EOC Study Guide - Student Fill-In
advertisement

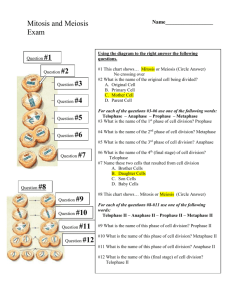
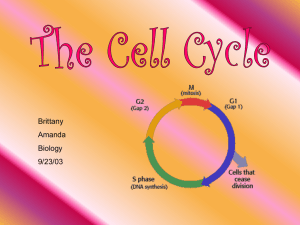
EOC STUDY GUIDE Chapter 1 List steps in the scientific method:_________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________ Define (give example if necessary): Control:_________________________________________________ Independent (experimental) Variable:__________________________ Dependent Variable:________________________________________ Variable:_________________________________________________ What are the 5 Characteristics of Life 1_________________ 2.___________________ 3.____________________ 4._____________________ 5._____________________ (only for the survival of a species!!!) Chapter 2: Principles of Ecology 2.1 Define Ecology:___________________________________________ Abiotic factor:________________________________________ Biotic factor:_________________________________________ Population:__________________________________________ Ecosystem:__________________________________________ What’s the difference between a habitat and niche?___________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________ Symbiosis:_______________________________________________ Circle the correct answer for the following and list 1example Mutualism: win-win win-lose win-doesn’t matter ex:________________________________________________ Commensalism: win-win win-lose win-doesn’t matter Ex:________________________________________________ Parasitism: win-win win-lose win-doesn’t matter Ex:________________________________________________ 2.2 Producers:___________________________________________ Heterotrophs:_________________________________________ Name the different types of heterotrophs (3) 1.__________________________ eats meat 2. __________________________ eats veggies 3. __________________________ eats meat and veggies Decomposers role:__________________________________________ Food chain vs. food web – what do they represent?_______________________________________________ Grass cricket bird human is an example of a ________________ Food web:_______________________________________________ Trophic levels = ______________ levels How much energy is lost at each trophic level?__________________ Who receives the least amount of energy, the top or bottom of the pyramid?________________________________________________ Review and act out with a partner the following cycles: Water Cycle, Carbon Cycle, Nitrogen Cycle, and Phosphorus Cycle 3.1 Communities Define the following and give examples: Limiting factor:__________________________________________ Tolerance:______________________________________________ Succession:_____________________________________________ Primary succession – pioneer species:_________________________ Climax community:_________________________________________ Secondary succession:______________________________________ 3.2 Biomes Give characteristics of each and example locations Terrestrial Biomes -influenced by latitude and climate Tundra:__________________________________________________ Taiga:___________________________________________________ Desert:__________________________________________________ Grasslands:_______________________________________________ Temperate Deciduous Forest:_________________________________ Tropical Rainforest:_________________________________________ -why TR is important (3) 1.__________________________________________ 2.__________________________________________ 3.__________________________________________ 4.1 Population Dynamics Compare the effects of the following that they have on population size: Population increase: when __________ increase and ____________decrease. Circle the correct answer for how they are shown graphically Exponential Growth: J S Carrying Capacity: J S Density Dependent Factor: examples Density Independent Factor: examples -Short life vs. Long life differences:____________________________ ________________________________________________________ Effects of competition within a population:______________________ ________________________________________________________ Effects of crowding and stress: _______________________________ 4.2 Human Population Birthrate = __________________________________________ Death rate=__________________________________________ Population Growth Rate formula=____________________________ Doubling time=___________________________________________ 5.1 Vanishing Species Biodiversity:______________________________________________ Extinction:________________________________________________ Endangered species:________________________________________ Human effect on species populations:__________________________ Types of pollution:_________________________________________ *Biodiversity Importance: stability, interdependent, people needs=medicine, oxygen, food… Types of Habitat Loss: Fragmentation, Edge Effects, Degradation, Pollution, Exotic Species 5.2 Conservation of Biodiversity Preserves – you know this in general Legal Protection of US Endangered Species Law of 1973 Habitat Corridors:__________________________________________ Captivity:________________________________________________ 6.1 Atoms and their Interactions Elements: H, O, N, C Be able to read a chemical formula C6H12O6 = 6 Carbons, 12 Hydrogens, and 6 Oxygens Reactants on the left Products on the right Covalent bonds vs. ionic bonds pH – 1-6 = ______________ 7= __________ 8-14=________ Atomic structure= 4 parts/ 1.___________________ 2. _________________ 3.___________________ 4.__________________ 6.3 Life Substances Study foldable!!! Add examples to help out! Carbohydrates:_________________________________________ Lipids:_________________________________________________ Proteins:________________________________________________ Enzymes:________________________________________________ Enzyme-Substrate Complex:_________________________________ Actions of Enzymes!!! Know the diagram p. 162 Think Puzzles or Lock and Key Nucleic Acids Know structure, examples, -endings for names 7.1 and 7.3: Cells, Microscope Usage Eukaryote = ____________________________________ Prokaryote=_____________________________________ Eukaryote Characteristics vs. Prokaryote Characteristics _____________________ _______________________ _____________________ _______________________ _____________________ _______________________ 2 Examples______________ 2 Examples_________________ ________________________ ___________________________ Answer the following questions What type of cell is the above an example of?______________________________________ Please fill in the answer below with the correct name for each letter 1 a. ________________________________ temporary storage unit for water and worn out parts 2 b._________________________________ site of protein synthesis (protein machine) 3 c. _________________________________ jelly-like substance 4 d._________________________________ maintains homeostasis 5 e. _________________________________ digestive sac that contains digestive enzymes 6 f. __________________________________ thin, hollow tubules that make-up cytoskeleton 7 g. __________________________________ sorts and packages proteins 8 h. __________________________________ smaller, solid protein fibers make this up 9 i. ___________________________________ “brain of the cell” 10 j. ___________________________________ where ribosomes are made 11 k. __________________________________ “powerhouse” of the cell; energy made here 12 l. __________________________________ can be rough with ribosomes – helps with proteins/ smooth – storage and production of lipids; most chemical reactions take place here 13 m. _________________________________ free floating-protein synthesis site _____________F A____________ D.__________________ ______________C G___________ ______________________J I-----------------B______________ ______________________H E_____ K______________________ ------------------------L What type of cell is the one above? __________________________________________ Fill in the blank with the corresponding organelle. A. __________________________________________________ (unique to plants only) B. _________________________________________________ C. __________________________________________________ D. __________________________________________________ E. __________________________________________________ (unique to plants only) F. __________________________________________________ G. __________________________________________________ H.___________________________________________________ I.____________________________________________________ (destroys worn out parts) J.____________________________________________________ K. ___________________________________________________ (pointing to jelly-like material) L.____________________________________________________ (pointing to dot-like structure) Fill in the blanks: Cells _____________ ____________ organ systems ____________ 7.2 and 8.1: Homeostasis and Plasma Membrane Homeostasis:____________________________________________________ Osmosis:________________________________________________________ Diffusion:________________________________________________________ Concentration Gradient:____________________________________________ Fill in the following chart: Types of Transport Transport Protein? (Y/N) Simple Diffusion Facilitated Diffusion Active Transport Direction of Requires Movement Energy? (With/Against) (Y/N) Classification of Transport (Passive/Active) Draw and define the following types of solutions Isotonic:________________________________________________ Hypotonic:______________________________________________ Hypertonic:_____________________________________________ Plasma Membrane Structure (Label Head and Tails) How many layers?____ Chapter 9: Cell Energy ATP:____________________________________________ Where is energy stored in ATP?__________________________ Aerobic Respiration uses _______________________________ Anaerobic Respiration uses _____________________________ Formula for Photosynthesis:_______________________________________ Formula for Cellular Respiration:___________________________________ Glucose:_______________ 8.2, 8.3 and 10.2: Mitosis vs. Meiosis Mitosis = _____________________ reproduction. Examples:_____________ Meiosis = _____________________reproduction. Examples:_____________ Stages of mitosis Interphase:_______________________ Prophase:________________________ Metaphase:_______________________ Anaphase:________________________ Telophase:________________________ Know what stages look like!!! Stages of Meiosis Interphase I:________________ Prophase I:_________________ Metaphase I:________________ Anaphase I:________________ Prophase II:________________ Metaphase II:_______________ Anaphase II:________________ Telophase II:_______________ 10.1, Ch. 12, and 13.1: Genetics Dominant allele:______________________________ (symbol) Recessive allele:______________________________ (symbol) Father of Modern Genetics:_____________________________________ Mendel’s favorite plant:__________________________ Females make______________, while men make ____________(gametes) What is sexual reproduction in plants called?________________________ What is pollen to a plant?___________________________ What does hetero- mean?_________________________ What does homo- mean?__________________________ What’s the difference between heterozygous and homozygous?____________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________ How many pairs of chromosomes do we have? What is the last pair responsible for?________________________________________________ Rr x rr What percentage of the offspring will be round? _______________ RR x rr What percentage of the offspring will be round? _______________ Rr x Rr What percentage of the offspring will be round? _______________ What are the symbols for a male, female, carrier female, and infected male in a pedigree? Draw them below in order. ________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________ What is incomplete dominance? Give an example. ________________________________________________________________ Do a Punnett square for a heterozygous fruit fly for red eyes (XRXr) and a whiteeyed male (XrY). What percent have red eyes? White eyes? Why do men tend to express a sex-linked trait found on the X chromosome?____________________________________________________ What are the different types of blood types?_________________________________________________________ How does Down Syndrome happen? Where does it happen? What are the effects?_________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________ What can result from an extra sex chromosome? (2 answers) ________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________ Ch.11, Ch 13.2, and 13.3: Molecular Genetics How does DNA replicate? ( 4 steps) 1.________________________ 2.________________________ 3.________________________ 4.________________________ DNA to Protein DNA ___________________-->RNA-__________________ __________ DNA RNA Double stranded Ribose Thymine A T and G C Give one example how DNA has benefited society:_________________________________________________________ Chapter 14-16: Evolution List 2 theories for the origin of life:__________________________________ Evolution:_______________________________________________________ Give 2 examples of fossils:_________________________________________ Fossil Record:___________________________________________________ Austrolapithecus afarenis:_________________________________________ Homo habilis:________________________ Homo erectus Natural Selection:_________________________________________________ Chapter 33: Kingdoms and Animal Behavior Mimicry:_________________________________________________________ Ex:_______________________________________________ Warning coloration:___________________________________________ Tropisms What are the three different tropisms? _________________tropism = touch _________________tropism = light _________________tropism = gravity Nastic movement=________________________________________________ Give example for each of the following Innate behavior:_________________________________________________ Instinct:_________________________________________________________ Reflex:__________________________________________________________ Stimlus:_________________________________________________________ Learned behavior:_________________________________________________ Conditioning:_____________________________________________________ Habit:___________________________________________________________ Insight and reasoning:_____________________________________________ Imprinting:_______________________________________________________ Define the following time patterns Nocturnal:________________________ Diurnal:__________________________ Circannual:_________________ Circadian rhythms:______________ Fill in the blank ___________________________ birds flying South ___________________________ bears stocking up for winter ____________________________ think squirrels in the winter Behaviors Who does the “waggle dance?” Why do they do it? ________________ ________________________________________________________ Courtship behaviors/rituals :________________________________ Coevolution:______________________________________________ What are the 6 Kingdoms? Give an example 1.______________________ __________________________ 2.______________________ __________________________ 3.______________________ __________________________ 4.______________________ ___________________________ 5.______________________ ___________________________ 6.______________________ ___________________________ Plants: Angiosperms:__________________________________________ Gymnosperms:_________________________________________ Stomata:______________________________________________ What do plant hormones do?_______________________________ Thigmotropism:______________________________ Phototropism:_______________________________ Hydrotropism:______________________________ Gravitropism:_______________________________ What are the 5 Classes of vertebrates? Give an example of each. 1. ___________________________________________________ 2. ___________________________________________________ 3. ___________________________________________________ 4. ___________________________________________________ 5. ___________________________________________________ What are the 5 classes of invertebrates? Give an example of each. 1.__________________________________________________ 2.__________________________________________________ 3. _________________________________________________ 4.__________________________________________________ 5.__________________________________________________ Be able to create and interpret a dichotomous key (True and false) Be able to read a cladogram (shows evolution with time for examplefish people on basis of backbone) Good Luck!!! You won’t need it, if you finish this packet