Chapter 11 Notes
advertisement

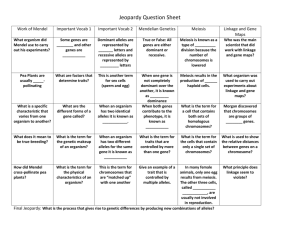
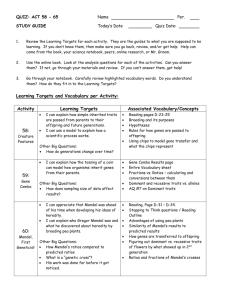
Chapter 11 lesson 1 Gregor Mendel= an Austrian monk who studied the genetics of Pea plants Self Pollination= 1 parent produces identical offspring (“True Breeding”) Cross Pollination= 2 Parents Male sex cells in 1 plant fertilize the egg cells of another *Mendel tried to stop self pollination from happening- he cut off the male parts of a flower. Then he pollinated ONLY the plants he wanted. Genes and Dominance 1. Traits= Specific characteristic that is different in organisms. (ExamplesPlant height or Plant color) P= parent generation F1= 1st generation of offspring 2. Hybrid= the offspring of parents with different traits 3. Alleles= different forms of a gene 1. Gene- height 2. Alleles- tall and short 4. Gene= chemical factor that determines traits 5. Segregation= separation of alleles 6. Gametes= Sex cells 1. Male- sperm 2. Female- egg Dominant: Capital letter when present. Will always be seen. Recessive: will remain hidden unless paired with another recessive gene Examples for gene height Tall= Dominant (T) Short= recessive (t) TT= Tall Tt= Tall tt= short Chapter 11 Lesson 2 Probability is used to predict the outcome of a genetic cross Punnet Square for Eye Color Cross B= Brown (dominant) b= blue (recessive) Parents-Bb= brown B b Bb B BB Brown Brown bb b Bb Brown blue Offspring 75% Brown 25% blue Or 3:1 Homozygous= same alleles (example- TT or tt) Heterozygous= different alleles (example- Tt AKA “Hybrid”) Phenotype- Physical characteristics What it looks like (blue eyes) Genotype- Genetic makeup Example- bb Chapter 11 Lesson3 Independent Assortment=traits do not influence the inheritance of other traits 1. Mendel’s 2 factor cross (Round & Yellow) RY and (Green and Wrinkled) ry Incomplete Dominance= mix of 2 alleles Example- Red Flowers (RR) and White Flowers (WW) gives you Pink Flowers (RW) Codominance= Both alleles are shown Example- Black Chickens (BB) and White Chickens (WW) = Black AND White Chickens (BW) Multiple Alleles: Genes with more than 2 alleles. Examples: rabbit coat color, Human eye color (brown, blue green), human blood type Polygenic Traits: Traits controlled by 2 or more genes. Different combinations of alleles make different phenotypes. Examples: Human skin color (this is the reason why we are all different.) Mendel’s Principles: (other scientists tested this) Also studied “Drosophila” (fruit Fly) Fruit Flies are useful in the study of genetics Easy to keep in a lab Produce a lot of offspring Reproduce quickly Chapter 11 Lesson 4 Meiosis Gametes: Sex cells (half the number of chromosomes) o Sperm o Egg Haploid:1 set N=4 o 1 copy of each gene Diploid: 2 sets 2N=8 o 2 copies of each gene Homologous: Chromosomes come from both parents (Mom and Dad)matching chromosomes Meiosis: Only occurs in Sex cells (gametes) The number of chromosomes per cell is cut in half Creates 4 genetically different haploid cells Phases of Meiosis 1. Meiosis 1 i. Chromosomes form a tetrad (4 Chromosomes) 1. Crossing over=reason for differences in offspring. Produces new combinations of alleles. 2. Meiosis 2 Chromosomes divide again. This time there is NO replication of chromosomes ½ The Chromosome Number 4 genetically different haploid cells Chapter 11 lesson 5 Independent Assortment- genes are linked. Chromosomes assort separately Chromosomes are groups of linked genes. Gene Maps- chromosomes are NOT Linked Forever. Crossing over prevents this. (Example- Asian eye shape and Brown hair) Distance between genes is mapped. Locations of each known human gene “Human Genome Project”