Genetics: Dihybrid Crosses
advertisement

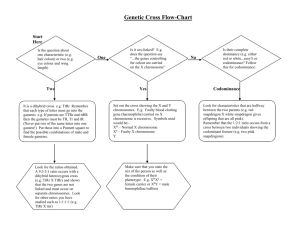
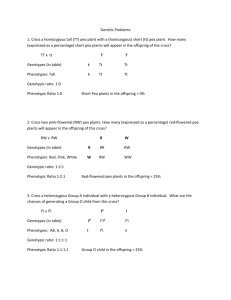
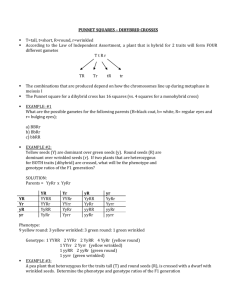
Biology 12 • These are crosses that involve genes for two different characteristics • The natural progression for Mendel was to study two characteristics at the same time. • Thus, the study of 2 pairs of contrasting traits at the same time = a dihybrid cross • ex.. round yellow seeds X wrinkled green seeds • Principle of Independent Assortment • When more then one trait is studied in the same cross, the genes for each trait sort into gametes independently of the genes of the other traits Let’s cross a homozygous round/yellow (AABB) with a homozygous wrinkled/green (aabb) plant…. Character Seed shape Seed colour Trait Allele Round A Wrinkled a Yellow B Green b 1. Determine Genotypes of Parents 2. Determine Genotypes of Gametes (remember gametes only have 1 copy of each gene) and think FOIL (from math class!) 3. Punnett Square: need 16 squares now, 4 gametes from each parent 4. Identify Phenotype Ratios in Offspring o In snapdragons… o Tallness (T) is dominant to dwarfness(t) o Red color is due to gene (R) and white to its corresponding allele (r). o The heterozygous condition results in pink (Rr) flower color. o A dwarf pink snapdragon is crossed with a plant homozygous for tallness and red flowers. Give the possible genotypes and corresponding phenotypes for all of the possible F1 generation. “A dwarf pink snapdragon is crossed with a plant homozygous for tallness and red flowers. “ Parent 1:Dwarf pink = ttRr Parent 2:Homozygous tall, red = TTRR Dwarf pink = ttRr tR tr tR tr Homozygous tall, red = TTRR TR TR TR TR The Punnett square determines the genotypes of the offspring tR Gametes from dwarf pink parent tr tR tr Gametes from TALL red parent TR TR TR TR TtRR TtRR TtRR TtRR Tall, red = 8/16 Tall, pink = 8/16 TtRr TtRr TtRr TtRr TtRR TtRR TtRR TtRR TtRr TtRr TtRr TtRr Tall, white = 0/16 Short, red = 0/16 Short, pink = 0/16 Short, white = 0/16 • Page 154 questions 1, 3 (and then try #2)