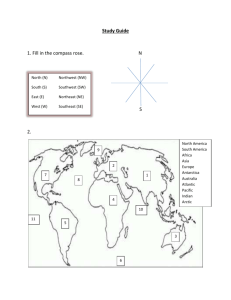
Types of Maps: NOTES
advertisement

Types of Maps: NOTES Name: ________________ 1. ______________________: Shows political (national and state) boundaries, like a globe. 2. ________________: Shows interstate system, highways, and smaller roads, depending on the map Used for navigation (getting from “here” to “there”) 3. _______________________: Shows pressure systems, cloud cover, rainfall, weather forecasts 4. _______________________: Shows the ocean floor, ocean features (Topography of the ocean) 5. _______________________: Shows the differences in elevation (relief) of an area Shows man-made features of the land as well as its natural features A. Paper maps are Flat 2-Dimensional Representations of Earth’s Surface. Problems: • Not as accurate as a 3-D _________________ model • Earth’s features become _______________________ (they don’t look right) B. Map Making ►_________________: Use distance and elevation information from known points to create maps Known points of elevation are called: ____________ ______________, they are metal stakes placed in stone and marked with the location and elevation Aerial (from the sky) photography also helps make maps. Modern surveyors use: Compass, Infrared theodolite, and GPS C. Map Projections ►_______________________ (map makers) illustrate world maps as a projection to reduce distortion ►Map _________________ – transferring a curved surface (the Earth, sphere) to a flat one (the map). ►Common map projections: ________________, _______________(Polar), & (Poly)_____________. I. The ________________ map projection shows the view of Earth as if a large ______________of paper had been wrapped around the globe. This is the most common type of projection. -Disadvantage Major _______________ effects near the poles. Land looks larger than what it really is. +Advantage Indicate true directions as straight lines of latitude and longitude makes a rectangular grid pattern II. A ______________ or _______________ projected map is created as if a piece of paper had been placed on a point on the Earth. The (Poly)________________ map projection shows the view of Earth as if a large paper ___________had been wrapped around the globe. This type of map is useful for mapping areas in the middle latitudes. __________________ ________________ _________________ label each map projection REVIEW: What type of halves is the Earth divided into? • North-South Hemispheres are separated by the imaginary line called the __________________. • East-West Hemispheres are separated by imaginary lines called the ________________ ______________(Greenwich Meridian) and the _________________ _________ __________. Latitude and Longitude: Grid of IMAGINARY lines placed over Earth Every location on the Earth has a specific latitude and longitude “address.” • Latitude lines circle the Earth__________________________, parallel to the Equator (0 Degrees) • Latitude is measured in Degrees _____________ or ______________ of the equator (0-90 Degrees) • • D. • • • Longitude lines are half-circles that extend ___________________ between the poles Longitude is measured in Degrees _________ or __________of the Prime Meridian (0-180 Degrees) How do you know the size of landforms or the distance between cities on a map? The ______ ________indicates how the map’s features and distances compare with the actual Earth The comparison is given as a ______________: For example 1:24,000 1 : 24,000 means that 1 map unit equals = 24,000 units on Earth E. How do you determine direction on a map? ►Usually, most modern maps place North at the top ►________________ ______________ indicates (shows) direction ►Geographic North v/s Magnetic North, are they the same? _______, because Earth is tilted on its axis! Earth Observing System: The ________________ in the Earth Observing Systems (EOS) will contain sensors to monitor (check on) global climate change. Global Positioning System: GPS is a _____________ ____ ______________ _____ ______________ that allow accurate positioning on the Earth. * 24 satellites work together to gather and compute information.