Bohr Model – suggested that electrons move around the nucleus in
advertisement

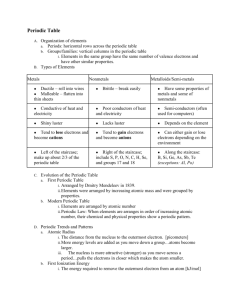
Periodic Table Notes Periodic Table Dimitri Mendeleev-1869- developed the first version of the periodic table. He expressed the regularities as a periodic function of the atomic mass. Henry Moseley- revised Mendeleev periodic table by describing regularities in physical and chemical properties as periodic functions of the atomic number Groups (family) – vertical column Elements with similar valence electrons configurations Group 1 – alkali metals – reactive Group 2 - alkaline earth metals – reactive Group 3-12 – transition metals – transition valence e-, can have mult. charges Group 15 – nitrogen family – N & P essential to life Group 16 – oxygen family – reactive Group 17 – halogens – very reactive Group 18 – noble gases – very stable Periods – horizontal rows Period number corresponds to the principal quantum number of valence electrons Periodic Trends 1. Atomic Size Increases – down a group Decreases – across a period Size of ions Cation Anion Ca+2/Ca S-2/S Ca larger because Ca+2 lost 2 electrons S-2 larger because S-2 gained 2 electrons 2. Ionization Energy – energy required to remove an electron from an individual atom in a gas phase M(g) M+(g) + e• Metals lose electrons to non-metals so relatively low energy is needed • High ionization energy means an electron is hard to remove Decreases – down a group Increases - across a period 3. Electron Affinity – Electron affinity is the energy involved when an electron is added to a gaseous atom. • Negative values of energy mean that energy was released during the process. Atoms with negative values of electron affinity have a very strong attraction for electrons. • Positive values of electron affinity have very little attraction for electrons.(energy involved in negative ions) Decreases – down a group Increases - across a period 4. Electronegativity is the tendency of an atom to draw electrons to itself when in a covalent bond. Consequently, the trends are the same as for electron affinity. The atoms with the highest electronegativity are fluorine, then oxygen, then nitrogen. It is also important to know that the electronegativity of hydrogen is slightly less than that of carbon. Decreases – down a group Increases - across a period 5. Metallic Character Increases – down a group Decreases – across a period Summary of Trends Electronegativity Electronegativity