Animal and Plant Life Cycle Study Guide
advertisement

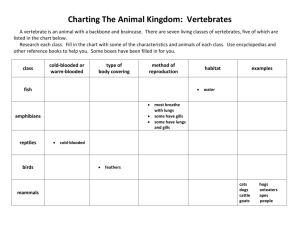
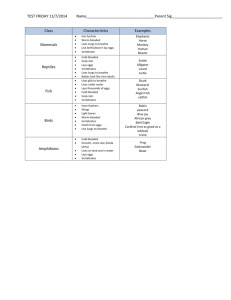
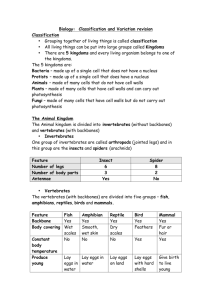
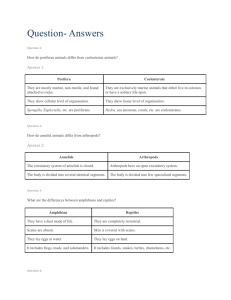
Animal and Plant Life Cycle Study Guide Life cycle- Stages of growth and change in an organism. All organisms follow the same general pattern of Birth, growth, reproduction, death Heredity - When a trait is passed from parents to offspring. Germination is the process where a seed turns into a seedling. Fertilization is the joining of female and male sex cell Pollination-Transfer of pollen grain to the pistil (the female part of the flower) Seeds form and grow from pollination, fertilization, dispersal and germination. Seeds may be dispersed by wind, water, and animals. Annual-Plants with a life cycle of one year. Perrenial- Plants with a life cycle of several years. Insects grow from a series of molts because they have a hard exoskeleton. Vertebrates: backbone or spinal column Invertebrates: no backbone or spinal column Cold blooded vertebrates are: reptiles, amphibians and fish Characteristics: reptiles: scales, breath through lungs, most lay eggs; fish: scales, gills, most lay eggs; amphibians: two lives, slimy skin, gills to lungs, most lay eggs_ Warm blooded vertebrates are: birds and mammals. Characteristics: birds: feathers, most lay eggs, lungs; mammals: fur or hair, most live birth, lungs What is the job of each of the following plant structures? Leaf making food stem transports water and nutrients, supports plant, root anchors plant, absorbs water. Gymnosperms do not flower but have seeds on cones examples include pine trees. Angiosperms flower and have seeds. Fruit trees, oak trees and tomato plants are examples. Some plants reproduce by spores. They are tiny cells that grow into plants. Examples include ferns. Some plants reproduce by growing from part of the plant. An example is a potato plant. Roots, tubers, runners. Another example is a strawberry plant.