Regents Biology
advertisement

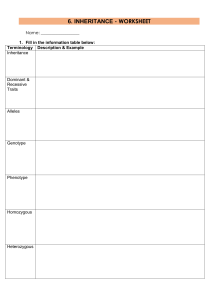
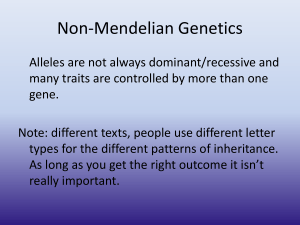
Regents Biology Test #5 Outline Key Terms and Important Stuff to Know Genetics and Patterns of Heredity Be able to complete crosses for all laws of inheritance Make sure you can answer all questions in practice packet Gregor Mendel: “Father of Genetics” Mendel’s Laws of Inheritance Rule of Unit Factors Law of Dominance: Dominant vs. recessive Law of Segregation of Traits: traits separate during gamete formation and recombine in offspring Law of Independent Assortment: traits for different factors are inherited independently of each other Seen in dihybrid cross Other Laws of Inheritance (Non-Medelian) Incomplete Dominance: hybrid is an intermediate between parents phenotypes Ex: red petal x white petal = pink petals Co-Dominance: hybrid offspring shows both parental phenotypes Ex: red hair x white hair = roan horse (both red and white hairs) Sex Determination: XX = female, XY = male (mothers can only contribute X, father determines sex of offspring) Sex Linkage: certain alleles are carried on sex chromosomes Ex: Hemophilia and Colorblindness gene is carried on X chromosome Multiple Alleles Ex: ABO blood groups (can be type A, B, AB, O) Effects of Environmental Factors on Gene expression Test Cross: cross an unknown to a pure recessive Gene-Chromosome Theory Genetic Mutations Linked Genes: lie close to each other on same chromosome and tend to get inherited together Crossing Over Nondisjunction Chromosomal Disorders (extra or missing chromosomes caused by nondisjunction during meiosis) Down Syndrome (trisomy 21) Klinefelters Turner’s Syndrome Other Genetic Disorders Sickle Cell Anemia PKU Tay Sachs Disease Amniocentesis Testing Karyotyping (be able to read and interpret) Pedigree Charts (be able to read and interpret) Textbook: Chapters 11 and 14 UPCO Review Book: Pgs. 101-112