Numeracy - Using Empty Number Lines
advertisement

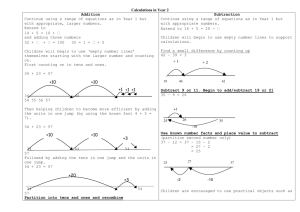
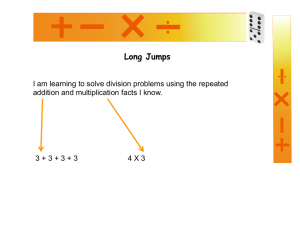
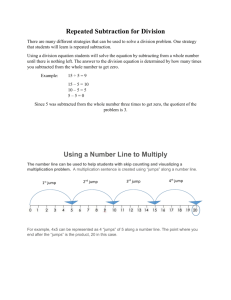
ADDITION AND SUBTRACTION Leicestershire Primary Numeracy Team 2003 Before children can begin to use an empty number line, they need to have had lots of experience of counting on and back using numbered lines, bead strings and partly numbered lines. COUNTING ON 8+5 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Use a numbered line to count on in ones. 11 12 13 14 15 Use a bead string to illustrate the bridge through ten (count on 2, then 3). 0 5 10 Bridge through ten using a partly numbered lines. 15 Use a bead string to illustrate counting on two tens. 18 + 20 Count on in tens using a partly numbered line. 0 10 20 30 40 COUNTING BACK 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 Use a numbered line to count back in ones. 13 - 5 Use a bead string to illustrate the bridge through ten (count back 3, then 2). 0 5 10 15 Bridge through ten using a partly numbered line. Use a bead string to illustrate counting back two tens. 38 - 20 0 10 20 30 40 Count back in tens using a partly numbered line. PREREQUISITE SKILLS Children need to have had the opportunity to practise these skills and become confident with them before adding or subtracting pairs of two-digit numbers using an empty number line. Position a number on a number line Draw an arrow to show number 38 on a 0 to 100 line. Jump to a number from zero e.g. To jump to number 29 you could do two jumps of 10 and nine jumps of 1 OR a jump of 20 and a jump of 9 OR three jumps of 10 and a jump back of 1 OR a jump of 30 and a jump back of 1 Add / subtract a multiple of 10 to or from any two-digit number (without crossing 100) e.g. Add 30 to 56 by counting on 3 tens Recall addition and subtraction facts for all numbers to at least 10 (and use this knowledge to add / subtract a single digit number to or from a two-digit number, without crossing the tens boundary) e.g. When adding 5 to 43 use the knowledge that 3+5=8 to deduce that 43+5=48 Bridge through 10 (and use this strategy to add / subtract a single digit number to or from a two-digit number, crossing the tens boundary) e.g. To add 5 to 28 use two steps, crossing a multiple of 10 as a middle stage. 28+5=28+2+3 =30+3 =33 Know the complement to the next multiple of 10 for any two-digit number e.g. Know that 6 must be added to 34 to make 40 Use knowledge of place value to add a single digit number to a multiple of 10 e.g. Recombine 70 and 3 to give 73 Teachers need to help children to use empty number lines efficiently when adding or subtracting any pair of two-digit numbers. COUNTING ON (not crossing tens boundary) COUNTING ON (crossing tens boundary) 34+23 37+25 Count on in jumps of 10 and jumps of 1 +10 34 +10 +10 +1 44 54 +1 55 56 37 57 Adding 3 in one jump (using the known fact 4+3=7) +10 34 +10 44 57 37 +10 47 +1 59 +3 57 60 +1 61 +2 60 62 Adding 20 in one jump +20 57 58 +1 Adding 5 in 2 jumps (by bridging through 10) +3 54 +1 Help children to become more efficient by: +20 +1 57 +10 Adding 20 in one jump 34 47 +3 54 +10 +1 Help children to become more efficient by: Count on in jumps of 10 and jumps of 1 37 +3 57 +2 60 62 62 COUNTING BACK (not crossing tens boundary) COUNTING BACK (crossing tens boundary) 47-23 42-25 Count back in jumps of 10 and jumps of 1 24 25 -1 26 -1 27 37 17 47 -1 -1 - 10 Subtracting 3 in one jump (using the known fact 7-3=4) 24 27 19 -1 20 -1 37 -10 -1 20 22 -2 47 42 -10 -10 32 42 -10 Subtracting 20 in one jump 17 20 -3 -20 32 -10 -10 27 -3 -1 22 Subtracting 5 in 2 jumps (by bridging through 10) 17 47 Subtracting 20 in one jump 24 21 Help children to become more efficient by: -3 -3 18 - 10 Help children to become more efficient by: Count back in jumps of 10 and jumps of 1 22 -2 42 -20 COUNTING UP Build up children’s mental imagery of the number line. For some calculations, they can then use this mental image to work out the answer in their heads. 82-47 Count up from 47 to 82 in jumps of 10 and jumps of 1 +1 47 +1 48 +10 +1 49 50 +10 60 +10 +1 70 80 +1 81 82 Help children to become more efficient by: Jumping to first multiple of 10 and from the last multiple of 10 in one jump +10 +3 47 50 +10 60 +10 70 +2 80 82 Jumping between the first multiple of 10 and the last multiple of 10 in one jump +30 +2 +3 47 50 80 82 Leicestershire Primary Numeracy Team 2003