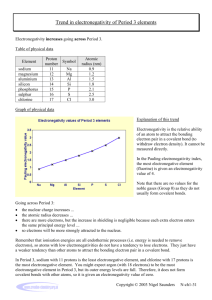
Midterm review 2014 Models of atom and where electrons are found
advertisement

Midterm review 2014 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. 32. 33. 34. 35. 36. 37. 38. 39. 40. Models of atom and where electrons are found Masses of subatomic particles How is spectra produced Energy amounts of electron shells – further from nucleus more energy Counting subatomic particles, definition of isotopes Properties related to structure – O3 vs O2 Determe element from proton number Picking elements with similar chemical properties Electronegativity meaning and application Definition of temperature Sublimation as solid to gas Identifying a homogeneous mixture Identifying Hydrogen bonding – FON Physical properties – MP, BP, solubility, density, magnetism Properties of organic compounds relate to functional groups Names of nuclear reactions – nat trans, art trans, fission, fusion Using table N Matching lines in a bright line spectrum mixture Determing the charge of a particle given the amounts of subatomic particles Periodic trends in a group or period Excited state electron configuration vs ground state configuration Counting electrons in a bond – 1 bond = 1 pair of electrons = 2 electrons total Identifying ionic and molecular compounds from formulas Converting C to Kelvin and Kelvin to C Using q=mCΔT, q=mHf, q=mHv Definition of element and compound Unsaturated vs Saturated hydrocarbons Definition of a radioisotope Half life problems, fractions with the number of half lifes Expaining sizes of ions compared to atoms Addition and substitution reactions Identifying a homologous series of hydrocarbons Identifying bond type given a formula Explaining stability of bonded atoms and ions compared to unbounded atoms Distillation, evaporation, filtration as means of separating mixtures Relating Boiling points to imf strength Identifying a compound with ionic and covalent bonds Explaining polarity in terms of electronegativity differences Lewis diagrams for common molecules – water, ammonia, methane, oxygen, nitrogen Reactant location vs product location in a chemical reaction 41. Homogeneous vs Heterogeneous mixtures 42. Using a the density formula (triangle) to solve for mass or volume 43. Writing a decay equation for alpha decay or beta decay 44. 45. 46. 47. 48. 49. 50. 51. Honors extension s and p electron configurations orbital diagrams properties of metals vs non metals Van der Waals forces identification Molecular geometries of common molecules – water, carbon dioxide, ammonia, methane Lewis dot structures Molecular polarity Transition metals are colorful