STEMI standing orders
advertisement

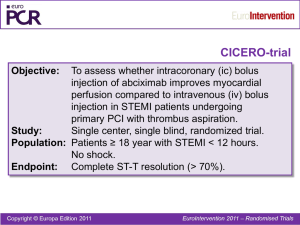
ST-Elevation MI (STEMI) STANDING ORDERS Based on 2007 ACC/AHA STEMI Focused Updatea and 2009 ACC/AHA STEMI/PCI Guidelines Focused Updatesb Patient ___________________________ ___________________________ _______ (LAST NAME) (FIRST NAME) (MI) Age: ______ Weight: _________ Height: __________ Male Female Medication allergies: _______________________________________________ Initial Orders: Check all that apply DIAGNOSTICS Stat ECG, obtain old ECG and medical record Stat ACS lab panel: complete metabolic panel, magnesium, CBC/diff., T/INR/aPTT, CK+CK-MB, troponin-I, lipid profile Calculate creatinine clearance (CrCl) : ________________ mL/min CrCl mL/min = (140 – age) weight (kg)/(serum creatinine 72) multiply by 0.85 if female Stat portable CXR Cardiac monitor and SaO2 monitor Other _________________________________________________________ STEMI confirmed (check all that apply) Anterior Inferior Lateral Posterior LBBB ANTI-ISCHEMIC THERAPY Oxygen 2 L/min nasal cannula (titrate to keep arterial saturation >90%) IV – D5W KVO _______mL/hr Opiate: ____________________________________ ______ mg IV (suggest morphine sulfate) Discontinue all NSAIDs except aspirin. Do not initiate during acute phase of management. 1 ST-Elevation MI (STEMI) STANDING ORDERS Based on 2007 ACC/AHA STEMI Focused Updatea and 2009 ACC/AHA STEMI/PCI Guidelines Focused Updatesb MEDICATIONS Aspirin 162-325 mg po chewed NITROGLYCERIN THERAPY Hold if patient has taken a phosphodiesterase inhibitor for erectile dysfunction in the last 24 hours (48 hours for tadalafil). Nitroglycerin 0.4 mg SL q5min x 3 prn chest pain; HOLD IF: SBP <100 mm Hg Nitroglycerin IV – start infusion at 10 µg/min, then titrate up by 10-20 µg/min every 5-10 min as needed to control pain, if BP permits Nitroglycerin, transdermal, 0.2 to 0.8 mg/h q12h, tolerance in 7 to 8 h Oral -Blocker Metoprolol tartrate ____________ mg _____________________ IV -Blocker (optional; recommended if persistent ischemic symptoms, hypertension, or tachycardia and no signs of hemodynamic instability) Drug: _____________________________ 2 _______ mg IV for ____ doses every __ hrs ST-Elevation MI (STEMI) STANDING ORDERS Based on 2007 ACC/AHA STEMI Focused Updatea and 2009 ACC/AHA STEMI/PCI Guidelines Focused Updatesb SELECT REPERFUSION STRATEGY Fibrinolytic Therapy: Within 12 hours of symptom onset and primary PCI cannot be achieved in <90 minutes of first medical contact OR patient cannot be transferred to primary PCI center with anticipated time from first medical contact to balloon to be <90 minutes Fibrinolytic Therapy Orders (goal door to needle <30 min) Primary PCI: Within 12 hours of symptom onset, with primary PCI facility available, with anticipated first medical contact to balloon time <90 minutes Primary PCI Orders (goal door to balloon <90 min) Medical Management: Contraindications to reperfusion therapy Medical Management Strategy Orders 3 ST-Elevation MI (STEMI) STANDING ORDERS Based on 2007 ACC/AHA STEMI Focused Updatea and 2009 ACC/AHA STEMI/PCI Guidelines Focused Updatesb FIBRINOLYTIC THERAPY ORDERS (goal door to needle <30 min) Indications: chest pain <12 hours, ECG ST elevations or new left bundle branch block Assess for contraindications to fibrinolytic therapy: Absolute contraindications: Any prior ICH Known structural cerebral vascular lesion (eg, AVM) Known malignant intracranial neoplasm (primary or metastatic) Ischemic stroke within 3 months EXCEPT acute ischemic stroke within 3 hours Suspected aortic dissection Active bleeding or bleeding diathesis (excluding menses) Significant closed head or facial trauma within 3 months Relative contraindications: Hx of chronic, severe, poorly controlled HTN Severe uncontrolled HTN on presentation (SBP >180 mm Hg or DBP >110 mm Hg) Hx of prior ischemic stroke >3 months, dementia, or known intracranial pathology not covered in contraindications Traumatic or prolonged (>10 min) CPR or major surgery (<3 wk) Recent (within 2-4 wk) internal bleeding Noncompressible vascular punctures For streptokinase/anistreplase: prior exposure (>5 days ago) or prior allergic reaction to these agents Pregnancy Active peptic ulcer Current use of anticoagulants: the higher the INR, the higher the risk of bleeding If fibrinolytic contraindicated, call STAT cardiology consult Dr. _________________ FIBRINOLYTIC THERAPY (choose one): Reteplase 10 U IV over 2 minutes, repeat after 30 minutes or Tenecteplase 30-50 mg IV over 5 seconds, based on weight: - 30 mg for weight <60 kg - 35 mg for 60-69 kg - 40 mg for 70-79 kg - 45 mg for 80-89 kg - 50 mg for ≥90 kg or Streptokinase 1.5 MU IV over 30-60 minutes 4 ST-Elevation MI (STEMI) STANDING ORDERS Based on 2007 ACC/AHA STEMI Focused Updatea and 2009 ACC/AHA STEMI/PCI Guidelines Focused Updatesb FIBRINOLYTIC THERAPY ORDERS continued ANTICOAGULANT THERAPY (choose one with fibrinolytics): Unfractionated Heparin: 60 U/kg IV bolus (maximum 4000 U), followed by IV infusion of 12 U/kg/h (maximum 1000 U/h) initially, adjusted to maintain goal aPTT 1.5 to 2.0 times control (approximately 50 to 70 s); check aPTT in 6 h and adjust heparin as indicated. When using a fibrinolytic, use Unfractionated Heparin Dosing Chart. Note: Regimens other than UFH are recommended if anticoagulant therapy is given for more than 48 hours because of the risk of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia with prolonged UFH treatment (see appendix for titration nomogram) or Enoxaparin (provided the serum creatinine is <2.5 mg/dL in men and 2.0 mg/dL in women): - Patients <75 years of age: 30 mg IV bolus, followed 15 min later by 1 mg/kg SC q12h (if CrCl <30 mL/min, give 1 mg/kg every 24 h). Continue for at least 48 hours, and preferably for the duration of hospitalization, up to 8 days. - Patients ≥75 years of age: No bolus; 0.75 mg/kg SC q12h. Continue for at least 48 hours, and preferably for the duration of hospitalization, up to 8 days. or Fondaparinux 2.5 mg IV initially, followed by 2.5 mg SC once daily (avoid if CrCl <30 mL/min). Continue for at least 48 hours, and preferably for the duration of hospitalization, up to 8 days. For patients treated initially with fondaparinux who later undergo PCI, administer additional IV treatment with an anticoagulant possessing anti-IIa activity (such as UFH or bivalirudin), taking into account whether GP IIb/IIIa inhibitors have been administered. Note: Because of the risk of catheter thrombosis, fondaparinux should not be used as the sole anticoagulant to support PCI. ANTIPLATELET THERAPY Clopidogrel 300 mg po loading dose if age <75 years (75 mg po loading dose if age ≥75 years) ASSESS FOR REPERFUSION ECG 60 minutes after initial bolus of fibrinolytic. Assess for reperfusion based on angina intensity, ST resolution on 60-minute ECG and/or hypotension. Cardiology consultation, if possible reperfusion failure Call Dr. __________________________________________________________________ Physician/NP/PA Signature: _________________________ Date: _______ Time: _______ 5 ST-Elevation MI (STEMI) STANDING ORDERS Based on 2007 ACC/AHA STEMI Focused Updatea and 2009 ACC/AHA STEMI/PCI Guidelines Focused Updatesb RISK STRATIFICATION (non–PCI-capable facility) High risk (recommend early transfer <6 hours for PCI) Low risk (recommend admission to CCU; monitor for ischemia) If high risk: Transfer for PCI Initiate preparatory antithrombotic (anticoagulant plus antiplatelet) Anticoagulant: _________________________ at _______________________ Antiplatelet: __________________________ at _______________________ It is reasonable for high-risk patients who receive fibrinolytic therapy as primary reperfusion therapy at a non–PCI-capable facility to be transferred as soon as possible to a PCI-capable facility where PCI can be performed either when needed or as a pharmacoinvasive strategy. Consideration should be given to initiating a preparatory antithrombotic (anticoagulant plus antiplatelet) regimen before and during patient transfer to the catheterization laboratory (Class IIa, LOE: B).b Patients who are not at high risk who receive fibrinolytic therapy as primary reperfusion therapy at a non–PCI-capable facility may be considered for transfer as soon as possible to a PCI-capable facility where PCI can be performed either when needed or as a pharmacoinvasive strategy. Consideration should be given to initiating a preparatory antithrombotic (anticoagulant plus antiplatelet) regimen before and during patient transfer to the catheterization laboratory (Class IIb, LOE: C).b 6 ST-Elevation MI (STEMI) STANDING ORDERS Based on 2007 ACC/AHA STEMI Focused Updatea and 2009 ACC/AHA STEMI/PCI Guidelines Focused Updatesb Triage and Transfer for PCIb Adapted with permission from Kushner FG, et al. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2009;54(23):2205-2241. Note: A planned perfusion strategy using full-dose fibrinolytic therapy followed by immediate PCI may be harmful and is not recommended. 7 ST-Elevation MI (STEMI) STANDING ORDERS Based on 2007 ACC/AHA STEMI Focused Updatea and 2009 ACC/AHA STEMI/PCI Guidelines Focused Updatesb PRIMARY PCI STRATEGY ORDERS (goal door to balloon <90 min) ANTIPLATELET THERAPY (choose one): Clopidogrel 300-600 mg po loading dose or Prasugrel 60 mg po loading doseb,c and/or GP IIb/IIIa inhibitor GLYCOPROTEIN IIB/IIIA INHIBITOR THERAPY (choose one): Abciximab 0.25 mg/kg IV bolus, followed by IV infusion of 0.125 µg/kg/min (to a maximum of 10 μg/min). Continue for 12 hours. or Tirofiban 25 µg/kg IV bolus, followed by IV infusion at 0.15 µg/kg/min. Continue for 18 to 24 hours. or Eptifibatide 180 µg/kg IV bolus x 2, 10 min apart, followed by IV infusion of 2.0 µg/kg/min, reduce to 1.0 µg/kg/min if CrCl <50 mL/min. Continue until hospital discharge or for 12 to 18 hours. It is reasonable to start treatment with glycoprotein IIb/IIIa receptor antagonists (abciximab [Class IIa, LOE: A], tirofiban [Class IIa, LOE: B], or eptifibatide [Class IIa, LOE: B]) at the time of primary PCI (with or without stenting) in selected patients with STEMI.b 8 ST-Elevation MI (STEMI) STANDING ORDERS Based on 2007 ACC/AHA STEMI Focused Updatea and 2009 ACC/AHA STEMI/PCI Guidelines Focused Updatesb PRIMARY PCI STRATEGY ORDERS continued ANTICOAGULANT THERAPY (choose one): Unfractionated Heparin (for at least 48 hours) 60 U/kg IV bolus (not to exceed 4000 U), followed by IV infusion of 12 U/kg/h (not to exceed 1000 U/h) to achieve goal aPTT 1.5 to 2.0 times control (approximately 50 to 70 s). Target ACT in catheterization lab: 200-250 sec if concomitant GP IIb/IIIa inhibitor therapy, 250-300 sec if no concomitant GP IIb/IIIa inhibitor therapy; administer additional boluses to achieve target ACT if measured values below recommended ranges (see appendix for dosing) or Enoxaparin 30 mg IV, followed by 1 mg/kg SC q12h, first dose 15 minutes after bolus (if age >75 years, give 0.75 mg/kg every 12 hours with no bolus; if CrCl <30 mL/min, give 1 mg/kg every 24 h after bolus). If the last SC dose was given less than 8 hours prior to PCI, no additional enoxaparin required; if last SC was given 8 to 12 hours earlier or never given, an IV dose of 0.3 mg/kg of enoxaparin should be given. Discontinue after completion of the PCI procedure, unless continued anticoagulation is indicated. Enoxaparin can be used to support PCI after fibrinolysis; no additional anticoagulant is needed. or Bivalirudin 0.75 mg/kg IV bolus, followed by infusion of 1.75 mg/kg/h. If UFH was given previously, start bivalirudin 30 minutes later but before PCI. For patients proceeding to primary PCI who have been treated with ASA and a thienopyridine, recommended supportive anticoagulant regimens include the following: a. For prior treatment with UFH, additional boluses of UFH should be administered as needed to maintain therapeutic activated clotting time levels, taking into account whether GP IIb/IIIa receptor antagonists have been administered (Class I, LOE: C).b b. Bivalirudin is useful as a supportive measure for primary PCI with or without prior treatment with UFH (Class I, LOE: B).b In STEMI patients undergoing PCI who are at high risk of bleeding, bivalirudin anticoagulation is reasonable (Class IIa, LOE: B).b For prior treatment with fondaparinux, administer additional intravenous treatment with an anticoagulant possessing anti-IIa activity (such as UFH or bivalirudin), taking into account whether GP IIb/IIIa inhibitors have been administered. Note: Because of the risk of catheter thrombosis, fondaparinux should not be used as the sole anticoagulant to support PCI. 9 ST-Elevation MI (STEMI) STANDING ORDERS Based on 2007 ACC/AHA STEMI Focused Updatea and 2009 ACC/AHA STEMI/PCI Guidelines Focused Updatesb PCI PROCEDURES: THROMBUS ASPIRATION AND USE OF STENTS PCI PROCEDURES (check if applicable) Aspiration thrombectomy Aspiration thrombectomy is reasonable for patients undergoing primary PCI (Class IIa, LOE: B).b Stent Use (check one if applicable): DES BMS It is reasonable to use a drug-eluting stent (DES) as an alternative to a bare-metal stent (BMS) for primary PCI in STEMI (Class IIa, LOE: B). b A DES may be considered for clinical and anatomic settings in which the efficacy/safety profile appears favorable (Class IIb, LOE: B).b 10 ST-Elevation MI (STEMI) STANDING ORDERS Based on 2007 ACC/AHA STEMI Focused Updatea and 2009 ACC/AHA STEMI/PCI Guidelines Focused Updatesb MEDICAL MANAGEMENT STRATEGY ORDERS (NO REPERFUSION) ANTICOAGULANT THERAPY (choose one): Unfractionated Heparin: 60 U/kg IV bolus (maximum 4000 U), followed by IV infusion of 12 U/kg/h (maximum 1000 U/h) initially, adjusted to maintain goal aPTT 1.5 to 2.0 times control (approximately 50 to 70 s); check aPTT in 6 h and adjust heparin as indicated. When using a fibrinolytic, use Unfractionated Heparin Dosing Chart. Note: Regimens other than UFH are recommended if anticoagulant therapy is given for more than 48 hours because of the risk of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia with prolonged UFH treatment. or Enoxaparin 30 mg IV, followed by 1 mg/kg SC q12h, first dose 30 minutes after bolus (if age >75 years, give 0.75 mg/kg every 12 hours with no bolus; if CrCl <30 mL/min, give 1 mg/kg every 24 h after bolus). Continue for at least 48 hours, and preferably for the duration of hospitalization, up to 8 days in patients with no contraindications to anticoagulation. or Fondaparinux 2.5 mg IV initially, followed by 2.5 mg SC once daily (avoid if CrCl <30 mL/min). Continue for at least 48 hours, and preferably for the duration of hospitalization, up to 8 days in patients with no contraindications to anticoagulation. 11 ST-Elevation MI (STEMI) STANDING ORDERS Based on 2007 ACC/AHA STEMI Focused Updatea and 2009 ACC/AHA STEMI/PCI Guidelines Focused Updatesb AS-NEEDED MEDICATIONS Check/Initial/Date _____/_____ DOCUSATE SODIUM 100 mg po bid _____/_____ MAALOX PLUS EX STR 15 mL po q6h prn indigestion _____/_____ OXAZEPAM 15-30 mg po qhs prn insomnia _____/_____ ACETAMINOPHEN 650 mg po q4h prn headache _____/_____ MAGNESIUM HYDROXIDE 30 mL po daily prn constipation _____/_____ MAGNESIUM SULFATE Sliding Scale IV daily Call house officer if serum Mg <1.2; hold order for creatinine >1.9 If serum Mg <1.4 give 5 g MgSO4 IV If serum Mg <1.6 give 4 g MgSO4 IV If serum Mg <1.8 give 3 g MgSO4 IV If serum Mg <2.0 give 2 g MgSO4 IV _____/_____ _____/_____ LAB, MG, K daily KCL IMMEDIATE REL Sliding Scale Target K >4.5 mg/dL po daily Call house officer if K <3.4; hold order for creatinine >1.9 If K <3.7 give 60 mEq If K <4.1 give 40 mEq If K <4.6 give 20 mEq Additional Orders: ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 12 ST-Elevation MI (STEMI) STANDING ORDERS Based on 2007 ACC/AHA STEMI Focused Updatea and 2009 ACC/AHA STEMI/PCI Guidelines Focused Updatesb _____/_____ CHEST PAIN PROTOCOL _____/_____ ECG x 1 prn chest pain _____/_____ For CP: check VS, call house officer _____/_____ Mark if cardiac cath is planned: Time _________________ _____/_____ NPO except meds _____/_____ LAB, TYPE AND HOLD NEXT AVAILABLE _____/_____ NUTRITION CONSULT Patient admitted to cardiology ischemia pathway with known or suspected CAD. Please facilitate outpatient education in low-cholesterol, low-salt diet _____/_____ SOCIAL SERVICE CONSULT Patient admitted to cardiology ischemia pathway with known or suspected CAD. Please assess and assist in need for outpatient support (including VNA) services Now 13 After midnight ST-Elevation MI (STEMI) STANDING ORDERS Based on 2007 ACC/AHA STEMI Focused Updatea and 2009 ACC/AHA STEMI/PCI Guidelines Focused Updatesb DAY 2 OR LATER: REMINDERS Check/Initial/Date _____/_____ If on UFH (consult Unfractionated Heparin Dosing Chart) _____________________________________________ _____/_____ Calcium channel blocker (if β-blocker contraindicated) Drug: _______________________ ___mg ____times/d _____/_____ ACE inhibitor or ARB; recommended if diabetic Drug: _______________________ ___mg ____times/d _____/_____ Lipid-lowering therapy (statins) regardless of LDL; dose target to LDL <100 mg/dL (further reduction to <70 mg/dL reasonable) Drug: ____________________________ ___mg once daily _____/_____ Echocardiography. FIRST 24 HR if evidence of CHF, hemodynamic instability, mechanical complication _____/_____ Warfarin: RECOMMENDED if LV thrombus, extensive wall dyskinesis, LVEF <20%-30% 14 ST-Elevation MI (STEMI) STANDING ORDERS Based on 2007 ACC/AHA STEMI Focused Updatea and 2009 ACC/AHA STEMI/PCI Guidelines Focused Updatesb PRIOR TO DISCHARGE Check/Initial/Date _____/_____ _____/_____ Patient had stent implanted OR Patient had medical therapy without stenting MEDICATIONS _____/_____ Aspirin ________ mg/d for _________________________ _____/_____ Clopidogrel _________ mg/d for ______________________ OR Prasugrel 10 mg/d for ______________________________ _____/_____ _____/_____ -blocker Drug: __________________________________________ Dosage: ________________________________________ _____/_____ ACE inhibitor or ARB Drug: __________________________________________ Dosage: ________________________________________ _____/_____ Aldosterone receptor blocker Drug: __________________________________________ Dosage: ________________________________________ _____/_____ Calcium channel blocker Drug: ___________________________________________ Dosage: _________________________________________ _____/_____ Statin Drug: ___________________________________________ Dosage: _________________________________________ _____/_____ Nitroglycerin Drug: ___________________________________________ Dosage: _________________________________________ _____/_____ Drug: ___________________________________________ Dosage: _________________________________________ _____/_____ Drug: ___________________________________________ Dosage: _________________________________________ 15 ST-Elevation MI (STEMI) STANDING ORDERS Based on 2007 ACC/AHA STEMI Focused Updatea and 2009 ACC/AHA STEMI/PCI Guidelines Focused Updatesb PRIOR TO DISCHARGE cont PATIENT/FAMILY EDUCATION AND FOLLOW-UP INSTRUCTIONS Check/Initial/Date _____/_____ Medication instructions/disease education _____/_____ Smoking cessation _____/_____ Diabetes management _____/_____ Nutrition, weight, and blood pressure management _____/_____ Exercise program _____/_____ Referral to cardiac rehab Time: ______ Date: ______ Signature: ____________________________________ a Canadian Cardiovascular Society; American Academy of Family Physicians; American College of Cardiology; American Heart Association, Antman EM, Hand M, Armstrong PW, et al. 2007 focused update of the ACC/AHA 2004 guidelines for the management of patients with STelevation myocardial infarction: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2008;51(2):210-247. b Kushner FG, Hand M, Smith SC Jr, et al. 2009 focused updates: ACC/AHA guidelines for the management of patients with ST-elevation myocardial infarction (updating the 2004 guideline and 2007 focused update) and ACC/AHA/SCAI guidelines on percutaneous coronary intervention (updating the 2005 guideline and 2007 focused update): a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2009;54(23):2205-2241. c In STEMI patients with a prior history of stroke and transient ischemic attack for whom primary PCI is planned, prasugrel is not recommended as part of a dual-antiplatelet therapy regimen. 16 ST-Elevation MI (STEMI) STANDING ORDERS Based on 2007 ACC/AHA STEMI Focused Updatea and 2009 ACC/AHA STEMI/PCI Guidelines Focused Updatesb 17 ST-Elevation MI (STEMI) STANDING ORDERS Based on 2007 ACC/AHA STEMI Focused Updatea and 2009 ACC/AHA STEMI/PCI Guidelines Focused Updatesb Heparin Adjustment Nomogram for Standard Laboratory Reagents With a Mean Control aPTT of 26-36 s aPTT (s) Bolus Dose (U) Stop Infusion (min) Rate Change (mL/h) Repeat aPTT 3000 0 +2 6h 40-49 0 0 +1 6h 50-75 0 0 0 (no change) Next AM 76-85 0 0 –1 Next AM 86-100 0 30 –2 6h 101-150 0 60 –3 6h >150 0 60 –6 6h <40 aPTT indicates activated partial thromboplastin time. Heparin infusion concentration = 50 U/mL. Target aPTT = 50-75 s. For aPTTs obtained before 12 h after initiation of thrombolytic therapy: 1. Do not discontinue or decrease infusion unless significant bleeding or aPTT >150 s. 2. Adjust infusion upward if aPTT <50 s. For aPTTs obtained 12 h after initiation of thrombolytic therapy, use entire nomogram: Deliver bolus, stop infusion, and/or change rate of infusion based on aPTT, as noted on appropriate line of nomogram. Adapted with permission from Hirsh J, Raschke R, Warkentin TE, Dalen JE, Deykin D, Poller L. Heparin: mechanism of action, pharmacokinetics, dosing considerations, monitoring, efficacy, and safety. Chest. 1995;108(4 suppl):258S-275S. Reprinted with permission from Ryan TJ, Anderson JL, Antman EM, et al. ACC/AHA guidelines for the management of patients with acute myocardial infarction. A report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines (Committee on Management of Acute Myocardial Infarction). J Am Coll Cardiol. 1996;28(5):1328-1428. 18