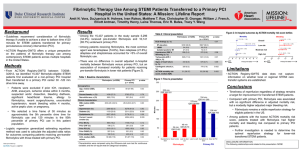
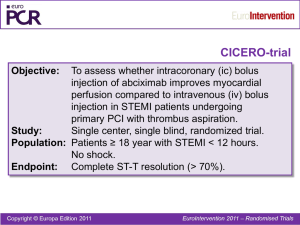
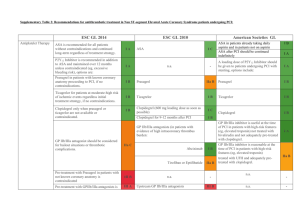
STEMI
advertisement

Alyssa Morris, R5 Thanks to Drs Rob Hall and Lisa Campfens ASA Plavix BB Morphine Nitro Heparin Reperfusion CURE CLARITY SYNERGY COMMIT TACTICS GUSTO DANAMI SHOCK ISIS CRUSADE FRISC 38 NNT to prevent one Death in STEMI with ASA 35 NNT to prevent one Death in STEMI with streptokinase NO Mortality decrease AVOID - Hypotension - Cardiogenic Shock CAUTION - HR<50 - RV infarct - Recent viagra or cialis AHA guidelines state “reasonable”( II a) CRUSADE study AVOID hypotension, shock, tenuous respiratory status Focus should be on other anti-ischemic therapy! Main evidence is for secondary prevention of the next MI Limited evidence from early 80s when used as monotherapy COMMIT TRIAL 5 fewer vfib episodes 5 fewer reinfarctions 11 more cardiogenic shock NO Benefit of early IV beta-blockade Rapid Atrial Fibrillation Ventricular arrythmias Hypertensive + Tachycardic …….or just use iv nitro Oral Beta-Blockade should be initiated within 24 hours (Class I, Level B) as long as none of: Signs of CHF 2nd or 3rd degree heart block, PR. 0.24 Low output states (shock, confusion, oliguria) Increased risk for cardiogenic shock (HR > 110, SBP < 120, age > 75) IV Beta-Blockade is reasonable for control of hypertension (not tachycardia alone) if no contraindications are present STEMI Fibrinolysis ▪ 300-600mg PCI ▪ 300- 600mg Clopidogrel should be held for 5, preferably 7 days before CABG STEMIs got lytic, followed by cath b/w 2-8 days Endpoint = death, recurrent MI, occluded artery on angiography 21% - 15%, ARR 6%, NNT 16 Benefit was gained artery occlusion rates on angiography not mortality or recurrent MI rates NOT a benign treatment NNH 50 for minor bleeding NNH 100 for major bleeding NNT of 40-80 for benefits of composite end points of recurrent angina, MI, death, urgent revascularization NO benefit in low risk patients STEMIs Fondaparinux or UFH PCI or Medical Mx Reperfusion with fibrinolytics UFH 60U/kg max 4000U Enoxaparin 30mg IV bolus Fondaparinux 2.5mg IV Reperfusion with PCI UFH Enoxaparin Fondaparinux How long has the patient been symptomatic? Are there absolute or relative contraindications to lytic? How long of a transport to PCI? Is the patient in CHF, shock, arrhythmias Is there a mechanical complication requiring surgery? How bad is this particular STEMI? Mortality 75% 0.25 - 1%, NNH 100-400 Rates increase with number of risk factors > 75 years old < 70 kg BP > 169/95 Prior CVA Excessive anticoagulation Inferior STEMI Mortality 5% Inferior + RV STEMI Mortality 8% Anterior STEMI Mortality 12% 20 New LBBB 27 Anterior MI 125 Inferior MI Outcome Lytic PCI ARR NNT Mortality 9% 7% 2% 50 Death/MI/ CVA 14% 8% 6% 16 PCI vs LYTIC 30d mortality 46% vs 56% 6m mortality 50% vs 63% >30m chest pain At least 1mm STE in at least 2 limb leads or At least 1mm STE in 2 contiguous precordial leads New or presumed new LBBB True posterior STEMI ABSOLUTE Prior ICH Malignant intracranial neoplasm Cerebral vascular lesion (AVM) Ischemic CVA<3m Ao Dissection Active bleeding or bleeding diathesis Sig CHI or Facial trauma <3m RELATIVE Chronic, severe HTN SBP>180 DBP>110 Hx ischemic stroke >3m, dementia Traumatic or prolonged CPR Recent major surgery <3w Recent internal bleeding <4w Noncompressible vascular puncture Pregnancy Active PUD Current use of OAC: higher INR= higher risk of bleeding Door to Needle 30 min Door to Balloon 90 min DTB-DTN>1hr Prolonged transport DTB>90min REACT trial CARESS-AMI TRANSFER-AMI 2009- TRANSFER TO PCI CENTER Lytic treated STEMI meeting high risk criteria Non-high risk who received lytic may be considered for transfer asap to a PCI center for PCI prn TNK 30-50mg single dose ASA 162-325mg chewed Plavix 300mg (or up to 600mg) Heparin UFH Enoxaparin Fondaparinux ASA 162-325mg chewed Plavix 300-600mg Heparin UFH* Enoxaparin Fondaparinux