CICERO-trial
advertisement
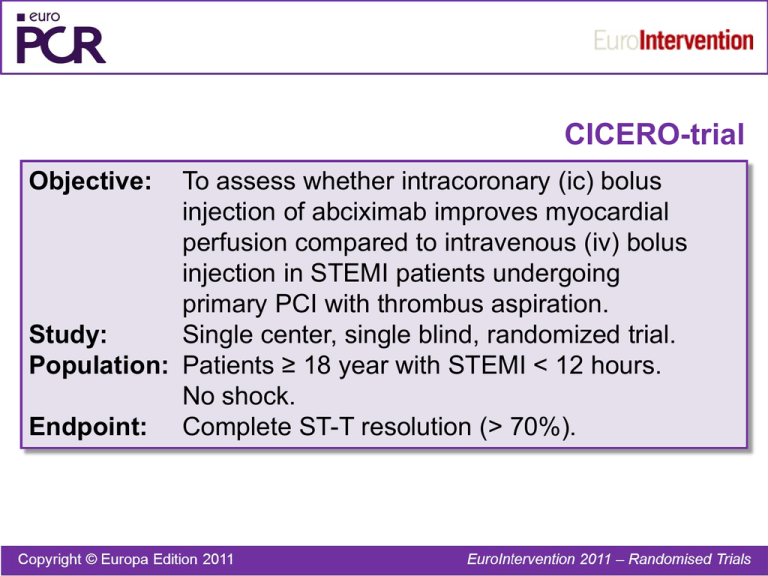
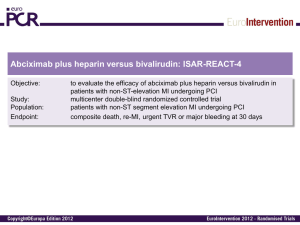
CICERO-trial Objective: To assess whether intracoronary (ic) bolus injection of abciximab improves myocardial perfusion compared to intravenous (iv) bolus injection in STEMI patients undergoing primary PCI with thrombus aspiration. Study: Single center, single blind, randomized trial. Population: Patients ≥ 18 year with STEMI < 12 hours. No shock. Endpoint: Complete ST-T resolution (> 70%). CICERO-trial Abciximab 0.25 mg/kg ic N=271 Patients enrolled N=534 Abciximab 0.25 mg/kg iv N=263 Thrombectomy PCI CICERO-trial ST-T resolution 100 80 60 40 20 0 >70% <30% 10 26 64 IC Myocardial blush grade 3 30-70% 10 28 62 IV 100 80 60 40 p=0.844 20 0 2 24 34 42 34 34 33 IC IV 0/1 p=0.052 CICERO-trial IC n=126 4 2 0 2,92 1,17 IV n=122 3,31 1,71 p=0.006 p=0.032 AUC CK-MB x 100 AUC troponin T CICERO-trial Conclusion: In STEMI patients undergoing primary PCI with thrombus aspiration, an ic bolus injection of abciximab does not improve myocardial reperfusion as assessed by ST-segment resolution. Enzymatic infarct size was smaller in the intracoronary abciximab group. Gu et al. Circulation 2010;21;122(25):2709-11