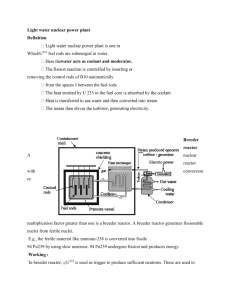
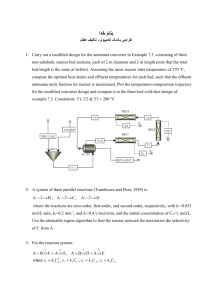
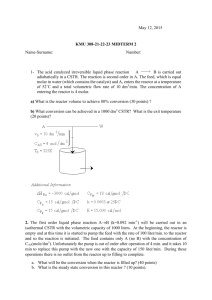
Neutron Activation Analysis (NAA)
advertisement

Neutron Activation Analysis (NAA) Alexis Popkow H191 - Neutron Physics - 4/7/10 What is NAA? Determine the chemical composition of a sample Lunar samples, artifacts, forensics Can identify up to 74 different elements in gases, liquids, solids, and mixtures Can also determine the concentration of the elements of interest: Requires Neutrons A nuclear reactor A source that emits neutrons by fission (e.g. Californium) Alpha Source (like Radium) with Beryllium D-T fusion Some elements of interest Arsenic Chromium Selenium Chlorine Mercury Magnesium Used to Find: Impurities in industrial products and foods Poisons in human hair Hazardous material at dumps Trace elements in archaeological remains Testing for elements in air filters How? Hit source with neutrons Sources become radioactive Then decay in predictable ways How? Detect the gamma-rays (prompt and delayed) - with gas detector, scintillators, semiconductors Bin number of counts at each energy Gamma-ray Spectroscopy Gamma spectrum is characteristic of the nuclides in the source (or elements that are activated in NAA) Equipment: Detector (NaI, HPGe) - voltage pulse Amplifiers or multi-channel analyzers - shape the pulse ADCs - collects data, produces spectrum Benefits Small sample sizes (.1mL or .001gm) Non-destructive Can analyze multiple element samples Doesn’t need chemical treatment High sensitivity, high precision Resources N.C. State University Reactor Program University of Wisconsin Nuclear Reactor Wikipedia Reed Research Reactor University of Missouri Research Reactor