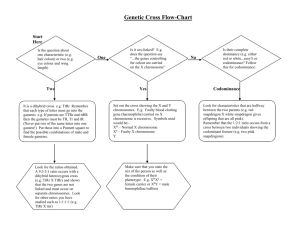
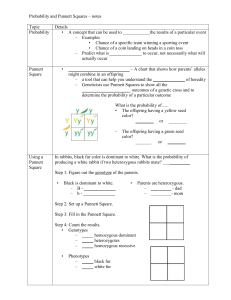
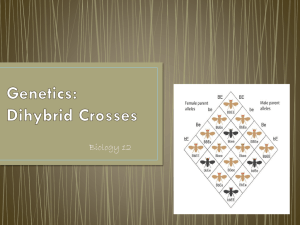
Mrs. Gesualdo Genetics Worksheet Write in the definitions for the
advertisement

Mrs. Gesualdo GENETICS WORKSHEET Write in the definitions for the following terms: Term Homozygous Heterozygous Genotype Phenotype Monohybrid Dihybrid Dominant Recessive Definition You can fill this in!!!!! You can fill this in!!!!! You can fill this in!!!!! You can fill this in!!!!! You can fill this in!!!!! You can fill this in!!!!! You can fill this in!!!!! You can fill this in!!!!! Read each question. Using the steps required by your teacher, answer each question THOROUGHLY on a separate sheet of paper 1. A gardener has two tall pea plants. How can the gardener determine whether the two plants are homozygous or heterozygous for the gene determining tallness? Show the two Punnett squares as evidence for your conclusion. What is this type of cross called? T= tall; t=short a. b. c. 2. In rabbits, the allele for black coat color (B) is dominant over the allele for brown coat color (b). What would be the results of a cross between an animal homozygous for black coat color (BB) and one homozygous for brown coat color (bb)? Show the gametes, Punnett square, and phenotypic and genotypic ratios. B=black; b=brown a. b. c. 3. 4. Show a monohybrid cross: cross BB x bb Phenotypic ratio: 4 black : 0 brown Genotypic ratio: 0 BB: 4 Bb: 0 bb In guinea pigs, the allele for rough coat (R) is dominant over the allele for smooth coat (r). In order for all the offspring to be smooth coated, what should the phenotype and genotype of the male and female parents be? Show the Punnett square to support your answer. R = Rough; r = smooth a. The parents must both have smooth coats (homozygous recessive). Any trait for rough coat would overpower the recessive. b. Show a monohybrid cross: rr x rr What would the results of a cross between two pea plants that were heterozygous for both tall plants and round seeds? Show the Punnett square, and state the genotypic and phenotypic ratios. T=tall; t=short; R=round; r=wrinkled a. b. c. 5. The gardener must perform a test cross to determine whether the two plants are homozygous dominant or heterozygous. Show two monohybrid crosses: cross TT x tt; cross Tt x tt Test Cross Show a dihybrid cross: TtRr x TtRr (both sides = TR, Tr, tR, tr) Genotypic Ratios: TTRR: 1 TTRr: 2 TTrr: 1 TtRR: 2 TtRr: 4 Ttrr: 2 ttRR: 1 ttRr: 2 ttrr: 1 Phenotypic Ratios: Tall, round: 9 Tall, wrinkled: 3 Short, round: 3 Short, wrinkled: 1 Suppose that you are an explorer who has found a new species of plant. Some of the plants have red flowers and some have yellow flowers. You cross a red-flowered plant with a yellow-flowered plant and all the offspring have orange flowers. What is the most probable explanation? How would you prove it? Support your answer with a Punnett square. R = Red Flowers R’ = Yellow Flowers RR’ = Orange Flowers Show a monohybrid cross: RR x R’R’ Both alleles are codominant. When they are expressed together, a plant with the phenotype of RR’ will produce orange flowers. The only way for red flowers or yellow flowers to be expressed is if the alleles are homozygous (RR or R’R’).