PBR Pressure Drop: Ergun Equation & Conversion Problems
advertisement

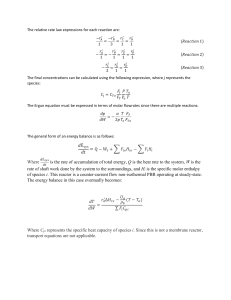
Title: Pressure drop in PBR Topic Covered: Chapter 4 Fogler, 3rd Edition 1. Mole balance 2. Rate law 3. Stoichiometry 4. Ergun equation Summary: in gas phase reaction, the concentration of the reacting species is proportional to the total pressure. So proper expression of concentration with pressure drop is the key factor of calculation. Tricks: 1. Using the pressure drop and Ergun equation to calculate 2. Determining the relation between and cross sectional area, particle diameter. Question: #1 The irreversible gas phase reaction A+B2C is carried out in a PFR reactor. The reaction is non-elementary in that it is first order in A and zero order in B. The feed is equal molar in A and B, and the pressure at the entrance is 10atm and the pressure at the exit is 2atm. Additional information: FA0=100 mol/s K=1dm3/kg.s CA0=1mol/ dm3 1) What is the conversion exiting the reactor? 2) If the flow were turbulent, what would be pressure drop if the cross sectional area is increased by a factor 2 and the particle size decreased by a factor of 10? All other conditions remain the same. (Hint: in the turbulent flow, the Ergun equation neglects the part of 150(1-) /Dp. Reference: R.B.Bird, transport phenomena (New York, Wiley, 1960), p. 200.)