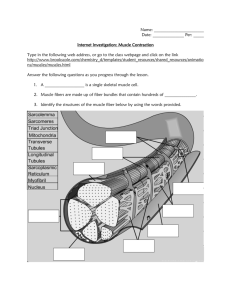
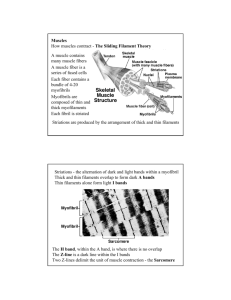
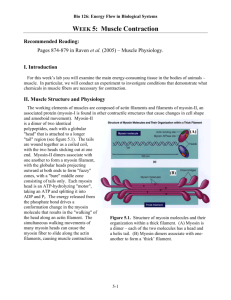
Chapter 6 Study Sheet 1.Ballet dancers normally have their feet in

Chapter 6 Study Sheet
1.Ballet dancers normally have their feet in what position?
a.eversion
b.dorsiflextion
c.plantar flexion
d.supination
2.In anatomical position, the hand has been
a.pronated
b.supinated
c.rotated
d.everted
3.Which of these is correct?
a.Z lines anchor myosin thick filaments to the ends of the sarcomere
b.myosin cross bridges contain calcium binding sites
c.the sarcoplasmic reticulum stores acetylcholine
d.actin and regulatory proteins are located in thin filaments
4.According to the sliding filament theory of muscle contraction
a.thick filaments made of actin and myosin walk along cross bridges toward the
center of the sarcomere
b.calcium causes myosin heads to release from actin when contraction is over
c.tendons push the muscle ends together which causes sarcomere shortening
d.sarcomeres shorten when thin filaments move toward the center of the sarcomere
5.Which of these is not a function of skeletal muscle?
a.maintains posture
b.produces movement when muscles shorten
c.pumps blood
d.generates heat
6.The ____ is strengthened when we do crunches.
a.rectus abdominis
b.erector spinae
c.dorsal rectus
d.rectus femoris
7.The correctly paired antagonists are the
a.pectoralis major-deltoid
b.biceps brachii-triceps brachii
c.masseter-buccinator
d.rectus femoris-vastus lateralis
8.In order for muscles to move bones they must have all the following characteristics
except
a.during contraction the point of insertion moves toward the point of origin
b.they must cross two successive joints
c.they can pull but not push
d.most of the muscle mass is located proximal to the joint crossed
9.A whole skeletal muscle contracts
a.by sustaining contractions which lead to tetanus
b.following the all-or-none law of contraction
c.by muscle twitches which can not be summed
d.by responding to stimuli with graded responses
10.____ allows cross bridge release and recocking of myosin cross bridges during muscle
contraction.
a.enzymes
b.ATP
c.calcium ions
d.action potentials
11.Isometric contraction occurs when sarcomeres do not shorten. An example of this is
a.a 100 pound boy trying to lift a refrigerator
b.walking down a steep stairway carrying a 45 pound backpack
c.swimming in saltwater
d.throwing a baseball
12.Intramuscular injections are best given in the ___ muscles.
a.gluteus medius and deltoid
b.gluteus medius and triceps brachii
c.gluteus maximus and triceps brachii
d.gluteus maximus and deltoid
13.Which of these is not an abdominal muscle?
a.external rectus
b.internal oblique
c.rectus abdominus
d.transversus abdominus
14.A motor unit
a.is the site of attachment of a neuron and the muscle at the motor end plate
b.is the contractile unit of a muscle cell
c.is the amount of acetylcholine used to produce one contraction
d.is one neuron and all the muscle cells it stimulates
15.The neurotransmitter ____, released from axon terminals of motor neurons, stimulates an
action potential in a muscle cell, causing it to contract.
a.ATP
b.action potential
c.calcium
d.acetylcholine
16.Starting from anatomical position, when the elbow is moved behind the body it is called
a.abduction
b.arm flexion
c.arm extension
d.rotation
17.A sheetlike muscle on the anterolateral neck that does not originate or insert on bone is
called the
a.orbicularis oris
b.platysma
c.sternocleidomastoid
d.rectus
18.The negative effects of using anabolic steroids for increasing muscle mass include all but
a.liver damage
b.increased psychiatric problems
c.enhanced cardiovascular function
d.decreased fertility
19.The function of tetanic contraction is
a.to activate single motor units
b.to provide the energy for muscle contraction
c.to have the muscle contract smoothly and for prolonged periods
d.to produce graded and all-or-none responses
20.Which of these is NOT true about aerobic exercise?
a.it makes one more coordinated
b.it dramatically increases muscle size
c.it increases the number of mitochondria in muscle cells
d.it improves digestion