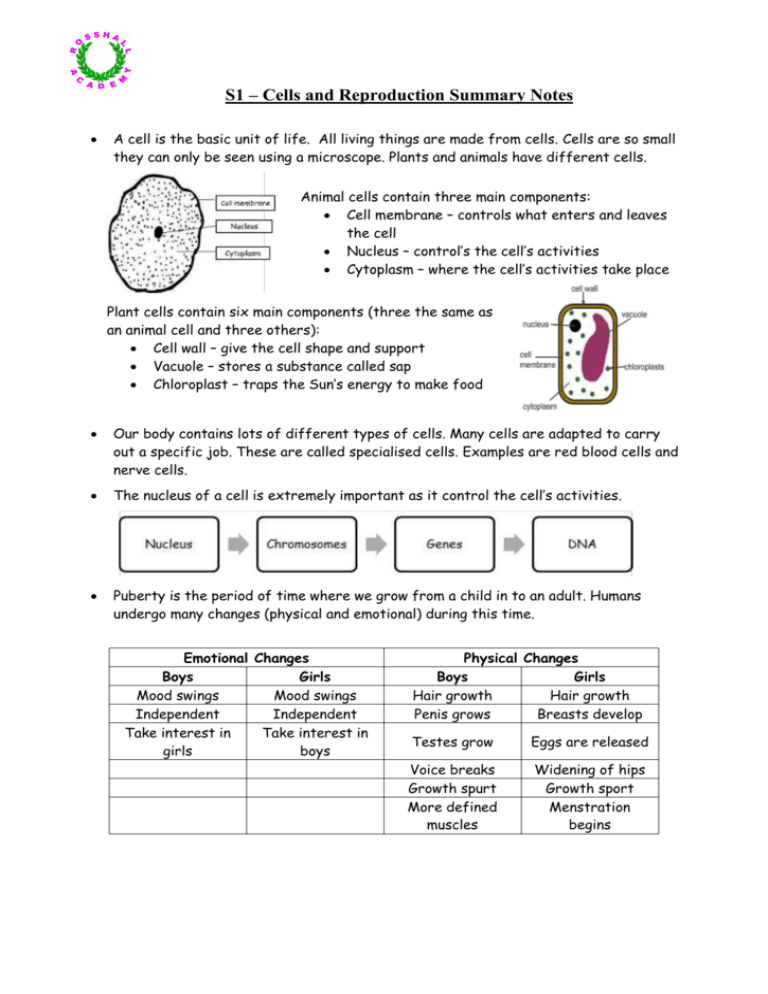
S1 – Cells and Reproduction Summary Notes A cell is the basic unit of life. All living things are made from cells. Cells are so small they can only be seen using a microscope. Plants and animals have different cells. Animal cells contain three main components: Cell membrane – controls what enters and leaves the cell Nucleus – control’s the cell’s activities Cytoplasm – where the cell’s activities take place Plant cells contain six main components (three the same as an animal cell and three others): Cell wall – give the cell shape and support Vacuole – stores a substance called sap Chloroplast – traps the Sun’s energy to make food Our body contains lots of different types of cells. Many cells are adapted to carry out a specific job. These are called specialised cells. Examples are red blood cells and nerve cells. The nucleus of a cell is extremely important as it control the cell’s activities. Puberty is the period of time where we grow from a child in to an adult. Humans undergo many changes (physical and emotional) during this time. Emotional Changes Boys Girls Mood swings Mood swings Independent Independent Take interest in Take interest in girls boys Physical Changes Boys Girls Hair growth Hair growth Penis grows Breasts develop Testes grow Eggs are released Voice breaks Growth spurt More defined muscles Widening of hips Growth sport Menstration begins Reproduction is making a copy of something else. When animals reproduce they make a “baby version” of themselves (e.g. humans reproduce to make a baby) The parts of the body involved in reproduction are called the reproductive organs The male sex cell is called a sperm. Sperm have a head containing a nucleus and a tail The female sex cell is called an egg Eggs contain a nucleus and a large food store At fertilisation the head of the sperm cell enters an egg cell. The nucleus of the sperm joins with the nucleus of the egg. At this point a zygote (the first cell of an individual) is formed. At one point you were only one cell Fertilisation occurs in the oviduct the fertilised egg divides into 2, 4, 8, 16 and so on until it forms a ball of cells. This ball of cells then implants in the spongy lining of the uterus. The developing embryo makes an organ called the placenta that lets it exchange nutrients and waste with the mother. Pregnancy lasts approximately 9 months. This is called the gestation period. There are some risks to the developing embryo such as: o Smoking o Drinking alcohol o Drugs These harmful substances can cross the placenta from the mother in to the baby. However useful substances like antibodies can also cross the placenta. S1 – Cells and Reproduction Practice Test 1. Copy and complete the below table: Component Nucleus Vacuole Cell membrane (4 marks) Function Helps keep shape of cell Stores sap Found in Plant and animal cells Plant cells Plant and animal cells 2. Name one physical change that occurs in boys during puberty. (1 mark) 3. Name on emotional change that occurs in girls during puberty. (1 mark) 4. Name female and male sex cells. (2 marks) 5. Label the diagram of the male and female reproductive systems. (2 marks) 6. Name two risks to embryonic development and explain why they are risks. (2 marks) 7. Give an example of a specialised cell in the body. (1 mark) 8. Where are the sex cells produced in males and females? (1 mark) 9. What is the name given to the ball of cells formed during fertilisation? (1 mark)