Quantitative Analysis Babylon University 2010/2011 Practical
advertisement

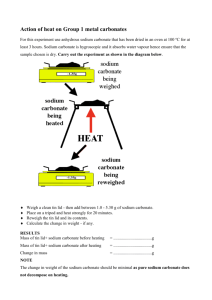
Quantitative Analysis 2010/2011 Babylon University Practical chemistry 1. Acid – Base Titration A- Standardization of Hydrochloric acid with anhydrous sodium carbonate Sodium carbonate is a salt of a weak acid. When titrated with hydrochloric acid carbonate decomposes, yielding carbon dioxide and water: Na2CO3 + 2HCl → 2NaCl + CO2 + H2O Evolving carbon dioxide acidifies the solution, and the end point in its presence is detected too early. To avoid titration errors we boil titrated solution to remove carbon dioxide. Procedure to follow: Place 10 ml of 0.1 N of anhydrous sodium carbonate into 250 mL Erlenmeyer flask. Add 1-2 drops of methyl orange solution. Titrate with about 0.1M HCl solution till the first color change from red to yellow Calculations NHCl x VHCl = NNa2CO3 x VNa2CO3 B - Standardization of Hydrochloric acid with Borax Borax has relatively high equivalent mass, which means potential errors in the standardization are smaller than in the case of other substances. The advantages of sodium tetraborate decahydrate (borax) are: (i) it has a large relative molecular mass,381.44 (that of anhydrous sodium carbonate is 106.00); (ii) it is easily and economically purified by recrystallisation; (iii) heating to constant weight is not required; (iv) it is practically nonhygroscopic; and (v) a sharp end point can be obtained with methyl red at room temperatures, since this indicator is not affected by the very weak boric acid. Reaction taking place during neutralization is 1 Quantitative Analysis 2010/2011 Babylon University Practical chemistry Na2B4O7 + 2HCl + 5H2O → 4H3BO3 + 2NaCl Boric acid is so weak, that its presence doesn't interfere with end point detection (compare with standardization against sodium carbonate). Procedure Place 10 ml of 0.1 N of dried Borax into 250 mL Erlenmeyer flask. Add 2-3 drops of Methyl red indicator Titrate against HCl solution till the first color changed from red to yellow. Calculations NHCl x VHCl = NBorax x VBorax Burette containing hydrochloric acid Conical Flask containing Borax and Methyl Red Experiment 2 2 Quantitative Analysis 2010/2011 Babylon University Practical chemistry Standardization and titration of Sodium hydroxide against HCl solution Theory Sodium hydroxide reacts with hydrochloric acid solution as follows: NaOH + HCl 1mol. of NaOH NaCl + H2O 1 mol. of HCl Depending on the above equation eq.wt of HCl = Mo.wt. eq.wt of NaOH = Mo.wt. is not primary standard substance because I's hygroscopic where it absorbs the water vapor from air , and it forms a layer of carbonate around it Sodium hydroxide 3