Advanced Biology
advertisement

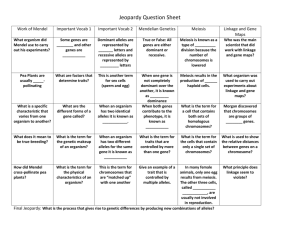
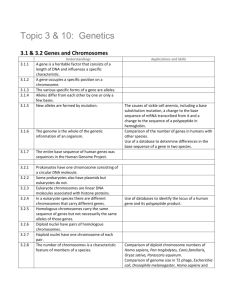
Advanced Biology Chapter 11 Vocabulary genetics: scientific study of heredity fertilization: process in sexual reproduction in which male and female reproductive cells join to form a new cell true-breeding: term used to describe organisms that produce offspring identical to themselves if allowed to selfpollinate trait: a specific characteristic that varies from one individual to another hybrids: the offspring of crosses between parents with different traits gene: sequence of DNA that codes for a protein and thus determines a trait alleles: one of a number of different forms of a gene segregation: separation of alleles during gamete formation gametes: specialized cell involved in sexual reproduction probability: likelihood that a particular event will occur Punnett square: a diagram showing the gene combinations that might result from a genetic cross homozygous: term used to refer to an organism that have two identical alleles for a particular trait heterozygous: term used to refer to an organism that has two different alleles for the same trait phenotype: physical characteristics of an organism genotypes: genetic make up of an organism independent assortment: independent segregation of genes during the formation of gametes incomplete dominance: situation in which one allele is not completely dominant over another codominance: a situation in which both alleles contribute to the phenotype of the organism multiple alleles: three or more alleles of the same gene polygenic traits: trait controlled by two or more genes homologous: term used to refer to chromosomes that each have a corresponding chromosome from the opposite sexparent diploid: term used to refer to a cell that contains both sets of homologous chromosomes haploid: term used to refer to a cell that contains only a single set of chromosomes and therefore only a single set of genes meiosis: process by which the number of chromosomes per cell is cut in half through the separation of homologous chromosomes in a diploid cell tetrad: structure containing 4 chromatids that forms during meiosis crossing-over: process in which homologous chromosomes exchange portions of their chromatids during meiosis gene map: diagram showing the relative locations of each known gene on a particular chromosome