File
advertisement

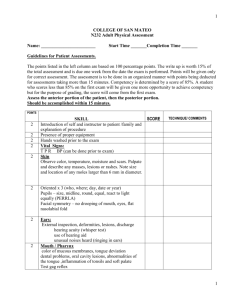
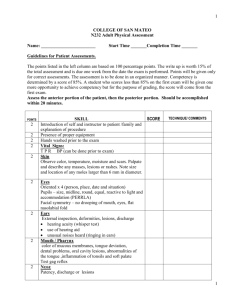
PHYSICAL ASSESSMENT/ EXAMINATION HEAD TO TOE BY : NELSON MUTHALI DIP/RN D A T E : 0 8 TH M A R C H , 2 0 1 3 OBJECTIVES By the end of the topic students should be able to:1. Define physical assessment 2. Describe the four techniques used in physical assessment 3. Know how to do a head to toe assessment Physical assessment is a systematic data collection method that uses the senses of sight, hearing, smell and touch to detect health problems. There are four techniques used in physical assessment and these are: Inspection, palpation, percussion and auscultation. Usually history taking is completed before physical examination. Inspection Inspection is the use of vision to distinguish the normal from the abnormal findings. Body parts are inspected to identify color, shape, symmetry, movement, pulsation and texture. Principals of inspection Availability of adequate light Position and expose body part to view all surfaces Inspect each area for size, shape, color, symmetry, Position and abnormalities. If possible compare each area inspected with the same area on the opposite side. Use additional light to inspect body cavities Palpation Palpation involves use of hands to touch body parts for data collection. The clinician uses fingertips and palms to determine the size, shape, and configuration of underlying body structure and pulsation of blood vessels. It help to detect the outline of organs such as thyroid, spleen or liver and mobility of masses. It detects body temperature, moisture, turgor, texture, tenderness, thickness, and distention. Principles of palpation Help client to relax and be comfortable because muscle tension impairs effective assessment. Advise client to take slow deep breaths during palpation Palpate tender areas last and note nonverbal signs of discomfort. Rub hands to warm them, have short fingernails and use gentle touch Percussion Percussion is the technique in which one or both hands are used to strike the body surface to produce a sound called percussion note that travels through body tissue. The character of the sound determines the location, size and density of underlying structure to verify abnormalities. An abnormal sound suggests a mass or substance like air, fluid in an organ or cavity. Auscultation It involves listening to sounds and a stethoscope is mostly used. Various body systems like cardiovascular, respiratory and gastrointestinal have characterized sounds. Bowel, breath, heart and blood movement sounds are heard using the stethoscope. It is important to know the normal sound to distinguish from abnormal. Preparation for physical exam Infection prevention Follow standard/universal precaution through out procedure. Environment P/A requires privacy and away from other distractions. Equipment Gather all the necessary equipment, equipment needs to be warmed before being placed on the body e.g. rubbing diaphragm of the stethoscope briskly between hands. Preparation cont… Patient preparation Prepare the patient physically and make the patient comfortable throughout the physical assessment for successful exam. Explain to the patient everything to be done. HEAD TO TOE ASSESSMENT General survey The assessment of the patient/client begins on the first contact. It includes apparent state of health , level of consciousness, and signs of distress. The general height, weight, and build can be noted including skin color, dressing, grooming, personal hygiene, facial expression, gait, odor, posture and motor activity. NOTE: If there is a sign of acute distress comprehensive health assessment is deferred until when patient is stable. Vital signs Assessment of vital signs is the first physical assessment because positioning and moving the client during examination interferes with obtaining accurate results. Specific vital signs can be also obtained during assessment of individual body system. Skin, Hair, scalp and Nails Inspect all skin surfaces first or gradually while assessing the systems. Use the skills of inspection, palpation, and olfactory to assess the function. Skin Inspect skin for color, edema, lesions, scars and vascularity. Palpate to notice moisture, temperature, and skin turgor. Hair and scalp Assess and note type of hair i.e. long, coarse, thick, brittle. Note the color, distribution, quantity, thickness, texture and lubrication. On inspection separate the hair to determine the scalp. Wear clean gloves if lesions and lice are probable. Nails The condition of the nails reflects the general health, state of nutrition, occupation, and level of self care. Nail biting can reveal the person’s psychological state. Inspect the nail bed for color, cleanliness, length, texture, angle between nail and nail bed and folds around the nail. Palpate the nail for inflamation Head and neck The assessment of the head includes:- eyes, ears, nose, mouth and pharynx. The assessment of the neck includes:- lymph nodes, carotid artery, thyroid gland and trachea. Eyes Assess visual acuity, position and alignment of the eyes, eyebrows and eyelids. Note any abnormal discharges and color of conjunctiva and sclera. Ears It determines the intergrity of the ear structures and hearing acuity. Inspect for sore and discharges Nose and sinuses Assess the integrity of the nose and sinuses by using inspection and palpation. Nose Observe for shape, size, skin color, and presence of deformity or inflammation. Sinuses The exam involves palpation. Incase of allergy or infection the inside is inflamed and swollen so palpate for tenderness Mouth and pharynx Assess mouth and pharynx to determine overall health and hygiene. Use pen light and tongue depressor to assess oral cavity. Lips Inspect lips for color, texture, hydration, contour, sores and lesions. Buccal mucosa, gums, and teeth Ask client to clench teeth and smile to observe to observe teeth occlusion, symmetry. A symmetrical smile shows normal nerve function. Inspect teeth for hygiene, position, and alignment. Let client open with lips relaxed, use tongue depressor to inspect the mucosa for color, moisture and sores. Inspect gums for color, edema, retraction, bleeding and lesions. Tongue and floor of mouth Carefully inspect tongue on all sides as well as floor of mouth for color, size, position, texture, moisture sores and lesions. Palate Have client extend the head backwards, holding the mouth open, inspect the hard and soft palate for color, shape, texture and extra bonny prominences or defects. Pharynx Let the client tip the head back slightly, open mouth wide and say “Ah”, with penlight inspect the uvula and soft palate, they should rise centrally as the client say “Ah” to determine the function of cranial( vagus ) nerve function. Check the uvula and tonsils for redness and inflammation. Neck Palpate the muscles, lymph nodes, carotid artery jugular veins for tenderness and distention. Thyroid gland Ask client to hyperextend the neck and view the thyroid and palpate for masses. Normally thyroid gland is not visible. Chest Inspect the skin for scars, sores, color, lesions, chest, movement and respiratory rate. Palpate to notice any masses, and tenderness in axillae and breast. Lungs Auscultate to assess respiratory and sounds from the lungs and chest cavity. Percussion is done to detect accumulation of fluid or air in the chest cavity. Heart Auscultate to hear the heart sound. Learn to know the normal heart sound to be able to detect the abnormal Breast Inspect the breast for skin color, scars and lesions. Palpate to notice any presence of masses. Extremities Upper and lower extremities Inspect hand and legs for symmetry, alignment, skin color, temperature, sores, scars, lesions inflammation and varicosity. Palpate for tenderness, edema and pulsation of arteries. Use the brachial, radial, ulna, femoral, popliteal, posterior tibia and dorsalis pedis pulses. Check capillary refill on nails, clubbed toes /fingers and joint mobility. Deep tendon reflexes Normally done on high risk patients and needs specialized practice and special hammer to assess the reflexes. Areas that are assessed are on biceps, triceps, patella, and Achilles. Abdomen Inspect the skin for color, sores, lesions, scars, position of umbilicus, distention and contours. Palpate for tenderness, masses and enlargement of other organs like liver, spleen and kidney. Ask for bowel and bladder elimination. Percussion is used to detect the location of organs that are normally palpable e.g. liver, spleen and intestines. Always auscultate before palpation or percussion because touching can alter mobility of bowel and increase sound. Genitalia Start assessment of genitalia with asking questions and do inspection to confirm a positive answer. Female Ask about presence of abnormal discharge, sores, warts and itching Male Ask any presence of sores, itching, warts and abnormal discharge. Rectum and anus Inspect for the skin color, sores, hemorrhoids and lesions. Do digital palpation to examine the anal canal for masses and sphincters function only when important. Reference 1. Ruth F. Craven Constance J. Hirnle, Fundamentals of Nursing, Human Health and Function, sixth edition(2009), Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. 2. Potter. Perry, Fundamentals of Nursing, 7th edition(2009) Mosby Elsevier. 3. Barbara F. Weller, Nurses Dictionary for nurses and health care workers, 24th edition,Elsevier.