Prehistoric People
advertisement

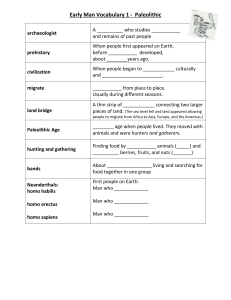
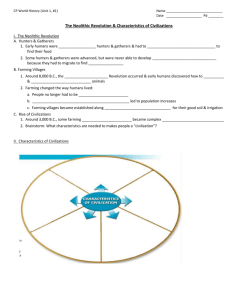
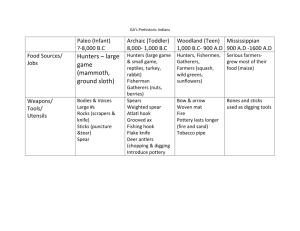
Prehistoric People (8000BC – 3000BC) Prehistory – period of time before the invention of writing Paleolithic Age “Old Stone Age” Lasted from about 2.3 million years ago – 10,000 years ago 900,000 years ago & before – people only live on grasslands of eastern and southern Africa Movement: Climate cooled / Glaciers formed and spread Sea levels fell exposing new land – land bridges Connected Africa to Asia and Europe Migrate – to make way to new area 900,000 – 700,000 – people migrate to Asia and Europe 40,000 – 10,000 – people migrate to Americas Obtaining Food Hunter / gatherers Lived in bands (groups of about 30 members) Lived to age 20-25 years Children killed by illness or animals Home territory – 2sq mile area per band member Stayed until food ran out Women: gathered barriers, nuts, fruit & eggs Honey & roots Men: hunted meat Making tools Made life easier Sticks and stones at first – then shaped stones Olduvan pebble tools – oldest known tools Found in Olduvai Gorge in Eastern Africa Making Fire Natural fires – lightening Spark fires – rubbing sticks/stones Uses: warmth/dry Weapon/animal trap Clear brush Cook food (less time eating) Shelter Pits/dry riverbeds Caves – emergency until 100,000 years ago 1 Clothing Skins for protection/warmth Drying then pounding fat Allowed for movement into colder regions Language Made sounds or pointing to objects /Hand signals Made possible to work together, share ideas, Pass on beliefs and stories Made learning easier Neanderthals Homo habilis “skillful man” Homo erectus “man who walks upright” Homo sapiens “man who thinks” Neanderthal Discovered near Neander River, Germany (1865) Population 1 million Hunters Used pitfalls (large covered hole) Builders Covered wood frames w/ skins First to bury dead Found remains w/ flowers, tools, food Cro-Magnons Discovered in France (1868) First Modern human beings Burin – chisel like tool Make tools of antler, bone, ivory, shell Spears Bone/antler points - spears fly faster/farther Hunters at safer distances Axe, jewelry, artists Cave paintings Religious significance Animals had spirits Represent ceremonies, traditions, history Social gatherings Exchange information Neolithic Age (8000BC) “New Stone Age” “Neolithic Revolution” Food gatherers food producers 2 Hunters farmers Growing food (wheat & barely) Herd animals (domestication) Population begins to grow 5 mil in 8000 BC 90 mil in 4000 BC Early Civilizations River Valleys Nile R. – Egypt Tigris & Euphrates R. – Iraq Indus R. – India Huang Ho R. – China Characteristics - Produce surplus food - Created large towns/cities w/ gov’t - Division of Labor: different people perform different jobs - *Calendar or writing Metals Copper – 1st metal Weapons, tools, utensils & jewelry Bronze – alloy of copper & tin (5000 BCE) Marks end of Stone & beginning of Bronze Age Iron – smelting in forge (3200 BCE) Marks end of Bronze & beginning of Iron Age Family Women Men - Managed family Food, clothing, pottery, weaving Responsible for food supply Hunted less Plow & animal on farm Religion Chiefs = priests Offered prayers for rich soil, healthy animals, water for crops Prayed to the forces of nature Mother Earth: goddess of fertility Alters first built in home Moved to separate buildings Multiple pagan goddesses & gods 3 Early villages 150 – 200 people in areas w/ good soil & water Built permanent shelters Jericho: in Israel (8000BC) Abu Hureyra: in Syria (7500 BC) Catal Huyuk: in Turkey (6500 BC) Found blackened wood & cloth Bricks of mud Lintel Posts Building Structures Post and lintel No doors / no windows protection Farms - Irrigation: ditches & canals used to carry water from rivers to fields Plow & domesticated animals speed up process Government Land ownership demanded rules & rulers Flood control projects War Gain wealth through herd or pasture takeover Fight between herders & farmers Water rights Specialization 4 Development of occupations Artisans: skilled workers Potters, weavers, metal workers Development of trade Excess supplies traded for needed items Cultural diffusion – spread of aspects of culture from one culture to another Calendar Cycle of moon Predict valley flooding Writing Record keeping Preserve past Pass ideas & information Development: - Pictures represent things (pictograms/graphs) - Pictures symbolize ideas - Pictures stand for sounds - Signs represent consonants or vowels 5