GENETICS WORKSHEET NAME________________________
advertisement

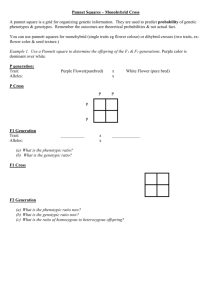
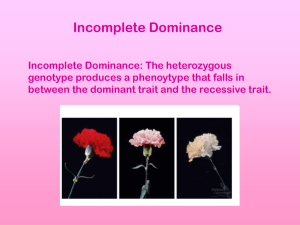
GENETICS WORKSHEET NAME________________________ USE YOUR NOTES, TEXTBOOK OR OTHER RESOURCES TO ANSWER THE FOLLOWING QUESTIONS ABOUT GENETICS AND PUNNETT SQUARES. 1. What is the difference between genotype and phenotype? Genotype is the actual genes present in an organism; phenotype is the expression of the genes (appearance) 2. What is a gamete? A haploid reproductive cell (egg, sperm) 3. What is an allele? An alternate form of a gene (e.g., round and wrinkled are both alleles for the trait “seed shape”) 4. What is the difference between a homozygous and heterozygous gene pair? Homozygous pairs = both alleles are the same form of the trait; heterozygous = both alleles are different 5. How many forms of a trait can a parent give its offspring? Only 1 6. What is the probability of an offspring of any species being male or female? 50% 7. Which gamete determines the sex of an organism? The sperm, because it may contain the Y chromosome. Eggs contain only X chromosomes 8. What is a sex-linked trait? a trait that is on the sex chromosome, generally the X chromosome. Some examples are hemophilia, baldness, and colorblindness 9. What is the difference between dominance as Mendel knew it and incomplete dominance? With complete dominance, one allele completely masks the presence of the other in the phenotype; with incomplete dominance, neither allele is fully expressed, resulting in a third phenotype somewhere between the two heterozygotes. For example, certain flowers may be either red or white in each homozygote, but pink in the heterozygote. 10. Why can parents have seven boys and one girl, even though that is not the correct probability? Because of the random uniting of the egg and sperm, and the fact that each event is independent of the other. Once born, a child has no influence over which egg and sperm will encounter each other if his parents have another child. 11. Which of the following would be the best sample to use to determine the probability of a trait a. 1 family b. 100 families c. 900 families d. 10 families e. 6 families PUNNETT SQUARES: PERFORM A PUNNETT SQUARE TO DETERMINE THE PROBABILITY OF THE OCCURANCE OF A TRAIT IN THE FOLLOWING PROBLEMS (GENOTYPIC AND PHENOTYPIC) a. What is the probability of offspring having the following trait if these parents are crossed? Homozygous tall pea plant x heterozygous tall pea plant Genotypic: 50% TT, 50% Tt Phenotypic: 100% tall b. What is the probability of offspring having the following trait if these parents are crossed? Heterozygous black mouse x homozygous brown mouse Genotypic: 50% Bb, 50% bb Phenotypic: 50% black, 50% brown c. What is the probability of offspring having the following two traits if these parents are crossed in pea plants? Heterozygous tall Heterozygous yellow x x homozygous short homozygous green Genotypic: 1 TtYy : 1 Ttyy : 1 ttYy : 1 ttyy Phenotypic: ¼ tall, yellow : ¼ tall, green : ¼ short, yellow : ¼ short, green