Unit 1 Study Guide with answers
advertisement

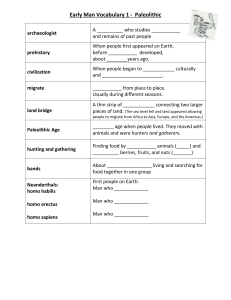
Pre-Historic Man Study Guide-Answer Key You must understand all of the following material that will be on the common assessment on Wednesday, Sept. 23rd. 1. Define the following words-make sure you can provide examples Artifacts- objects made by people; can be moved (coins, pottery) Features- These are made by people but cannot be moved without changing the site-cave paintings Ecofacts- Natural objects found with artifacts and features. They tell how the people responded to their surroundings.-animal bones, fossils Primary sources-historical documents, written accounts by a firsthand witness or objects that have survived from the past (ex. Letters, government documents, photographs, diary, stamps, coins) Secondary sources-accounts of past events create by people some time after the event occurred. (ex. Textbook) Prehistory-time period before there were written accounts/records Hominid-early ancestor of humans (4 types-Australopithecus, Homo Habilis, Homo Erectus, Homo Sapiens) Culture-the knowledge, beliefs, customs, and values of a group of people Specialization of labor- learning a specific skill/job (farmers, tailors, artists, blacksmiths) Anthropology-the study of the past looking at the culture of a specific group or civilization Archaeology-the study of the past using artifacts to discover clues about the ancient civilizations Neolithic Revolution-time period when people discovered how to farm and domesticate animals Geography-study of the earth’s physical and cultural features Society- community of people who share a common culture 2. Where did ancient people settle near? Why?-Water; food source, survival, to irrigate farmland, transportation; fertile rich soil 3. Which discovery ended the Paleolithic Age?-Farming and domestication of animals; agriculture 4. List some achievements the Paleolithic people made to make life easier. Stone tools, fire, developed language 5. List some achievements the Neolithic people made to make life easier. Stone tools, 2 story, mud brick houses with ladders to prevent animal attacks, planting seeds to grow crops in order to have a stable food supply 6. What were several ways that agriculture changed the lives of the Neolithic people? Stable food supply, permanent settlements, increased population and specialization of labor; disease and wars 7. What does it mean to have a stable food supply? Have enough food to survive with surplus goods 8. Which discovery led to the end of the Neolithic time period? Metal tools 9. Compare and contrast the lives of the Paleolithic and Neolithic Ages (examples- food supply, shelter, culture, etc). Be able to describe these differences. See graphic organizer on page 42 of the interactive notebook. 10. Identify the 4 types of hominids and explain how their capabilities/technology changed over time. a. Australopithicus Afarensis, Homo Erectus, homo habilis, homo sapien b. First used branches as a tool and eventually invented the fish hook, bow/arrow, spear in order to make life easier while hunting for food. 11. Why did early humans choose to migrate during the ice age? What allowed them to cross into the Americas? Migrated/moved to obtain food and water sources; land bridge (Beringia) 12. What were some reasons why prehistoric man created cave paintings? Homo Sapiens created for religious purposes, teach hunting practices, and to express themselves/communication 13. Identify the aspects of culture. Food, beliefs/religion, clothing, language, recreation, art, shelter, literature, customs/traditions 14. What are some ways early man adapted to new environments? a. Shelter, food, clothing, customs/traditions