Subject: The Adult Health Screening Physical
advertisement

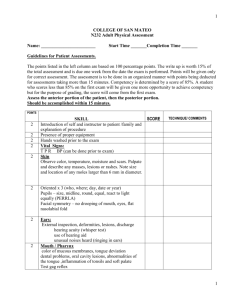
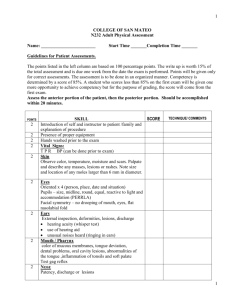
Subject: The Adult Health Screening Physical Effective Date: June 19, 2006 Page 1 of 3 Revised Date: Policy Screening physicals are the use of standardized tests given under medical direction in the assessment of an individual to detect the existence of diseases or health deviations, or to identify for more definitive studies individuals suspected of having certain diseases. Purpose 1. Services are aimed at prevention and early detection of illness in asymptomatic non-pregnant adults. 2. Services shall focus on the early detection of hypertension, diabetes, glaucoma, breast cancer, cervical cancer, oral cancer, prostate cancer and colon cancer. 3. Abnormalities found upon exam, which are new, different or unusual and have not been previously and/or currently evaluated by a physician will be referred for evaluation. Procedure (Physical Assessment) A. Assessment of the skin 1. Examine both hands and inspect the nails. 2. For the rest of the assessment, examine skin with corresponding \regional assessment for color, pigmentation, hair distribution, scars, and vascularity. B. Assessment of the head and neck 1. Head a. Inspect and palpate scalp, hair and cranium. b. Inspect face, expression, symmetry, edema or masses. c. Palpate the maxillary sinuses and the frontal sinuses. 2. Eyes a. Inspect external eye structures. b. Inspect conjunctivae, scleras, corneas, and irides. c. Test pupil: size, response to light and accommodation. d. Using an ophthalmoscope, inspect ocular fundas: red reflex, disc, vessels, and retinal background. Subject: The Adult Health Screening Physical Effective Date: June 19, 2006 Page 2 of 3 Revised Date: 3. Ear a. Inspect the external ear. b. Move auricle and push tragus for tenderness. c. Using an otoscope inspect the canal, then the tympanic membrane for color, position, landmarks and integrity. d. Assess gross hearing. 4. Nose a. Inspect the external nose. b. Inspect the nasal mucosa for color, discharge, lesions, swelling, exudates, and bleeding. 5. Mouth and Throat a. Inspect the lips, gums, teeth, hard palate, buccal mucosa, tongue and floor of mouth using flashlight and tongue blade for color, lesions, moisture, ulcers, cracks, pigmentation, nodules, swelling, bleeding, normal alignment and position, and symmetry. b. Grade tonsils, if present. c. Test odor of client’s breath. 6. The Neck and Nodes a. Inspect the neck. Palpate the pre-auricular, post auricular, occipital, tonsilar, submaxillary, submental, superficial cervical, post cervical, deep cervical, supraclavicular, axillary and epitrochlear lymph nodes for size, shape, location, tenderness, delimitation, mobility and consistency. b. Palpate the parotid glands. c. Palpate the thyroid gland for size, shape, symmetry, location, tenderness, nodules and masses. d. Test range of motion and muscle strength. C. Assessment of the client 1. Assess respirations. 2. Percuss over all lung fields for resonance, dullness or hyperresonance, measure diaphragmatic excursion bilaterally. 3. Auscultate lungs for presence/absence of normal breaths sounds and adventitious sounds. D. Assessment of the Heart 1. Assess rate. Rhythm and volume of pulse. 2. Ausultate the heart sounds. E. Assessment of Breast and Axillae (Females) 1. See: Breast Health: A Guide for Health Departments Appendix I, Performing the Clinical Breast Examination. 2. Male Breast a. Inspect and palpate while palpating the anterior chest wall. b. Palpate the axilla and regional nodes. Subject: The Adult Health Screening Physical Effective Date: June 19, 2006 Page 3 of 3 Revised Date: F. Assessment of Abdomen 1. Auscultate bowel sounds. 2. Percuss all quadrants 3. Palpate: light palpation in all quadrants, then deep palpation in all quadrants. 4. Palpate for liver, spleen, kidneys, and aorta. 5. Test for abdominal reflexes, if indicated. G. Assessment of lower Extremities 1. Inspect: symmetry, skin characteristics, and hair distribution. 2. Inspect legs for varicose veins. H. Assessment of the Male Genitalia/Rectum 1. Inspect the perianal area. 2. Palpate the penis for lesions, masses and tenderness. 3. Inspect the scrotum for size, shape, symmetry, nodules, inflammation, ulcers, rashes, and contour. 4. Palpate the testes and epididymis for size, shape, consistency, nodules, swelling, excessive tenderness and normal anatomy of spermatic cord and vas deferens. 5. Inspect inguinal and femoral areas for hernias. 6. Palpate internal anus and rectum for hemorrhoids, masses, lesions, sphincter tone, tenderness and nodules. 7. Palpate prostate for size, shape, symmetry, nodules and tenderness. 8. Do Hemocult test. I. Assessment of the Female Pelvis 1. See Pap Smear Screening: A Guide For Health Departments, section 2, Procedure for Obtaining A Pap Smear and Genital – Bimanual Examination, pages 2-10. 2. Do Hemocult Test. J. Assessment of the Musculoskeletal system. 1. Inspect joints for size, shape, color, alignment, symmetry and deformity. 2. Palpate joints for tenderness, stiffness, swelling, stability and crepitation. 3. Palpate and assess muscle tone, strength and resistance. 4. Assess spine for lordosis, kyphosis and scoliosis. K. Assessment of the Neurological System 1. Assess mental status 2. Assess Gait. 3. Assess cerebellar function by using finger-to-nose test or rapidalternating-movements test (RAM”s). 4. Assess sensations by light touch, pain, and pressure.