Genetics Study Guide: ACT 58-65 - Inheritance & Heredity
advertisement

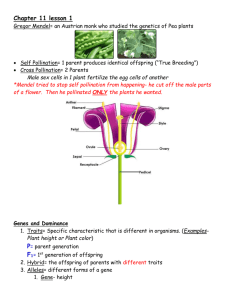
QUIZ: ACT 58 - 65 Name Per. STUDY GUIDE Today’s Date Quiz Date: 1. Review the Learning Targets for each activity. They are the guides to what you are supposed to be learning. If you don’t know them, then make sure you go back, review, and/or get help. Help can come from the book, your science notebook, peers, online research, or Mr. Groom. 2. Use the online book. Look at the analysis questions for each of the activities. Can you answer them? If not, go through your materials and review. If you can’t answer them, get help! 3. Go through your notebook. Carefully review highlighted vocabulary words. Do you understand them? How do they fit in to the Learning Targets? Learning Targets and Vocabulary per Activity: Activity Learning Targets 58: Creature Features I can explain how the tossing of a coin can model how organisms inherit genes from their parents. Other Big Questions: How does sampling size of data affect results? 59: 60: Mendel, First Geneticist Other Big Questions: How do generations change over time? Gene Combo I can explain how simple inherited traits are passed from parents to their offspring and future generations. I can use a model to explain how a scientific process works. Associated Vocabulary/Concepts I can appreciate that Mendel was ahead of his time when developing his ideas of heredity. I can explain who Gregor Mendel was and what he discovered about heredity by breeding pea plants. Other Big Questions: How Mendel’s ratios compared to predicted ratios What is a “genetic cross”? His work was done far before it got noticed. Reading pages D-23-25 Breeding and its purposes Hypotheses Rules for how genes are passed to offspring Using chips to model gene transfer and what the chips represent Gene Combo Results page Entire Vocabulary sheet Fractions vs. Ratios – calculating and conversions between them Dominant and recessive traits vs. alleles AQ #7 on Dominant traits Reading, Page D-31 – D-34. Stopping to Think questions / Reading Outline Advantages of using pea plants Similarity of Mendel’s results to predicted results How genes are transferred to offspring Figuring out dominant vs. recessive traits of flowers by what showed up in 2nd generation Ratios and fractions of Mendel’s crosses Activity Learning Targets 61: Gene Squares Other Big Questions: Why do geneticists use letters to represent alleles? 63: Show Me the Genes! I can explain what a chromosome is. I can explain the role that chromosomes play in the inheritance of genes. Other Big Questions: What are different methods of cell division? What process is necessary to make sex cells? Why is the number of chromosomes split in half to make sex cells? 65: Breeding Critters: More Traits I can explain and demonstrate how Punnett Squares predict patterns of inheritance. I can use simple ratios and fractions to show probabilities. I can distinguish between different methods of trait inheritance and model how they work. I can determine the sex of an organism as determined by their chromosomes. I can distinguish between environmental factors and hereditary factors. I can determine and identify genotypes and phenotypes. Associated Vocabulary/Concepts Try to do AQs for this Activity as practice! Other Big Questions: What are different ways that traits are passed to offspring besides simple dominant/recessive traits? Reading, page D-35- D37 Genotype vs. Phenotype Punnett Square and how to use them Homozygous vs. Heterozygous Hybrid Alleles Punnett Square Practice Sheet! Reading, page D-41 – 46 Reading Outline and Quiz Cell Division for repair and growth – called Mitosis Chromosomes – what happens to them during cell division Copying of chromosomes - replication Pairs of chromosomes Cell Division to make sex cells – called Meiosis Genes are part of DNA Mutations AQ#1 – relative sizes of things Critter Breeding Worksheet and how it works “Genotype determines phenotype” and how that works Incomplete Dominance traits Co-Dominant traits Determining sex of offspring Environmental factors can influence phenotype AQ #2-8