Biology Fall Final Exam Review Answers
advertisement

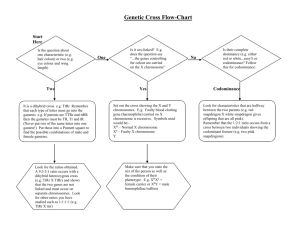
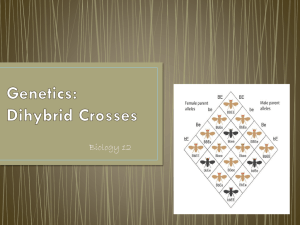
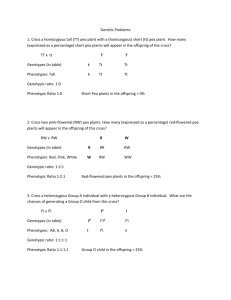
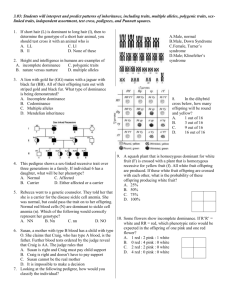
Name: _______________________________________________ Date: ____________________ Block: ______ Biology Fall Final Exam Review Answers CELLS 1. Contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Prokaryotic cells do not contain a nucleus or organelles, Bacteria are examples of prokaryotic organisms. Eukaryotic cells do contain a nucleus and organelles, Animals, plants, fungus and protists are examples of eukaryotic cells. Both types of cells have DNA, cell membrane, cell wall (plants) and ribosomes. 2. How can you tell the difference between plant and animal cells? Plant cells have a cell well, a large vacuole in the center of the cell and chloroplasts; Plant cells tend to be square due to their cell wall. Animal cells do not have a cell wall or chloroplasts and their vacuoles are smaller. Animal cells also have centrioles. 3. What is the purpose of the cilia and flagella? They help the cell move 4. What is the purpose of the cell membrane? To maintain homeostasis; control what enters and exits the cell. 5. What is produced in the ribosomes? Protein 6. What does cell specialization mean? Each cell has a particular function in the organism ECOLOGY 1. What organism(s) is (are) the producers? Algae 2. What organism(s) is (are) the consumers? Zooplankton (primary), shrimp (secondary), damselfish (tertiary), barracuda (4th consumer) 3. What is the main source of food for the shrimp? zooplankton 4. Draw an energy pyramid representing this food chain. Barracuda damselfish shrimp zooplankton algae 5. Which organism has the most energy available to them? Algae (energy from the sun) 6. Contrast between a population, community, and ecosystem A population is a group of organisms of the same species living in the same place, community is a group of organisms of different species living in the same place; an ecosystem is all the biotic (living) and abiotic (nonliving) in one area 7. How is energy transferred in this ecosystem? Through eating. PHOTOSYNTHESIS 1. In what organelle does PS occur? Chloroplast 2. Write the equation for PS. Name each molecule in the equation and label products/reactants. Water Carbon dioxide Glucose CO2 + H2O + Sunlight C6H12O6 + O2 Reactants Products Oxygen 3. 4. 5. 6. What is the purpose of PS? To make glucose for food for the plant What organisms perform PS? Plants, algae and bacteria In what organelle does CR occur? Mitochondria Write the equation for CR. Name each molecule in the equation and label products/reactants. C6H12O6 + O2 CO2 + H2O + ATP Reactants Products 7. How are the equations of PS and CR similar and different? Similar: contain glucose, water, oxygen & carbon dioxide Different: The reactants and products are switched 8. What is the purpose of CR? To make energy (ATP) for the cell 9. What organisms perform CR? All organisms! 10. Glycolysis, the Citric Acid/Krebs Cycle, and the electron transport chain are the three main steps in CR. What starting molecule are they breaking down to get energy? CR breaks down glucose for energy 11. Give two differences between ADP and ATP: 1) ATP has 3 phosphates (P) and ADP has 2 phosphates 2) ATP has more energy, ADP has less energy 12. What type of anaerobic CR is used to make beer and wine? Alcoholic fermentation 13. What type of anaerobic CR is used in your muscle cells when working out strenuously? Lactic Acid Fermentation CELL DIVISION 1. If the diploid number of a species is 20, what is its haploid number? N = 10 (half) 2. If the haploid number of a species is 20, what is its diploid number? 2N = 40 3. What process is occurring? Crossing Over In what phase of meiosis does it occur? Prophase I 4. How is cytokinesis different in plant and animal cells? In animal cells, the membrane pinches inward, forming a furrow to separate the two nuclei created in mitosis; in plant cells, the cell plate forms between the two nuclei and grows outward until it forms a cell wall 5. In what phase of the cell cycle is DNA replicated? Interphase 6. Name the following phases of the cell cycle above the pictures and number them in order below the pictures. Interphase Telophase Metaphase Anaphase Prophase ______1_________ ______5__________ _______3__________ _________4_________ _______2__________ 7. What types of cells are produced by mitosis? Body cells Are they haploid or diploid? Diploid 8. What types of cells are produced by meiosis? Gametes Are they haploid or diploid? Haploid 9. As the cell becomes larger the Volume (volume / surface area) increases faster than the Surface Area (volume / surface area). 10. What is the goal of the cell cycle? To produce more cells for the body DNA/RNA 1. Genes on your DNA provide information used to make Protein 2. List the steps of DNA replication. 1) Helicase unwinds the original nucleotide strands 2) DNA Polymerase adds new nucleotides complementary to the original nucleotides 3) two new DNA strands are created **In DNA replication, the new strands have one OLD strand and one NEW strand to make the double helix!** 3. Transcription and translation are the two steps of Protein synthesis 4. What happens during transcription? mRNA copy of ONE GENE is made in the nucleus 5. In what organelle does transcription occur? Nucleus 6. What happens during translation? mRNA is read three bases at a time (codon) to code for the order of amino acids in a protein 7. Where does translation occur? Cytoplasm at a ribosome 8. Which types of RNA makes up the ribosome? rRNA 9. Which type of RNA carries the information from the DNA to the cytoplasm? mRNA 10. Which type of RNA carries the amino acids to the ribosomes? tRNA 11. Write the complimentary DNA strand below - A G G C T G C C T A A C C T TCCGACGGATTGGA 12. Write the complimentary RNA strand below - A G G C T G C C T A A C C T UCCGACGGAUUGGA 13. The diagram to the right shows the normal sequence of genes on a chromosome. Identify the type of mutation shown in the chromosomes below: Inversion Deletion Duplication or insertion GENETICS 1. What are the sex chromosomes for a male? XY 2. What are the sex chromosomes for a female? XX 3. Which parent (mother, father) determines the sex of a child? WHY? The FATHER determines the sex of the child. The mother can only give a X chromosome to her child, but if the father gives an X chromosome too, the child will be a girl; if the father gives a Y chromosome, the child will be a male. 4. What is the chance of producing a daughter every time a couple reproduces? 50% 5. What is the chance of producing a son every time a couple reproduces? 50% 6. T = tall, t = short. Cross a homozygous tall plant with a homozygous short plant. Parents: TT x tt Possible Offspring Genotype: Tt Possible Offspring Phenotype: Tall 7. T = tall, t = short. Cross two heterozygous tall plants. Parents: Tt x Tt Possible Offspring Genotype: TT, Tt, tt Possible Offspring Phenotype: Tall, short T T t Tt Tt t Tt Tt T t T TT Tt t Tt tt 8. How many different phenotypes are possible in a gene that has… a. Complete dominance (dominant – recessive) 2 (dominant phenotype or recessive phenotype) b. Incomplete dominance 3 (dominant, recessive or the mixture in a heterozygote) c. Codominance 3 (dominant, recessive or both 9. What are two facts you can determine from the karyotype below? 1. Female (XX) 2. Trisomy (3 chromosomes) 21 = Downs Syndrome 10. Complete the Punnett Square below showing a dihybrid cross between tomato plants that area heterozygous tall with red fruit. TR Tr tR tr Key: T = tall stem t = short stem R = red fruit r = yellow fruit TR TTRR TTRr TtRR TtRr Tr TTRr TTrr TtRr Ttrr tR TtRR TtRr ttRR ttRr tr TtRr Ttrr ttRr ttrr a. What is the chance of having offspring that are tall with red fruit? Dominant for T and R ___9__/16 b. What is the chance of having offspring that are tall with yellow fruit? Dominant for T and recessive for R (rr) ______3______/16 c. What is the chance of having offspring that are short with red fruit? Recessive for T (tt) and dominant for R ______3______/16 d. What is the chance of having offspring that are short with yellow fruit? Recessive for T (tt) and R (rr) _____1_______/16 EVOLUTION 1. Which species are LEAST likely related to the others? Fish is least likely related to the others Why? These pictures show the development of animal embryos at three stages (A, B & C). Comparing the stage of each animal, you can see similarities among some of the animals. The embryos look MOST similar are the tortoise, chick, rabbit and human. Salamanders look different, especially at stage B, but still have legs. Fish look the most out of place – starting out looking like the others at A, but quickly looking different than the other embryos. Fish do not have legs and therefore are LEAST similar to the others and are LEAST likely to be related to the rest. 2. The picture on the right shows homologous structures. What are homologous structures? Homologous structures are structures in different organisms that are similar. This similarity is due to the organisms having a common ancestor that had the same structures. For example, the bones in the forelimb (arm) of a human, cat, whale and bat are very similar. The ancestor of these mammals must have had the same bones. 3. According to Darwin’s Theory of Evolution by Natural Selection, organisms produce more offspring than the environment can support and will compete for resources. The fittest organisms will survive, reproduce and pass on their beneficial traits to their offspring, allowing descent with modification. 4. Acquired characteristics are NOT inherited.