KEY
advertisement

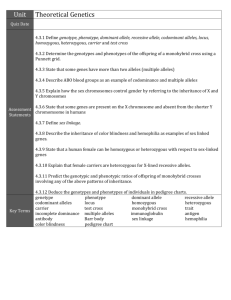
KEY Note Taking Guide Topic # 3033 Genotype and Phenotype Anna Blight Genetic terminology The creation of genetic material goes from __________(DNA) to _____________(RNA) to _____________ (protein). _______________ (Proteins) code for ___________ (genes), which code for _______________ (traits). Each pair of _______________ (chromosomes) carries a pair of ___________ (genes). _____________ (Alleles) are genes that occupy different loci on each ____________(chromosome) and affect the same trait. There are ______ (two) alleles, one on each chromosome of a _____________ (homologous pair). The alleles may correspond, which makes the animal ____________ (homozygous), or contrast, which makes the animal ___________ (heterozygous). Example: whether cattle are horned or polled is controlled by one or the other locus for horns. During gametogenesis, ________________ (homologous chromosomes) segregate and each new gamete gets one of the ___________ (alleles). A ___________ (dominant) allele overpowers the expression of its __________ (recessive) allele and is represented by a _________ (capital) letter. A recessive allele is represented by a _______ (lower case) letter, and is masked by a __________ (dominant) allele, unless the animal is _______ (homozygous recessive). In this case, the animal will have the appearance expressed by the recessive trait. Heterozygous animals (Aa) pass on _____ (A) to one gamete and ______ (a) to the other gamete. Homozygous animals (AA or aa) pass on ______ and ______ (either A and A or a and a) to each gamete. When male and female gametes combine to form a ________ (zygote) chances are _________ (equal) that one or the other allele of each parent will be passed on. Traits like coat color are determined by a ________________ (dominant allele) or homozygosity of ____________ (recessive) alleles. Females carry two ________ (XX) chromosomes and males carry ________(X and Y) chromosomes. Males therefore determine the _______ (sex) of the offspring by passing on either the ________ (X or Y). ____________ (Bird species) are opposite where females are _______ (XY) and ________________ (determine the sex) of the offspring. Compared to humans, who have ______ (23) pairs of chromosomes, most farm animals have more, and only swine have less with _____(19) pairs of chromosomes. ____________ (Genotype) is the genetic make up of an animal. ____________ (Phenotype) is the outward appearance of an animal, due to its genetic make up. For any pair of alleles, _______ (three) genotypes are possible, _____, ______, and _____. (AA, Aa, and aa). In sheep, ________ (black) wool is a recessive trait and both parents must carry the recessive _______ (allele), since the sheep must be ___________ (homozygous recessive) to show the trait. The _________ (Punnett) square is a table used to calculate the genotype and phenotype of an animal. A a A AA Aa a Aa aa If you cross two heterozygous parents, Aa and Aa, where A=white wool and a=black wool, you get a genotypic ratio of _________ (1:2:1 or 1 AA : 2 Aa : 1 aa) and a phenotypic ratio of _________ (3:1 or 3 white : 1 black). A A A AA AA a Aa Aa Cross one homozygous dominant, AA, with a heterozygous, Aa. The genotypic ratio is ___________ (1:1 or 50% homozygous, 50% heterozygous). The phenotypic ratio is ________ (100% white wool). A a a Aa aa a Aa aa Cross a homozygous recessive with a heterozygous animal. The result is 1:1 __________ (genotypic) ratio, and 50% __________ (white) to 50% ________ (black).