Circulatory & Respiratory Systems
advertisement
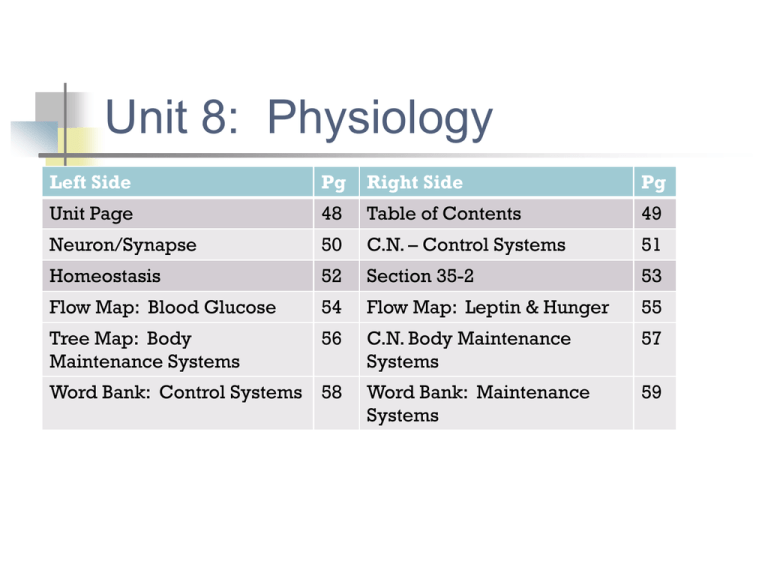
Unit 8: Physiology Left Side Pg Right Side Pg Unit Page 48 Table of Contents 49 Neuron/Synapse 50 C.N. – Control Systems 51 Homeostasis 52 Section 35-2 53 Flow Map: Blood Glucose 54 Flow Map: Leptin & Hunger 55 Tree Map: Body Maintenance Systems 56 C.N. Body Maintenance Systems 57 Word Bank: Maintenance Systems 59 Word Bank: Control Systems 58 Body Maintenance Systems Circulatory Respiratory Digestive Body Maintenance Systems Body maintenance systems have complementary activities to provide cells with oxygen and nutrients and remove toxic waste and carbon dioxide Together, they work to maintain homeostasis. I. Circulatory System II. Respiratory System III. Digestive System Cellular Respiration: use glucose & O2 C6H12O6 + 6 O2 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + ATP energy glucose + oxygen Carbon dioxide + water + energy Happens in the MITOCHONDRIA 3 Steps of Respiration: MITOCHONDRIA 1. Glycolysis 2. Krebs Cycle 3. Electron Transport Chain (ETC) I. Circulatory System FUNCTION: Transportation and delivery system that… 1) Delivers O2 & nutrients to cells 2) Removes CO2 & wastes from cells ORGANS: heart, blood vessels, & blood Heart: 4 chambered muscle that beats constantly to pump blood through vessels Atrium: upper chambers that receive blood returning from body and lungs Ventricles: lower chambers that pump blood to body and lungs Right side: deoxygenated blood Left side: Oxygenated blood Blood Vessels Arteries: carry blood away from heart to body or lungs Veins: carry blood to the heart from the body or lungs Capillaries: tiny blood vessels where nutrients and gases are exchanged between blood and cells Blood Transports and exchanges oxygen, carbon dioxide, nutrients, and waste II. Respiratory System FUNCTION: Respiration Respiration: breathing O2 in and CO2 out Occurs between the… 1. Environment & lungs (breathing) 2. Cells & the blood in capillaries (cellular respiration) ORGANS: nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, lungs, alveoli The Path of O2 1) Nose/Mouth - air enters body 2) Pharynx - passageway for food & air 3) Larynx - vocal chords 4) Trachea - windpipe (rings prevent collapse) 5) Bronchi (2) - take air to each lung 6) Alveoli - small air sacs surrounded by capillaries where O2 is exchanged for CO2 III. Digestive System FUNCTIONS: 1. Digestion: the breakdown of food into simple molecules 2. Absorption: nutrients in the digestive tract move into the blood 3. Elimination: getting rid of wastes ORGANS: mouth, esophagus, stomach, liver, pancreas, small intestine, large intestine, rectum The Path of Food 1. Mouth Teeth and saliva digest food mechanically and chemically 2. Esophagus Food tube squeezes food by peristalsis 3. Stomach Muscle that mixes food with acid and enzymes 4. Small Intestine Chemical digestion occurs and nutrients are absorbed into blood (circulatory system) Pancreas: secretes digestive enzymes into small intestine and insulin to control blood glucose levels Liver: stores sugars as glycogen and secretes bile, stored in gall bladder 5. Large Intestine Water is reabsorbed from waste 6. Rectum Waste collects here to be passed out of anus Review Cellular Respiration: glucose + oxygen Carbon dioxide + water + ATP energy Digestive Respiratory Respiratory & & & Circulatory Circulatory Circulatory body cells







