File
advertisement

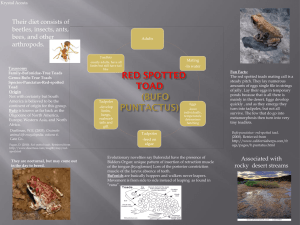
AMPHIBIANS Class: Amphibia Chapter 30.3 & 30.4 Characteristics Legs & Lungs Double-loop circulation Partially divided heart Cutaneous respiration Reproduce in a wet area Movement & Response Support from a strong internal skeleton Primary sensory organs = eyes & ears Tympanic membrane: eardrum, transmits sound to the inner ear Respiration Most adult amphibians breathe with lungs 1. Lungs = baglike organ that allows for oxygen & carbon dioxide to be exchanged 2. Gills 3. CUTANEOUS (through their thin, moist skin) respiration diffusion Circulation Partially divided heart: Left & right sides by a septum Bottom isn’t divided mixture of oxygen-rich & poor blood is given to the body tissues 3-chambered heart “Double-loop” circulation is an advantage over the “single-loop” of fish = FASTER blood flow to the body! Three main groups: salamanders, caecilians, & frogs and toads Salamanders Elongated bodies, long tails, smooth & moist skin 400 species Can’t stay away from water for long skin must stay moist Lay eggs in water, fertilization = internal A few species keep their gills when they become adults Caecilians Burrowing amphibians with small, bony scales embedded in their skin Legless & wormlike Blind Sexual reproduction, lay eggs or live young Frogs and Toads 4,000 species Carnivores & use their long, stick tongue to get food Body is adapted for jumping Toads = squat bodies & shorter legs, bumps on the body Reproduction = Metamorphosis • Need water to complete their life cycle • Eggs fertilized externally What’s killing them off?