Head and Neck
advertisement

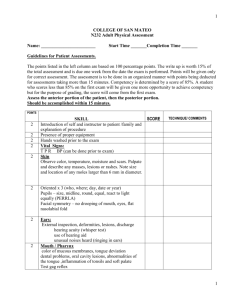
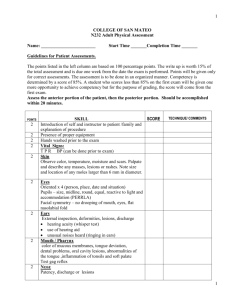
Head and Neck Including Regional Lymphatics N1037 Head and Neck & Regional Lymphatics Review and locate – The Skull (bones of the cranium and the face) Note the location of the CRANIAL BONES Frontal, Parietal, Occipital & Temporal Note the location of the sutures. Coronal, Sagittal, Lambdoid Unite adjacent cranial bones Note facial bones. Nasal, Lacrimal, Maxilla, Sphenoid & Zygomatic bones. Mandible (moves up, down, sideways) Head-facial muscles Facial expressions are formed by facial muscles Facial structures should be symmetric. Facial muscles are innervated by cranial nerve VII Note major Neck muscles. Sternocleidomastoids and trapezii muscles (each side of neck form 2 triangles- anterior & posterior cervical ) Thyroid gland and other landmarks Thyroid gland - largest endocrine gland -secretes T3 & T4 to regulate cellular metabolism -flattened butterfly shape structure - 2 lateral lobes connected by isthmus - isthmus rest on trachea, inferior to the criocoid cartilage (highest point Adam’s Apple) Note location of lymphatics 1. Preauricular, 2. post. auricular, 3. occipital, 4. submental, 5. submandibular, 6. Jugulodigastric or tonsillar, 7. superficial cervical chain, 8. deep cervical chain, 9. post. cervical, 10. supraclavicular. Lymph Nodes Usually less than 1 cm round or ovid in shape smooth in consistency when enlarged or tender - assess for infection or maligancy and the area the node drains ( see p322 example) BLOOD SUPPLY Major arteries to head and neck – common carotids bifurcate into – internal & external carotids Major veins from head and neck – internal an external jugular veins – and subclavian veins Head and Neck & Regional Lymphatics Health History Subjective Data Head and Neck & Regional Lymphatics- Health Hx facial or neck surgery • history of headaches or dizziness • allergies • Neck pain, limitation of movement • Lumps or swelling, difficulty swallowing or chewing, history of smoking • head injuries • Head: Inspect and palpate the skull Objective Data Head: Inspect and palpate the skull Size and Shape (I)Normocephalic: round, symmetric and approximated to body size. (P)Shape: symmetric and smooth, no tenderness reported. – Use finger pads on scalp & palpate all surfaces – Assess contour, masses, depressions,tenderness – Note deformities lumps and tenderness. Head: Inspect and palpate the scalp (I) Scalp should be shiny, intact and without lesions or masses. – Part hair repeatedly and inspect scalp (P) palpate with finger pads on the scalp for lesions or masses Head: Inspection of the face (I) Symmetry of facial features: – Observe facial expression, shape and symmetry of nose, eyes, eyebrows, mouth, ears (I) Shape and features of face – Note shape of face – Note swelling (edema) , abnormal features, disproportionate structures (stroke, Bell’s Palsy = cranial nerve 7 damage -facial nerve), and involuntary movement (the presence of tics normally none occur) (I) Facial expression: emotions – Note appropriateness to verbal and nonverbal Head: Palpate and Auscultation of Mandible Temporal Area (P)Temporal artery: above the cheek bone, between the eye and the top of ear. – Palpate with finger pads for pulse (P)Temporomandibular joint: articulates smoothly with no limitation, no crepitus, no clicking – use index and middle finger to palpate anterior to tragus of ear on both sides – ask pt to open & close mouth – observe smoothness of movement, any discomfort – clicking/crepitus could indicate arthritis or dislocation The Neck- Inspect and palpate Objective Data The Neck- Inspect and palpate What position do you ask the client to assume while you inspect the neck? Head erect and still, sitting up straight, head at your eye level The Neck- Inspect and palpate Symmetry Head position: centered, midline, erect, still Symmetry of the Sternocleidomastoid & trapezii muscles ROM of neck (flexion, lateral rotation, lateral bending, extension, test muscle strength:Touch chin to chest, ear to shoulder Turn head left to right Extend head backwards Motions should be smooth and controlled. resists movement of shoulder shrug and head turn side to side limited ROM with meningitis, muscle spasm, osteoarthritis The Neck- Inspect and palpate (P) Muscles - should be symmetrical & without palpable masses or spasms – palpate Sternocleidomastoid and trapezii muscles for tenderness, masses, spasms – spasms due to infections, trauma, chronic inflammation, neoplasm The Neck- Inspect and palpate Lymph Nodes (P) Lymph nodes - should not be palpable, but small discrete , movable nodes are often present Begin with preauricular lymph nodes and proceed in a systematic fashion (1 to 10) Use gentle pressure Deep cervical chain: tip head toward side Supraclavicular Node: hunch shoulders & elbows forward tender nodes = inflamed due to infection firm, non movable nodes may be = malignancy The Neck- Inspect and palpate Trachea Midline normal (note deviations) Palpate for tracheal shift: space should be symmetric on both sides. The Neck- Inspect, palpate, auscultate Thyroid Gland inspect for swelling using lamp (ask to sip and swallow water) – thyroid tissue moves up with swallowing observe for goiter - enlarged thyroid palpate -anterior/posterior approaches – have pt slightly lower head to relax neck muscles – palpate isthmus for nodules, masses, tenderness or enlargement while swallowing – then displace/stabilize lobe on one side and palpate the other side while pt swallows gland is smooth, soft, & no tenderness/enlrgmt/masses The Neck- Inspect, palpate, auscultate auscultate lobes for bruit – (use bell) – no bruit should be present bruits indicate blood supply r/t tumor or toxic goiter. Developmental Considerations Infant/Children Skull and fontanels Pregnant Female Cholasma on face = pregnancy mask Aging Adult Temporal arteries twisted and visible Rhythmic tremor of head may be present Perform ROM slowly to prevent dizziness