final exam review (FALL 2014)
advertisement

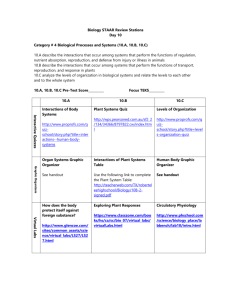
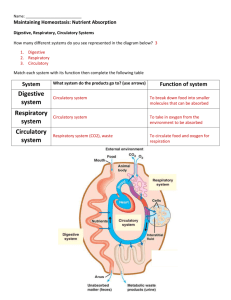
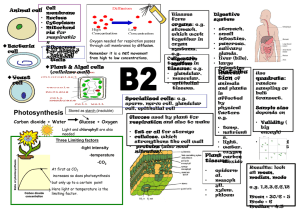
SBI 3U Final Examination Review Genetic Continuity Unit 2 Review Questions pages 192 to 195 # 1-9, 12, 13, 15-23 reasons for cell division (function of mitosis & meiosis) phases of the cell cycle (specific functions of mitotic phases, cytokinesis and 3 phases of interphase) structure of chromosomes what is a clone? steps required to clone an animal why was Dolly the sheep so special? biotechnology phases of meiosis (specific functions of each phase) similarities and differences between mitosis and meiosis process of gametogenesis (in both male and females) process of nondisjunction specific causes of nondisjunction disorders karyotype chart creation and interpretation interpret genotypes / phenotypes of parents, F1 and F2 progeny of the following crosses… - single-trait inheritance (single allele and multiple allele) - test crosses - incomplete dominance and codomimance - dihybrid crosses - crosses involving sex-linked traits (why do males only require one allele in order to become afflicted) what is selective breeding, inbreeding and hybridization? interpret pedigree charts law of independent assortment examples of human sex-linked traits structure of DNA human genome (what is the human genome project? what was the reason behind it?) what is DNA fingerprint (overview of process) key terms: alleles dihybrid cross dominant heredity heterozygous segregation law of independent assortment monohybrid cross pedigree chart phenotype Punnett square recessive homozygous hybridization hybrids genotype selective breeding phenotype Internal Systems and Regulation Unit 3 Review Questions pages 318 to 321 # 1-8, 10, 13, 18, 20 Function of the digestive system How do other body systems depend on the digestive system? How is the digestive system dependent on other systems? 4 components of digestion 2 factors that affect enzyme function How is digestion different in protozoa, hydra, birds and humans? The two voluntary movements in the digestive systems Ingestion - Function of saliva - Names and functions of each type of teeth - Function of tongue - Function of esophagus - What is peristalsis? Digestion - Function of stomach - Function of digestive enzymes, HCl(aq), mucus and hormones and describe which organs secretes these molecules and where - How is the digestive tract protected from enzymes/acids and bases? - Function of small intestine and pancreas - Functions of liver and gall bladder Absorption - How does the small intestine allow nutrients to be absorbed more quickly? - How/where is fat absorbed - How/where are carbohydrates/amino acids absorbed - Function and structure of large intestine - Function of fibre in the human diet - Names and functions of sphincters in the digestive tract - passive transport (diffusion, osmosis, facilitated diffusion) concentration gradient - active transport endocytosis (pinocytosis, phagocytosis) and exocytosis Function of the circulatory system Open v. closed circulatory systems Components of blood and their function Process of blood clotting Blood groups (their antigens and antibodies) Function of arteries and veins Differences of veins and arteries Names of main blood vessels (see page 254 of textbook) Pulmonary v. systemic v. cardiac circulatory systems Structure (and their function) of the mammalian heart How is cardiac muscle different from other types of muscles? How does the heart maintain its tempo? Cause of “lubb dubb” sounds of the heart Normal adult blood pressure? What does each of the numbers mean? Causes of cardiovascular disorders Two forces that regulate fluid movement between the blood and extracellular fluid (ECF) How do fluids move from the capillaries and ECF and vice versa – what are each of these processes called? How do starvation, hemorrhaging and an allergic reaction affect fluid movement? Function of the respiratory system 4 parts of respiration Function of respiratory membranes – skin, gills, lungs Advantages of lungs Countercurrent gas exchange in fish cellular respiration - products/reactants and function - structure and role of ATP - production of ATP (phosphorylation) - types of respiration - aerobic respiration VS. anaerobic respiration Breathing Pathway of air from the mouth to the lungs Function of diaphragm and rib cage (including intercostal muscles) External/Internal Respiration How does the partial pressure of O2 and CO2 promote gas exchange and transport? How is oxygen transported in the blood? The three ways in which carbon dioxide is returned to the lungs for expiration Mechanisms that maintain gas levels in the blood Common characteristic of all respiratory disorders Chapter 6 terms amylase bile salts capillary colon duodenum endoscope enterokinase erepsins pepsin gastrin gastrovascular cavity lacteals lipases microvilli mucus esophagus peristalsis pharynx secretin sphincters trypsin ulcer villi Chapter 7 terms anemia aneurysm antibodies antigen aorta arteriosclerosis artery atherosclerosis atrioventricular (AV) node atrioventricular (AV) valves atria autonomic nervous system coronary arteries diastole erythrocytes interstitial leukocytes lymph lymph nodes lymphocytes myogenic muscle parasympathetic nerves plasma platelets pulmonary circulatory system pulse Purkinje fibres bicuspid and tricuspid valves septum extracellular fluid (ECF) filtration sinoatrial (SA) node sinus sphygmomanometer sympathetic nerves systemic circulatory system systole tissues vasoconstriction vasodilation veins ventricles Chapter 8 terms alveoli breathing bronchi bronchioles buffer carbonic anhydrase cilia diaphragm epiglottis external intercostals muscles inspiratory reserve volume internal intercostal muscles larynx pleural membrane respiration pleural membrane trachea oxyhemoglobin carbaminohemoglobin Dalton’s law of partial pressure Diversity of Living Things 5(6) kingdoms Classify humans using the 7 levels of classification distinguishing features of each these categories Format for writing organism’s genus and species Use of dichotomous keys What is a species? Evolution – SEE pdf. under class documents for questions Review Questions pages 382-389 #1-12, 14, 15, 17-19, 21-25, 28, 30-36, 38, 39, 42, 44, 45, 47-49, 53, 59-61, 63, 65, 66, 70, 73, 7481, 90, 91, 93, 96, 97, 105, 108 Progression of early ideas about evolution Cuvier, Hutton, Lyell, Lamarck, Darwin, Gould Concept of catastrophism, actualism, gradualism, uniformitarianism, inheritance of acquired traits, natural selection Concept of natural selection versus artificial selection survival of the fittest, concept of adaptation examples of evidence of evolution eg.- fossil records, molecular record, homologous vs. analogous features, embryological development, vestigial structures, homologous genes and pseudogenes and modern day paleontology (continental drift) Patterns of selection – altruism, sexual, stabilizing, natural, cumulative, directional, and disruptive selection Evolutionary change without selection – genetic drift, gene flow, bottleneck effect, founder effect Hardy-Weinberg principle – equation, conditions, purpose of calculations, limitations Speciation allopatric versus sympatric reproductive isolating mechanisms * prezygotic mechanisms (ecological, temporal, behavioural, mechanical, gametic isolation) * postzygotic mechanisms ) zygotic immortality, hybrid inviability and hybrid infertility) Divergent and convergent evolution adaptive radiation coevolution cumulative selection Phylogeny – interpret phylogenetic trees to determine relatedness (cladograms) Human evolution